Question Number 184470 by SANOGO last updated on 07/Jan/23
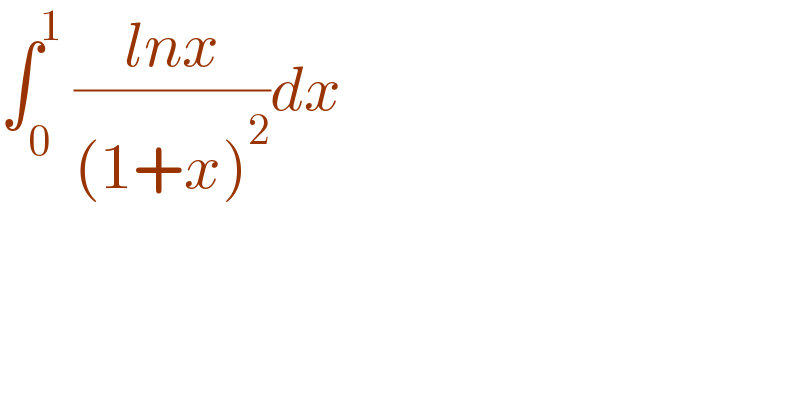
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{lnx}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 07/Jan/23
![=−∫_0 ^1 ln (x) d((1/(1+x))) =−[((ln x)/(1+x))]_0 ^1 +∫_0 ^1 (dx/(x(1+x))) =−[((ln x)/(1+x))]_0 ^1 +[ln (x/(1+x))]_0 ^1 =−ln 2 hint: ∫_0 ^1 ((ln x)/((1+x)^2 ))dx=lim_(a→0) ∫_a ^1 ((ln x)/((1+x)^2 ))dx](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q184471.png)
$$=−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{ln}\:\left({x}\right)\:{d}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\right) \\ $$$$=−\left[\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} +\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{dx}}{{x}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)} \\ $$$$=−\left[\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} +\left[\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${hint}: \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{x}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\underset{{a}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\int_{{a}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{x}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$
