Question Number 160194 by amin96 last updated on 25/Nov/21
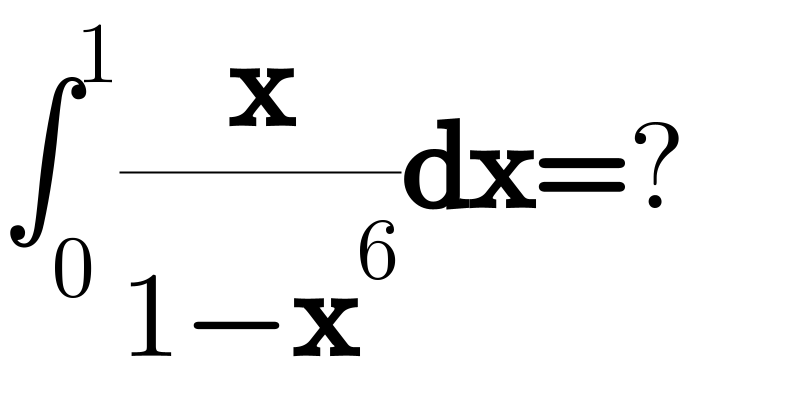
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}}{\mathrm{1}−\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\mathrm{6}} }\boldsymbol{\mathrm{dx}}=? \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 25/Nov/21
![=∫_0 ^1 x(1+x^6 +x^(12) +x^(18) +...)dx =[(x^2 /2)+(x^8 /8)+(x^(14) /(14))+(x^(20) /(20))+...]_0 ^1 =(1/2)+(1/8)+(1/(14))+(1/(20))+... =(1/2)Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/(3n+1)) =divergent!](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q160203.png)
$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {x}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{6}} +{x}^{\mathrm{12}} +{x}^{\mathrm{18}} +…\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\left[\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{8}} }{\mathrm{8}}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{14}} }{\mathrm{14}}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{20}} }{\mathrm{20}}+…\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{14}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{20}}+… \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$={divergent}! \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 25/Nov/21
![I=∫_0 ^1 (x/(1−x^6 ))dx=(1/2)∫_0 ^1 (dx/(1−x^3 ))=−(1/2)∫(dx/((x−1)(x^2 +x+1))) (1/(x^3 −1))=(a/(x−1))+((bx+c)/(x^2 +x+1))=(((a+b)x^2 +(a−b+c)x+(a−c))/(x^3 −1)) a=−b, a=(1/3), c=−(2/3) I=−(1/6)∫_0 ^1 ((1/(x−1))−((x+2)/(x^2 +x+1)))dx =−((ln∣x−1∣)/6)+(1/6)∫((1/2)∙((2x+1)/(x^2 +x+1))+(3/2)∙(1/((x+(1/2))^2 +(3/4))))dx =[−((ln∣x−1∣)/6)+(1/(12))ln(x^2 +x+1)+(1/4)∙(2/( (√3)))arctan(((2x+1)/( (√3))))]_0 ^1](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q160201.png)
$${I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{6}} }{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{{dx}}{\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}}=\frac{{a}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}+\frac{{bx}+{c}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\left({a}+{b}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({a}−{b}+{c}\right){x}+\left({a}−{c}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${a}=−{b},\:{a}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}},\:{c}=−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$${I}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}−\frac{{x}+\mathrm{2}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=−\frac{\mathrm{ln}\mid{x}−\mathrm{1}\mid}{\mathrm{6}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\int\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{4}}}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\left[−\frac{\mathrm{ln}\mid{x}−\mathrm{1}\mid}{\mathrm{6}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{12}}\mathrm{ln}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\mathrm{arctan}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 25/Nov/21
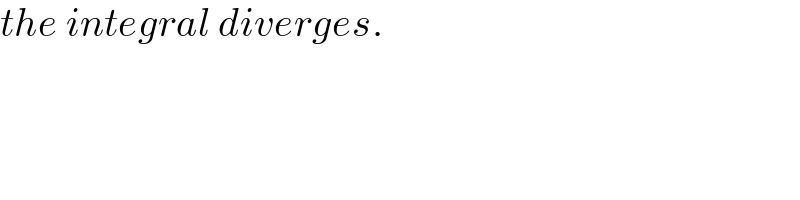
$${the}\:{integral}\:{diverges}. \\ $$
