Question Number 90424 by john santu last updated on 23/Apr/20
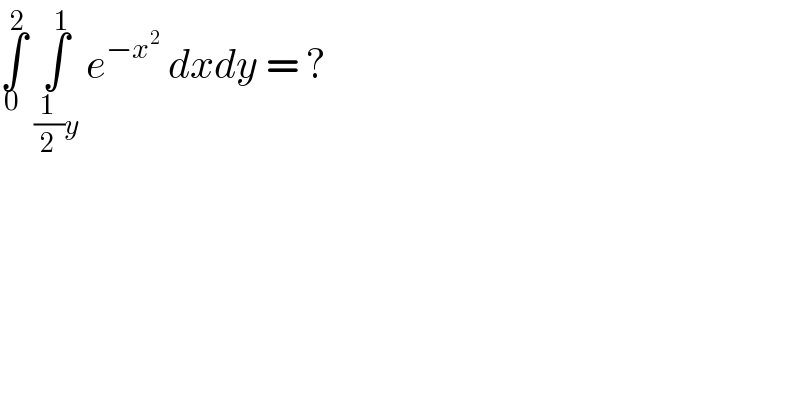
$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}} {\int}}\:\underset{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{y}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \:{dxdy}\:=\:?\: \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 23/Apr/20
![change order 0 <y<2 , (1/2)y<x<1 ⇒ ∫_0 ^1 ∫_0 ^(2x) e^(−x^2 ) dy dx = ∫ _0 ^1 ye^(−x^2 ) ]_0 ^(2x) dx = ∫_0 ^1 2xe^(−x^2 ) dx = −e^(−x^2 ) ]_0 ^1 = −(1/e)+1](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q90426.png)
$${change}\:{order}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{0}\:<{y}<\mathrm{2}\:,\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{y}<{x}<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}{x}} {\int}}\:{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \:{dy}\:{dx}\:=\: \\ $$$$\left.\int\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\:}}\:{ye}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \:\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:{dx}\:=\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\mathrm{2}{xe}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \:{dx}\: \\ $$$$\left.=\:−{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \:\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}}+\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$
