Question Number 153016 by joki last updated on 04/Sep/21

$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{xe}^{\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 04/Sep/21
![=−(1/2)∫_0 ^2 e^(4−x^2 ) d(4−x^2 ) =−(1/2)[e^(4−x^2 ) ]_0 ^2 =−(1/2)[1−e^4 ] =((e^4 −1)/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q153037.png)
$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{\mathrm{4}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {d}\left(\mathrm{4}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[{e}^{\mathrm{4}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\mathrm{1}−{e}^{\mathrm{4}} \right] \\ $$$$=\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{4}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by peter frank last updated on 04/Sep/21

$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{confirmation} \\ $$
Answered by peter frank last updated on 04/Sep/21
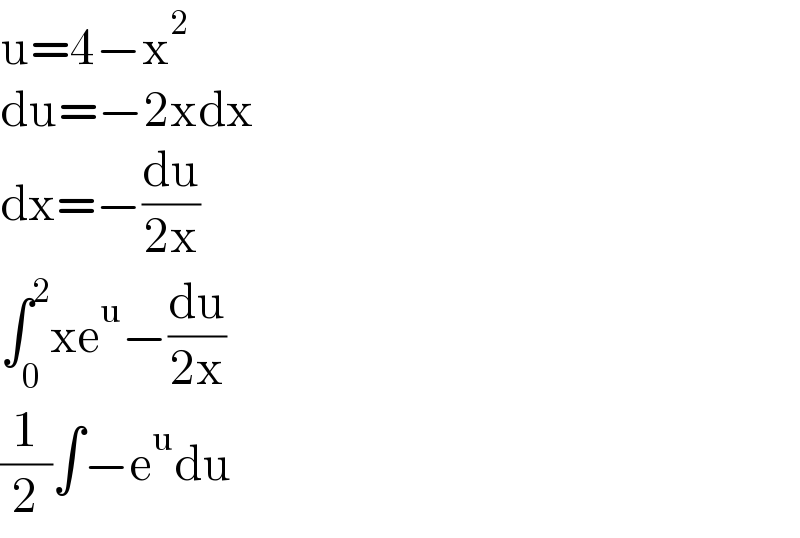
$$\mathrm{u}=\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{du}=−\mathrm{2xdx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{dx}=−\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{2x}} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{xe}^{\mathrm{u}} −\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{2x}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{u}} \mathrm{du} \\ $$
