Question Number 98244 by ~blr237~ last updated on 12/Jun/20
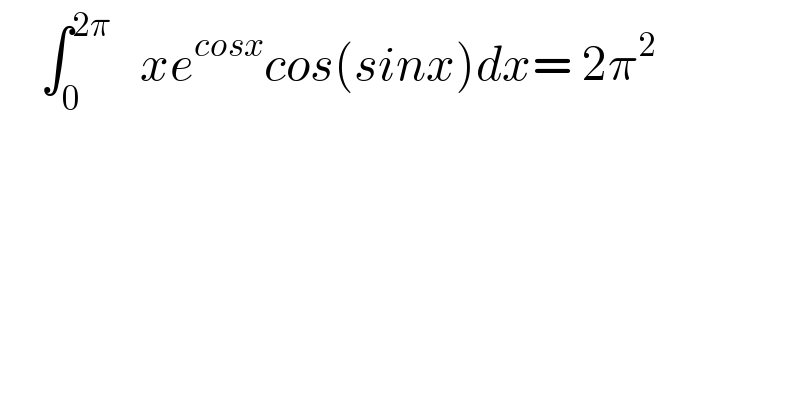
$$\:\:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}\pi} \:\:\:{xe}^{{cosx}} {cos}\left({sinx}\right){dx}=\:\mathrm{2}\pi^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by maths mind last updated on 15/Jun/20
![e^(cos(x)+isin(x)) =e^(cos(x)) (cos(sin(x))+isin(sin(x))) ∫_0 ^(2π) xe^(cos(x)+isin(x)) dx =∫_0 ^(2π) xe^e^(ix) dx =∫_0 ^(2π) Σ_(k≥0) x.(e^(ikx) /(k!)) =Σ_(k≥0) (1/(k!))∫_0 ^(2π) xe^(ikx) dx ∫_0 ^(2π) xe^(ikx) dx=[x(e^(ikx) /(ik))]−∫(e^(ik) /(ik))dx =((2π)/(ik)) ,k≠0 if k=0 ∫_0 ^(2π) xdx=2π^2 Re{∫_0 ^(2π) xe^e^(ix) dx}=∫_0 ^(2π) xe^(cos(x)) cos(sin(x))dx =Re[2π^2 +Σ_(k≥1) ((2π)/(ik.k!))] =2π^2 Σ(1/(kk!))=∫(e^x /x)dx=Σ_(k≥0) (x^k /(kk!)) ⇒∫xe^(cos(x)) sin(sin(x))dx=−2πE_i (1)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q98674.png)
$${e}^{{cos}\left({x}\right)+{isin}\left({x}\right)} ={e}^{{cos}\left({x}\right)} \left({cos}\left({sin}\left({x}\right)\right)+{isin}\left({sin}\left({x}\right)\right)\right) \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}\pi} {xe}^{{cos}\left({x}\right)+{isin}\left({x}\right)} {dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}\pi} {xe}^{{e}^{{ix}} } {dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}\pi} \underset{{k}\geqslant\mathrm{0}} {\sum}{x}.\frac{{e}^{{ikx}} }{{k}!} \\ $$$$=\underset{{k}\geqslant\mathrm{0}} {\sum}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}!}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}\pi} {xe}^{{ikx}} {dx} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}\pi} {xe}^{{ikx}} {dx}=\left[{x}\frac{{e}^{{ikx}} }{{ik}}\right]−\int\frac{{e}^{{ik}} }{{ik}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2}\pi}{{ik}}\:,{k}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${if}\:{k}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}\pi} {xdx}=\mathrm{2}\pi^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${Re}\left\{\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}\pi} {xe}^{{e}^{{ix}} } {dx}\right\}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}\pi} {xe}^{{cos}\left({x}\right)} {cos}\left({sin}\left({x}\right)\right){dx} \\ $$$$={Re}\left[\mathrm{2}\pi^{\mathrm{2}} +\underset{{k}\geqslant\mathrm{1}} {\sum}\frac{\mathrm{2}\pi}{{ik}.{k}!}\right] \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}\pi^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Sigma\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{kk}!}=\int\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{x}}{dx}=\underset{{k}\geqslant\mathrm{0}} {\sum}\frac{{x}^{{k}} }{{kk}!} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\int{xe}^{{cos}\left({x}\right)} {sin}\left({sin}\left({x}\right)\right){dx}=−\mathrm{2}\pi{E}_{{i}} \left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$
