Question Number 88104 by ar247 last updated on 08/Apr/20
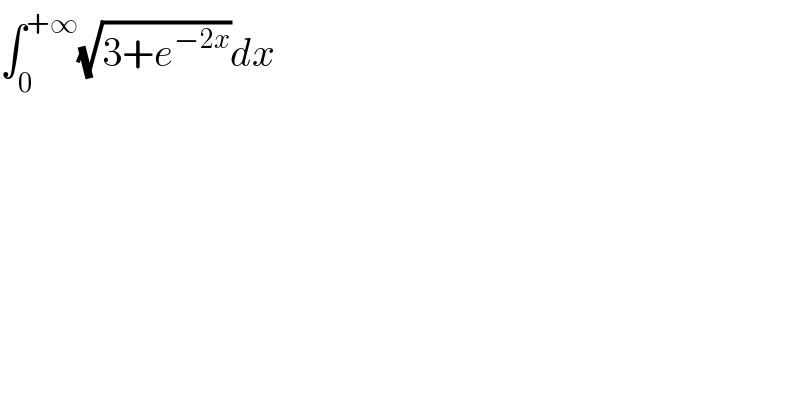
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \sqrt{\mathrm{3}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} }{dx} \\ $$
Commented by ar247 last updated on 08/Apr/20

$${with}\:{stap}\:{please} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 08/Apr/20
![let take a try I =∫_0 ^∞ (√(3+e^(−2x) ))dx changement (√(3+e^(−2x) ))=t give 3+e^(−2x) =t^2 ⇒e^(−2x) =t^2 −3 ⇒−2x =ln(t^2 −3) ⇒x =−(1/2)ln(t^2 −3) ⇒ I =∫_2 ^(√3) t(−(1/2))×((2t)/(t^2 −3))dt = ∫_(√3) ^2 (t^2 /(t^2 −3))dt =∫_(√3) ^2 ((t^2 −3+3)/(t^2 −3))dt =2−(√3)+3∫_(√3) ^2 (dt/(t^2 −3)) =2−(√3)+(3/(2(√3))) ∫_(√3) ^2 ((1/(t−(√3)))−(1/(t+(√3))))dt =2−(√3)+((√3)/2) [ln∣((t−(√3))/(t+(√3)))∣]_(√3) ^2 +C we have lim_(t→(√3)) ln∣((t−(√3))/(t+(√3)))∣=−∞ so this integral is dvergent...!](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q88147.png)
$${let}\:{take}\:{a}\:{try}\:\:{I}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \sqrt{\mathrm{3}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} }{dx}\:\:{changement}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} }={t}\:{give} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} ={t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\Rightarrow{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} ={t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}\:\Rightarrow−\mathrm{2}{x}\:={ln}\left({t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}\right)\:\Rightarrow{x}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left({t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{I}\:=\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \:\:{t}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)×\frac{\mathrm{2}{t}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}}{dt}\:=\:\int_{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}}{dt} \\ $$$$=\int_{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{3}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}}{dt}\:=\mathrm{2}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{3}\int_{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{{dt}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}}\:=\mathrm{2}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\:\int_{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\right){dt} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\left[{ln}\mid\frac{{t}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{{t}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\mid\right]_{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{C}\:\:\:{we}\:{have}\:{lim}_{{t}\rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \:{ln}\mid\frac{{t}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{{t}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\mid=−\infty \\ $$$${so}\:{this}\:{integral}\:{is}\:{dvergent}…! \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Joel578 last updated on 08/Apr/20
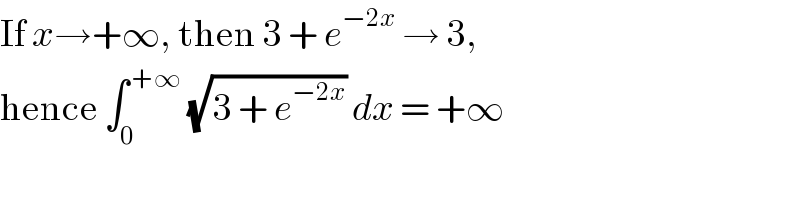
$$\mathrm{If}\:{x}\rightarrow+\infty,\:\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{3}\:+\:{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \:\rightarrow\:\mathrm{3}, \\ $$$$\mathrm{hence}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:+\infty} \:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}\:+\:{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} }\:{dx}\:=\:+\infty \\ $$
