Question Number 121972 by Lordose last updated on 13/Nov/20
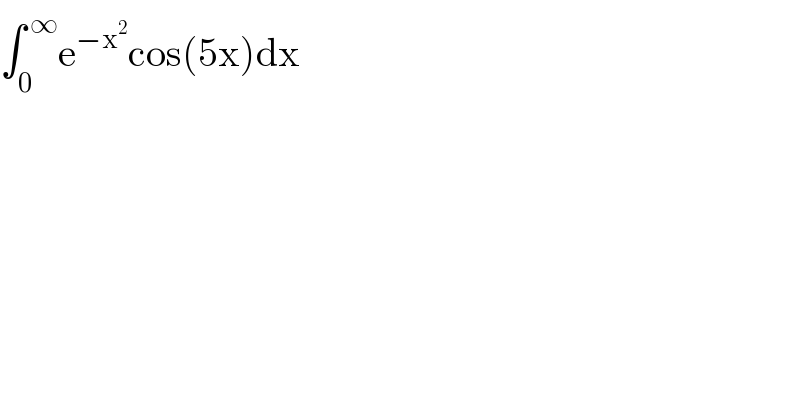
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\infty} \mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{5x}\right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Answered by Bird last updated on 13/Nov/20
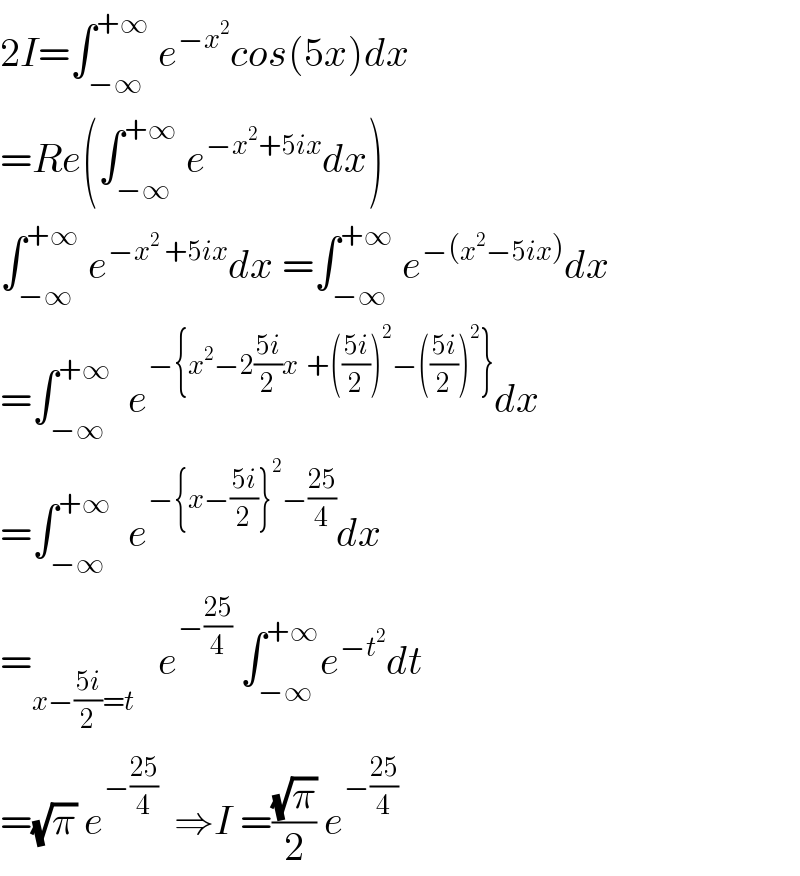
$$\mathrm{2}{I}=\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {cos}\left(\mathrm{5}{x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$={Re}\left(\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}{ix}} {dx}\right) \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{5}{ix}} {dx}\:=\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:{e}^{−\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}{ix}\right)} {dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:{e}^{−\left\{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\frac{\mathrm{5}{i}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}\:\:+\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \right\}} {dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:{e}^{−\left\{{x}−\frac{\mathrm{5}{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\right\}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{4}}} {dx} \\ $$$$=_{{x}−\frac{\mathrm{5}{i}}{\mathrm{2}}={t}} \:\:\:{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{4}}} \:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} {e}^{−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dt} \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\pi}\:{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{4}}} \:\:\Rightarrow{I}\:=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\:{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{4}}} \\ $$
