Question Number 144530 by EDWIN88 last updated on 26/Jun/21
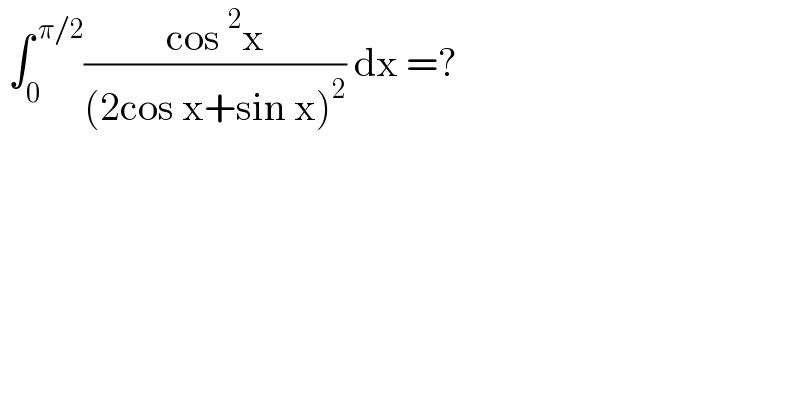
$$\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\pi/\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}{\left(\mathrm{2cos}\:\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\mathrm{dx}\:=? \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 26/Jun/21
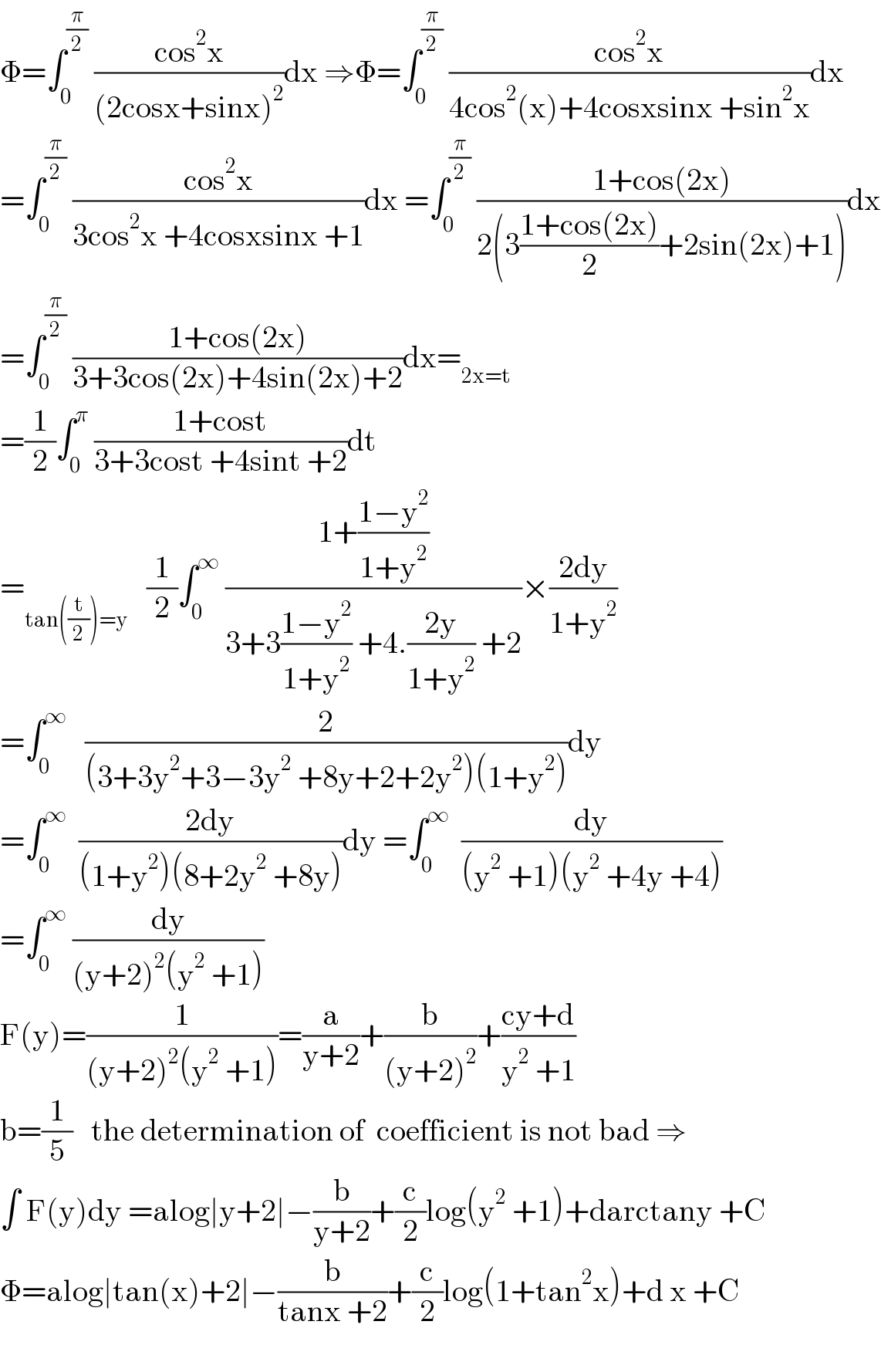
$$\Phi=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\frac{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}{\left(\mathrm{2cosx}+\mathrm{sinx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{dx}\:\Rightarrow\Phi=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\frac{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{4cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{x}\right)+\mathrm{4cosxsinx}\:+\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\frac{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{3cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\:+\mathrm{4cosxsinx}\:+\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{3}\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2sin}\left(\mathrm{2x}\right)+\mathrm{1}\right)}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2x}\right)}{\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{3cos}\left(\mathrm{2x}\right)+\mathrm{4sin}\left(\mathrm{2x}\right)+\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{dx}=_{\mathrm{2x}=\mathrm{t}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cost}}{\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{3cost}\:+\mathrm{4sint}\:+\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{dt}\: \\ $$$$=_{\mathrm{tan}\left(\frac{\mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\mathrm{y}} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{3}\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\mathrm{4}.\frac{\mathrm{2y}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\mathrm{2}}×\frac{\mathrm{2dy}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{3y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{3y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{8y}+\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{2y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\mathrm{dy} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{2dy}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{8}+\mathrm{2y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{8y}\right)}\mathrm{dy}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\left(\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4y}\:+\mathrm{4}\right)} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\left(\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\mathrm{F}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\left(\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{cy}+\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{b}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\:\:\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{determination}\:\mathrm{of}\:\:\mathrm{coefficient}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{bad}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\int\:\mathrm{F}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)\mathrm{dy}\:=\mathrm{alog}\mid\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{2}\mid−\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{darctany}\:+\mathrm{C} \\ $$$$\Phi=\mathrm{alog}\mid\mathrm{tan}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)+\mathrm{2}\mid−\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{tanx}\:+\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\right)+\mathrm{d}\:\mathrm{x}\:+\mathrm{C} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 26/Jun/21
![I=∫_0 ^(π/2) ((cos^2 x)/((2cosx+sinx)^2 ))dx=∫_0 ^(π/2) (dx/((2+tanx)^2 )) =∫_0 ^∞ ((2dt)/((2+t)^2 (1+t^2 )))=2∫_0 ^∞ (dt/((t+2)^2 (t^2 +1))) =2∫_0 ^∞ ((4/(25))∙(1/(t+2))+(1/5)∙(1/((t+2)^2 ))−(1/(25))∙((4t−3)/(t^2 +1)))dt =2[(4/(25))ln(t+2)−(1/5)∙(1/(t+2))−(2/(25))ln(t^2 +1)+(3/(25))arctan(t)]_0 ^∞ =[(4/(25))ln(((t^2 +2t+2)/(t^2 +1)))−(2/(5(t+2)))+(6/(25))arctan(t)]_0 ^∞ =−(4/(25))ln(2)+(1/5)+((3π)/(25))=(4/(25))ln((1/2))+(1/5)+((3π)/(25))](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q144604.png)
$$\mathrm{I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}{\left(\mathrm{2cosx}+\mathrm{sinx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{dx}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{tanx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\:\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{2dt}}{\left(\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{t}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{dt}}{\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\:\:=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{25}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{25}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{4t}−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\right)\mathrm{dt} \\ $$$$\:\:=\mathrm{2}\left[\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{25}}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{25}}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{25}}\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \\ $$$$\:\:=\left[\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{25}}\mathrm{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2t}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)}+\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{25}}\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \\ $$$$\:\:=−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{25}}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{25}}=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{25}}\mathrm{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{25}} \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 26/Jun/21
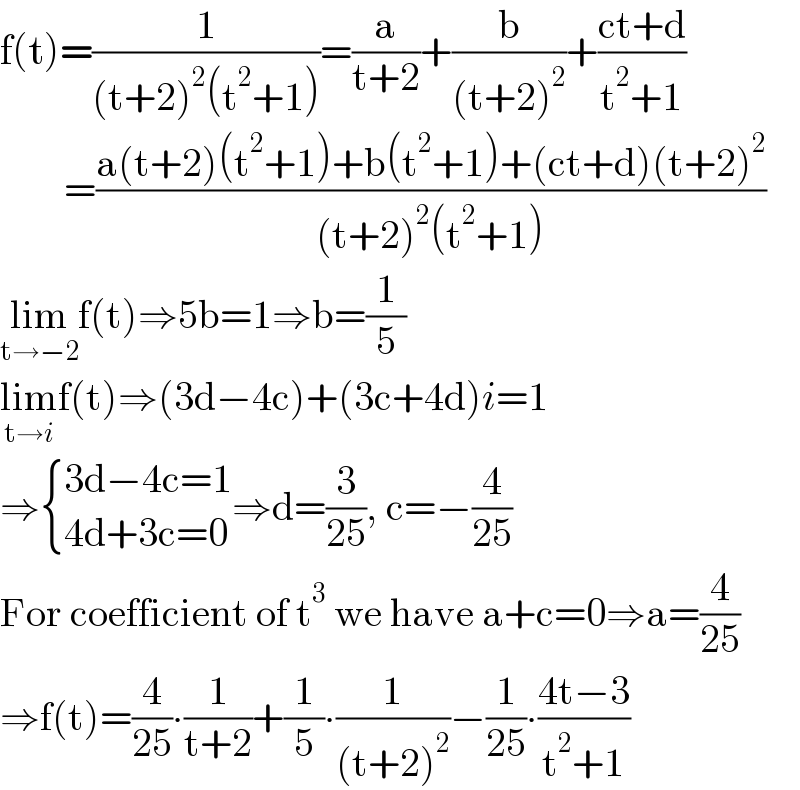
$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{ct}+\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{b}\left(\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)+\left(\mathrm{ct}+\mathrm{d}\right)\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{t}\rightarrow−\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}f}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{5b}=\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\mathrm{b}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{t}\rightarrow{i}} {\mathrm{lim}f}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{3d}−\mathrm{4c}\right)+\left(\mathrm{3c}+\mathrm{4d}\right){i}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{\mathrm{3d}−\mathrm{4c}=\mathrm{1}}\\{\mathrm{4d}+\mathrm{3c}=\mathrm{0}}\end{cases}\Rightarrow\mathrm{d}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{25}},\:\mathrm{c}=−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{25}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{For}\:\mathrm{coefficient}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{3}} \:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{c}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{25}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{25}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{25}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{4t}−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
