Question Number 149903 by bramlexs22 last updated on 08/Aug/21
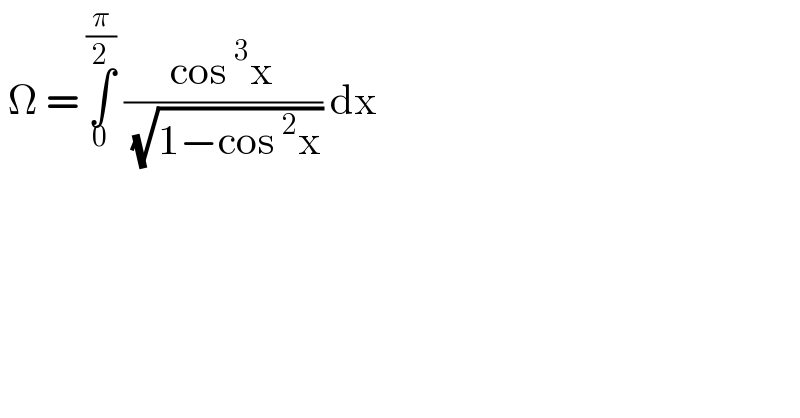
$$\:\Omega\:=\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{x}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}}\:\mathrm{dx}\: \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 08/Aug/21
![Ω=∫_0 ^(π/2) ((cos^3 x)/( (√(1−cos^2 x))))dx=∫_0 ^(π/2) ((1−sin^2 x)/( sinx))cosxdx =∫_0 ^1 ((1/u)−u)du=[lnu−(u^2 /2)]_0 ^1 =−(1/2)+∞ divergent](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q149904.png)
$$\Omega=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{3}} {x}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}}{dx}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{\:\mathrm{sin}{x}}\mathrm{cos}{xdx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}−{u}\right){du}=\left[\mathrm{ln}{u}−\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\infty \\ $$$$\mathrm{divergent} \\ $$
