Question Number 156793 by alcohol last updated on 15/Oct/21
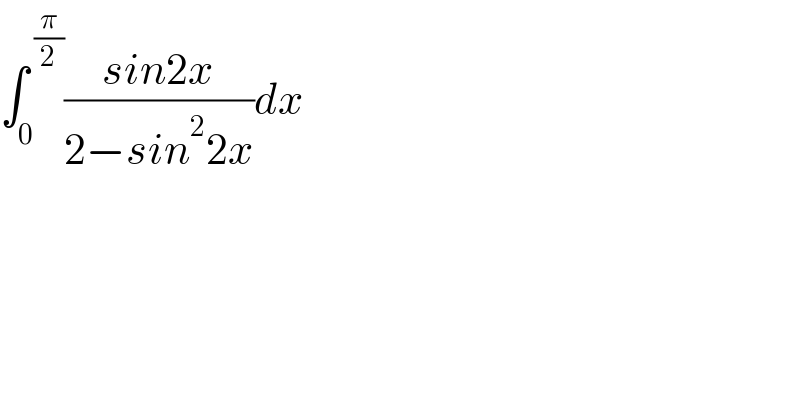
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{{sin}\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{2}−{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{2}{x}}{dx} \\ $$
Answered by FongXD last updated on 15/Oct/21
![=∫_0 ^(π/2) ((sin2x)/(1+cos^2 2x))dx=−(1/2)∫_0 ^(π/2) (((cos2x)′)/(1+cos^2 2x))dx =−(1/2)[arctan(cos2x)]_0 ^(π/2) =−(1/2)(−(π/4)−(π/4))=(π/4) therefore. ∫_0 ^(π/2) ((sin2x)/(2−sin^2 2x))dx=(π/4)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q156801.png)
$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{\mathrm{sin2x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{2x}}\mathrm{dx}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{\left(\mathrm{cos2x}\right)'}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{2x}}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{cos2x}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right)=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{therefore}.\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{\mathrm{sin2x}}{\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{2x}}\mathrm{dx}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
