Question Number 155252 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 27/Sep/21

$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {x}.{sin}^{\:\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right).{ln}\left({sin}\left({x}\right)\right){dx} \\ $$
Answered by phanphuoc last updated on 28/Sep/21
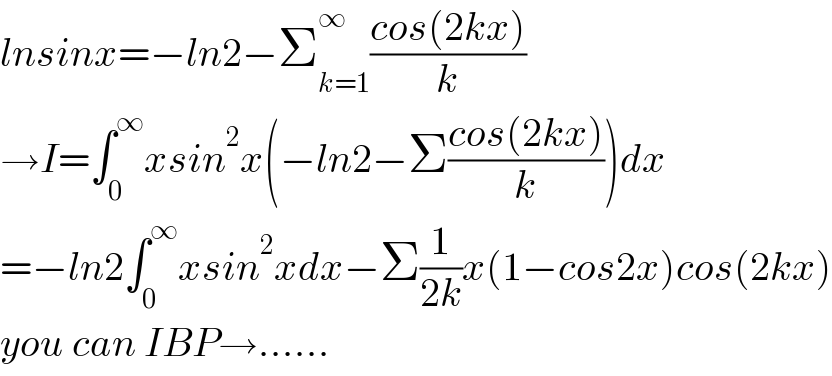
$${lnsinx}=−{ln}\mathrm{2}−\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \frac{{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{kx}\right)}{{k}} \\ $$$$\rightarrow{I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {xsin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\left(−{ln}\mathrm{2}−\Sigma\frac{{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{kx}\right)}{{k}}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=−{ln}\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {xsin}^{\mathrm{2}} {xdx}−\Sigma\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{k}}{x}\left(\mathrm{1}−{cos}\mathrm{2}{x}\right){cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{kx}\right) \\ $$$${you}\:{can}\:{IBP}\rightarrow…… \\ $$
