Question Number 120688 by bobhans last updated on 01/Nov/20
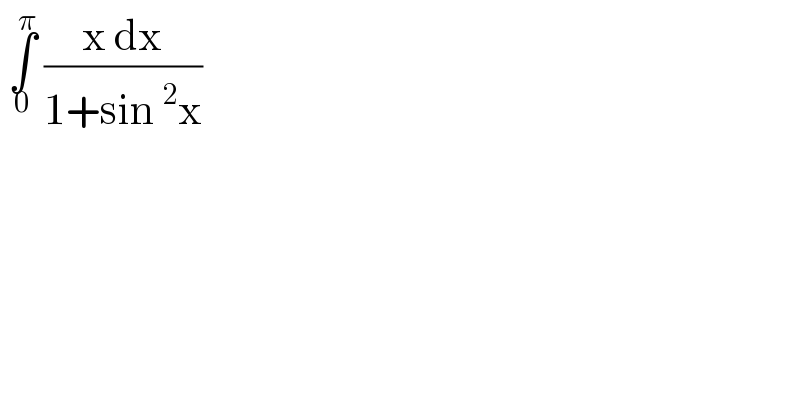
$$\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}\: \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 02/Nov/20
![ψ = ∫_0 ^π ((x dx)/(1+sin^2 x)) ; [ let x = π−w ] ψ = ∫_π ^0 (((π−x)(−dw))/(1+sin^2 (π−w)^2 )) = ∫_0 ^π ((π−w)/(1+sin^2 w)) dw adding the equation give 2ψ = ∫_0 ^π (π/(1+sin^2 x)) dx ψ=(1/2)∫_0 ^π (π/(1+sin^2 x)) dx =(π/2)∫_0 ^π ((cosec^2 x dx)/(cosec^2 x+1)) ψ=(π/2)∫_0 ^π ((cosec^2 x dx)/((1+cot^2 x)+1)) = (π/2)∫_(−∞) ^∞ ((1 dt)/(2+t^2 )) ; where t = cot x ψ=(π/2).(1/( (√2))) arc tan ((t/( (√2)))) ∣_(−∞) ^∞ ψ=(π/(2(√2))) [(π/2)−(−(π/2)) ]= (π^2 /(2(√2))) .▲](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q120695.png)
$$\:\psi\:=\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\:\frac{{x}\:{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}\:;\:\:\left[\:{let}\:{x}\:=\:\pi−{w}\:\right]\: \\ $$$$\psi\:=\:\underset{\pi} {\overset{\mathrm{0}} {\int}}\:\frac{\left(\pi−{x}\right)\left(−{dw}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\pi−{w}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\:\frac{\pi−{w}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {w}}\:{dw} \\ $$$${adding}\:{the}\:{equation}\:{give} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}\psi\:=\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}\:{dx}\: \\ $$$$\psi=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}\:{dx}\:=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{cosec}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\:{dx}}{\mathrm{cosec}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\psi=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{cosec}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\:{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cot}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right)+\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\underset{−\infty} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}\:{dt}}{\mathrm{2}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:}\:;\:{where}\:{t}\:=\:\mathrm{cot}\:{x} \\ $$$$\psi=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}.\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\mathrm{arc}\:\mathrm{tan}\:\left(\frac{{t}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)\:\mid_{−\infty} ^{\infty} \\ $$$$\psi=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\left[\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\left(−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:\right]=\:\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:.\blacktriangle \\ $$
