Question Number 82174 by jagoll last updated on 18/Feb/20
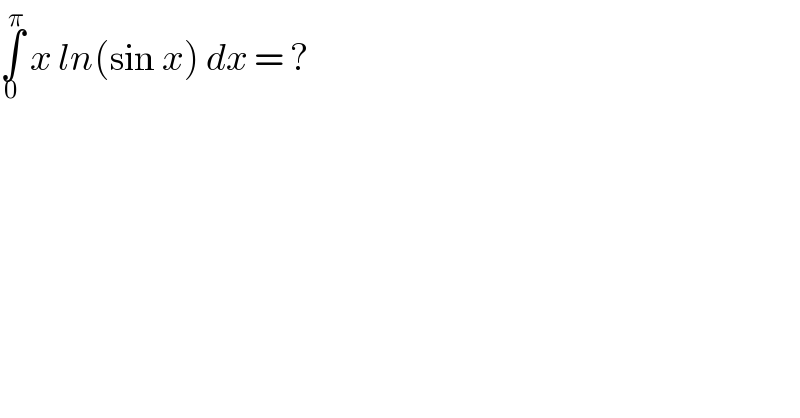
$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\:{x}\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right)\:{dx}\:=\:?\: \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 19/Feb/20
![let I =∫_0 ^π xln(sinx)dx ⇒I=∫_0 ^(π/2) x ln(sinx)dx +∫_(π/2) ^π xln(sinx)dx but ∫_(π/2) ^π x ln(sinx)dx =_(x=(π/2) +α) ∫_0 ^(π/2) ((π/2) +α)ln(cosα)dα =(π/2) ∫_0 ^(π/2) ln(cosα)dα +∫_0 ^(π/2) αln(cosα)dα ⇒ I =(π/2) ∫_0 ^(π/2) ln(cosα)dα +∫_0 ^(π/2) x(ln(sinx)+ln(cosx) dx =(π/2) ∫_0 ^(π/2) ln(cosα)dα +∫_0 ^(π/2) xln((1/2)sin(2x))dx =(π/2) ∫_0 ^(π/2) ln(cosα)dα −ln(2)∫_0 ^(π/2) x dx +∫_0 ^(π/2) xln(2x)dx_(→2x=t) =(π/2) ∫_0 ^(π/2) ln(cosα)dα −ln(2)[(x^2 /2)]_0 ^(π/2) +(1/2) ∫_0 ^π tln(t)(dt/2) =(π/2)∫_0 ^(π/2) ln(cosα)dα −ln(2){(π^2 /8)} +(1/4) I ⇒ (3/4) I =(π/2)(−(π/2)ln(2))−(π^2 /8)ln(2) =−(π^2 /4)ln(2)−(π^2 /8)ln(2) =−((3π^2 )/8)ln(2) ⇒ I =(4/3)(−((3π^2 )/8))ln(2) =−(π^2 /2)ln(2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q82240.png)
$${let}\:{I}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} {xln}\left({sinx}\right){dx}\:\Rightarrow{I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{x}\:{ln}\left({sinx}\right){dx}\:+\int_{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\pi} \:{xln}\left({sinx}\right){dx} \\ $$$${but}\:\int_{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\pi} \:{x}\:{ln}\left({sinx}\right){dx}\:=_{{x}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\alpha} \:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\alpha\right){ln}\left({cos}\alpha\right){d}\alpha \\ $$$$=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{ln}\left({cos}\alpha\right){d}\alpha\:+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\alpha{ln}\left({cos}\alpha\right){d}\alpha\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${I}\:=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{ln}\left({cos}\alpha\right){d}\alpha\:\:+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {x}\left({ln}\left({sinx}\right)+{ln}\left({cosx}\right)\:{dx}\right. \\ $$$$=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{ln}\left({cos}\alpha\right){d}\alpha\:+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {xln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{ln}\left({cos}\alpha\right){d}\alpha\:−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{x}\:{dx}\:+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{xln}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right){dx}_{\rightarrow\mathrm{2}{x}={t}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {ln}\left({cos}\alpha\right){d}\alpha\:−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\left[\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} {tln}\left({t}\right)\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{ln}\left({cos}\alpha\right){d}\alpha\:−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\left\{\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{8}}\right\}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\:{I}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{4}}\:{I}\:=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\left(−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right)−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{8}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:=−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{8}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\: \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{8}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:{I}\:=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{8}}\right){ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:=−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$
Answered by Kunal12588 last updated on 19/Feb/20
![I=∫_0 ^π x log(sin x) dx ⇒I=∫_0 ^π (x−π) log(sin x) dx ⇒I=(π/2)∫_0 ^π log(sin x) dx ⇒I=π∫_0 ^(π/2) log(sin x) dx [★ ∫_0 ^(π/2) log(sin x) dx=∫_0 ^(π/2) log(cos x)dx=−(π/2)log(2)] ⇒I=π(((−π)/2)log(2))=((−π^2 )/2)log(2) ∴ ∫_0 ^( π) x log(sin x) dx=−(π^2 /2)log (2) [★here “log a” means“log_e a”]](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q82271.png)
$${I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} {x}\:{log}\left({sin}\:{x}\right)\:{dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} \left({x}−\pi\right)\:{log}\left({sin}\:{x}\right)\:{dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} \:{log}\left({sin}\:{x}\right)\:{dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\pi\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({sin}\:{x}\right)\:{dx} \\ $$$$\left[\bigstar\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({sin}\:{x}\right)\:{dx}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({cos}\:{x}\right){dx}=−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\pi\left(\frac{−\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right)=\frac{−\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\pi} {x}\:{log}\left({sin}\:{x}\right)\:{dx}=−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{log}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\: \\ $$$$\left[\bigstar{here}\:\:“{log}\:{a}''\:{means}“{log}_{{e}} {a}''\right] \\ $$
Commented by Kunal12588 last updated on 19/Feb/20
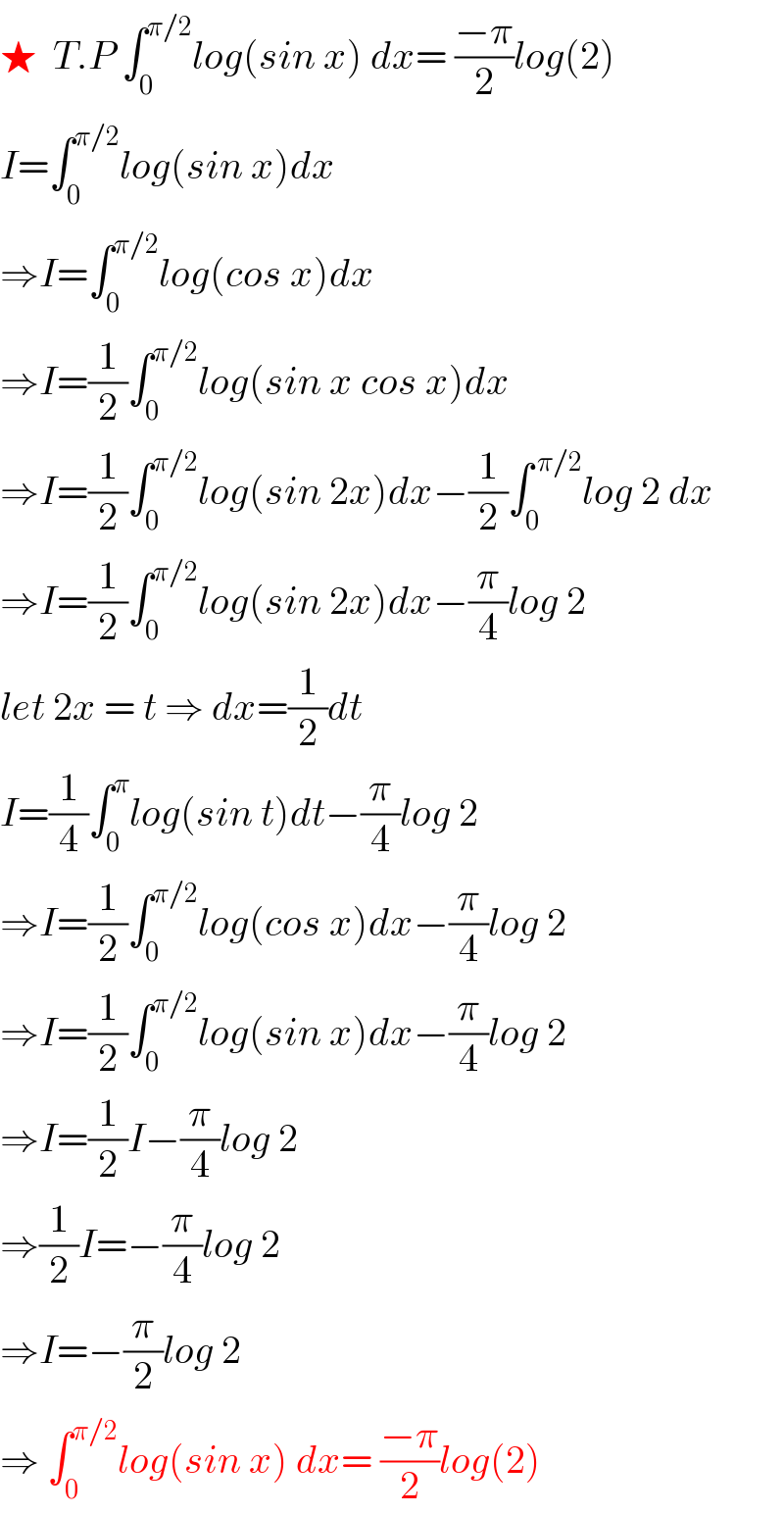
$$\bigstar\:\:{T}.{P}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({sin}\:{x}\right)\:{dx}=\:\frac{−\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({sin}\:{x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({cos}\:{x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({sin}\:{x}\:{cos}\:{x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\right){dx}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\:\mathrm{2}\:{dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\right){dx}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}{log}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${let}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:=\:{t}\:\Rightarrow\:{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{dt} \\ $$$${I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} {log}\left({sin}\:{t}\right){dt}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}{log}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({cos}\:{x}\right){dx}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}{log}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({sin}\:{x}\right){dx}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}{log}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{I}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}{log}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{I}=−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}{log}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{I}=−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{log}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {log}\left({sin}\:{x}\right)\:{dx}=\:\frac{−\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$
