Question Number 124251 by bramlexs22 last updated on 02/Dec/20
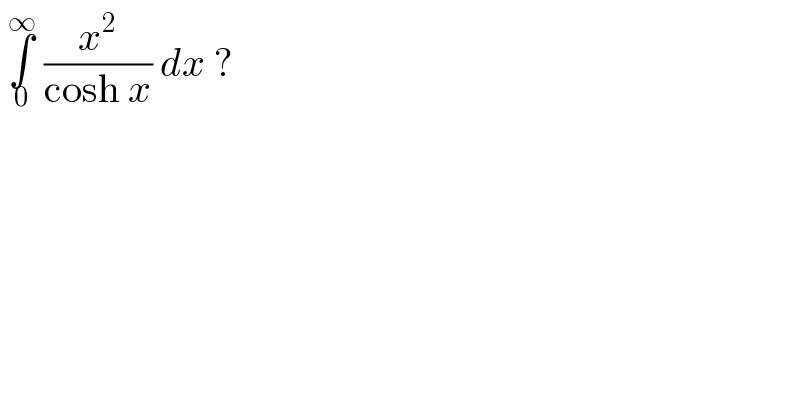
$$\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{cosh}\:{x}}\:{dx}\:? \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 02/Dec/20
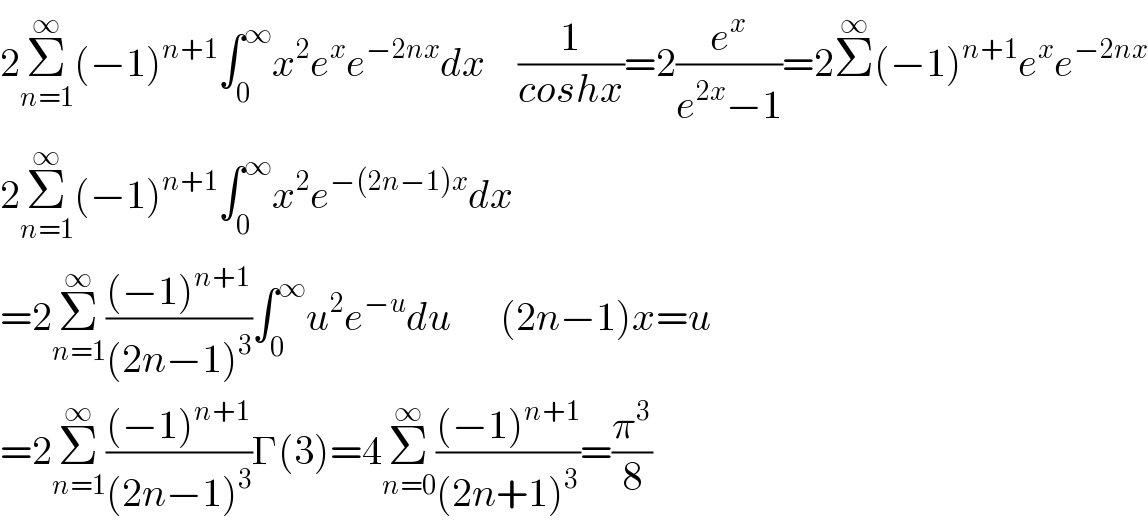
$$\mathrm{2}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{{x}} {e}^{−\mathrm{2}{nx}} {dx}\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{coshx}}=\mathrm{2}\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} −\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{2}\overset{\infty} {\sum}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} {e}^{−\mathrm{2}{nx}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}\right){x}} {dx}\:\:\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {u}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{u}} {du}\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}\right){x}={u} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\Gamma\left(\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{4}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }=\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$
