Question Number 102066 by bramlex last updated on 06/Jul/20

$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\int\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{ax}\right)\:\mathrm{dx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{ax}−\mathrm{b}}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\left(\mathrm{D}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{2D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{D}\right)\mathrm{y}\:=\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} +\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{x} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{3}\right)\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{area}\:\mathrm{between}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{curves} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{y}\:=\:−\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}\: \\ $$
Answered by bemath last updated on 06/Jul/20
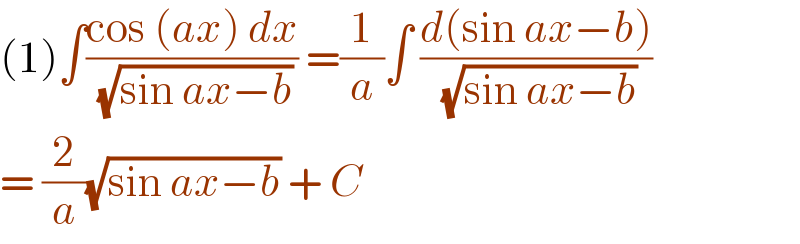
$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:\left({ax}\right)\:{dx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{sin}\:{ax}−{b}}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{a}}\int\:\frac{{d}\left(\mathrm{sin}\:{ax}−{b}\right)}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{sin}\:{ax}−{b}}} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{a}}\sqrt{\mathrm{sin}\:{ax}−{b}}\:+\:{C}\: \\ $$
Answered by PRITHWISH SEN 2 last updated on 06/Jul/20
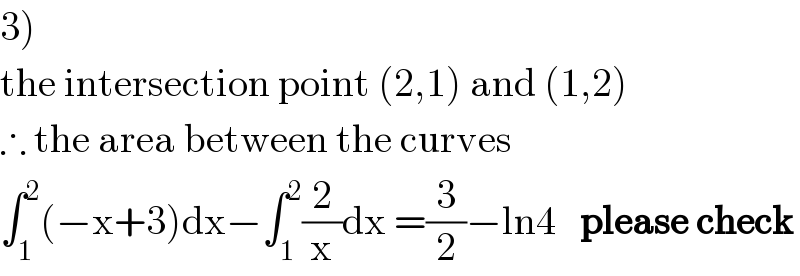
$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{intersection}\:\mathrm{point}\:\left(\mathrm{2},\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{and}\:\left(\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{area}\:\mathrm{between}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{curves} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \left(−\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}\right)\mathrm{dx}−\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}}\mathrm{dx}\:=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{ln4}\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{please}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{check}} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 06/Jul/20

$$\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}=−{x}+\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{1}{or}\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${point}\:{of}\:{intersecting}\:\left(\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2}\right)\:,\:\left(\mathrm{2},\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}+{x}−\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{log}\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{3}=\mid\mathrm{2}{log}\mathrm{2}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\mid=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{2}{log}\mathrm{2}\:\:\: \\ $$
