Question Number 164809 by mathlove last updated on 22/Jan/22
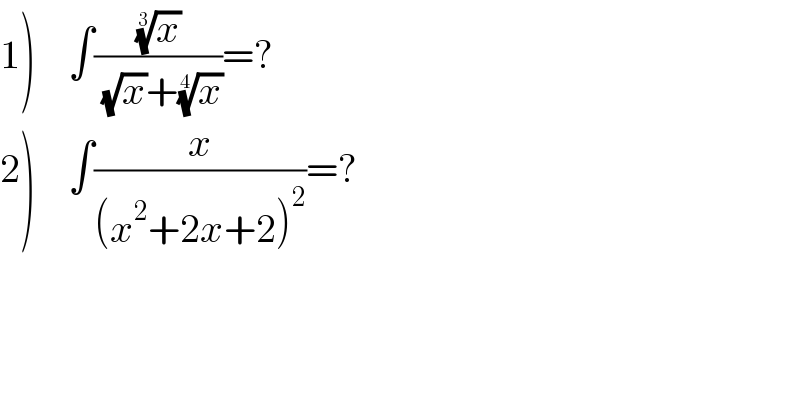
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:\:\:\int\frac{\sqrt[{\mathrm{3}}]{{x}}}{\:\sqrt{{x}}+\sqrt[{\mathrm{4}}]{{x}}}=? \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:\:\:\:\int\frac{{x}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=? \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 22/Jan/22
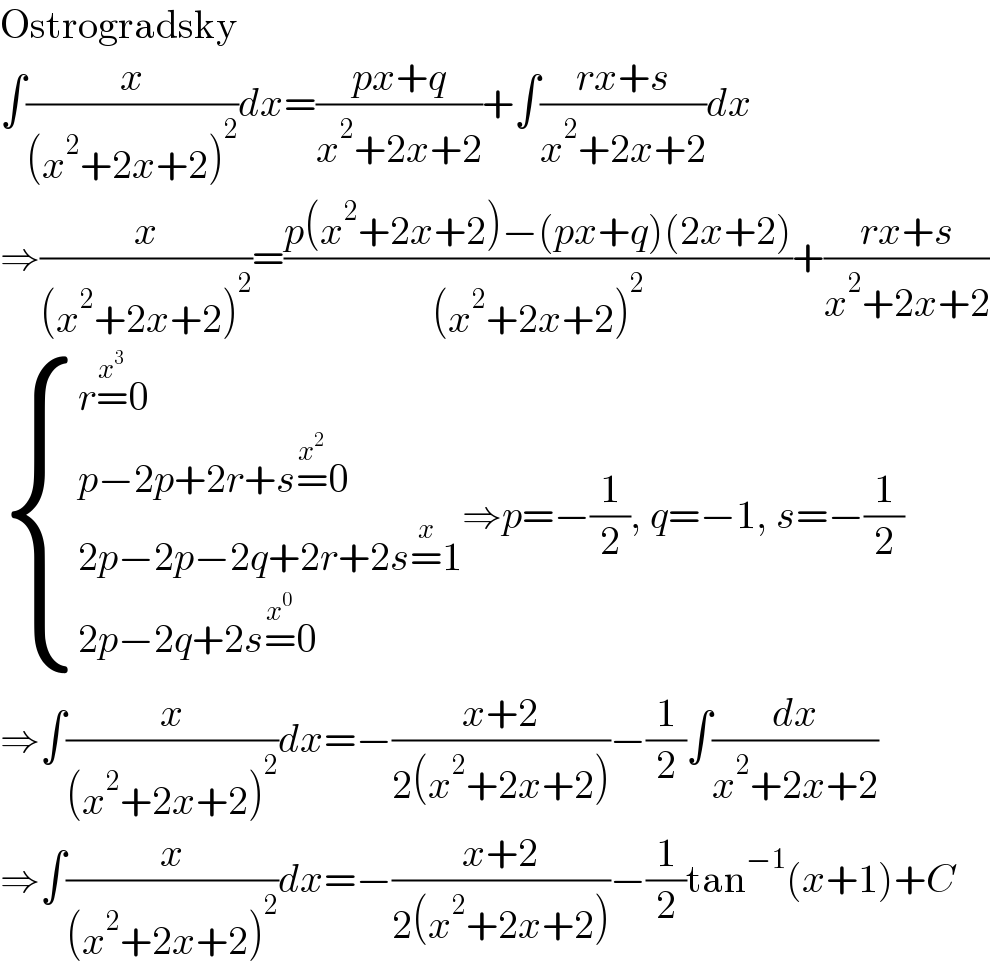
$$\mathrm{Ostrogradsky} \\ $$$$\int\frac{{x}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\frac{{px}+{q}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}}+\int\frac{{rx}+{s}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}}{dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{x}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{p}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)−\left({px}+{q}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{rx}+{s}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{{r}\overset{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} } {=}\mathrm{0}}\\{{p}−\mathrm{2}{p}+\mathrm{2}{r}+{s}\overset{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {=}\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{2}{p}−\mathrm{2}{p}−\mathrm{2}{q}+\mathrm{2}{r}+\mathrm{2}{s}\overset{{x}} {=}\mathrm{1}}\\{\mathrm{2}{p}−\mathrm{2}{q}+\mathrm{2}{s}\overset{{x}^{\mathrm{0}} } {=}\mathrm{0}}\end{cases}\Rightarrow{p}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}},\:{q}=−\mathrm{1},\:{s}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\int\frac{{x}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=−\frac{{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\int\frac{{x}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=−\frac{{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)+{C} \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 22/Jan/22
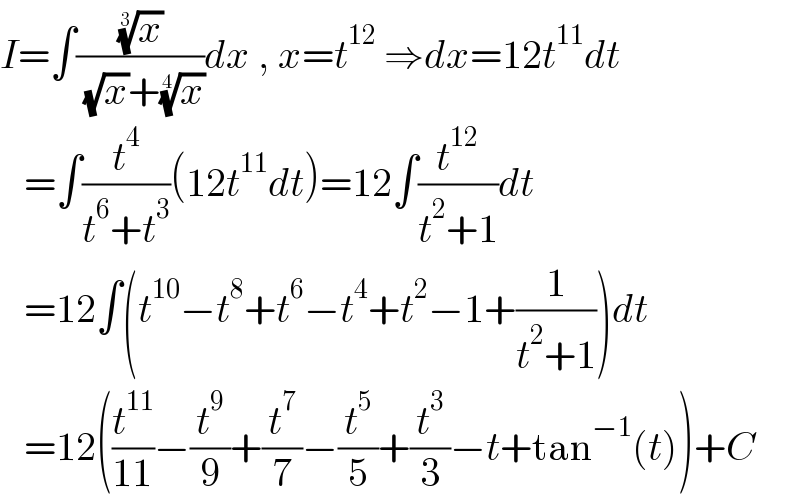
$${I}=\int\frac{\sqrt[{\mathrm{3}}]{{x}}}{\:\sqrt{{x}}+\sqrt[{\mathrm{4}}]{{x}}}{dx}\:,\:{x}={t}^{\mathrm{12}} \:\Rightarrow{dx}=\mathrm{12}{t}^{\mathrm{11}} {dt} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\int\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{4}} }{{t}^{\mathrm{6}} +{t}^{\mathrm{3}} }\left(\mathrm{12}{t}^{\mathrm{11}} {dt}\right)=\mathrm{12}\int\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{12}} }{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{dt} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\mathrm{12}\int\left({t}^{\mathrm{10}} −{t}^{\mathrm{8}} +{t}^{\mathrm{6}} −{t}^{\mathrm{4}} +{t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\right){dt} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\mathrm{12}\left(\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{11}} }{\mathrm{11}}−\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{9}} }{\mathrm{9}}+\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{7}} }{\mathrm{7}}−\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}}+\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}−{t}+\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({t}\right)\right)+{C} \\ $$
