Question Number 154780 by talminator2856791 last updated on 21/Sep/21
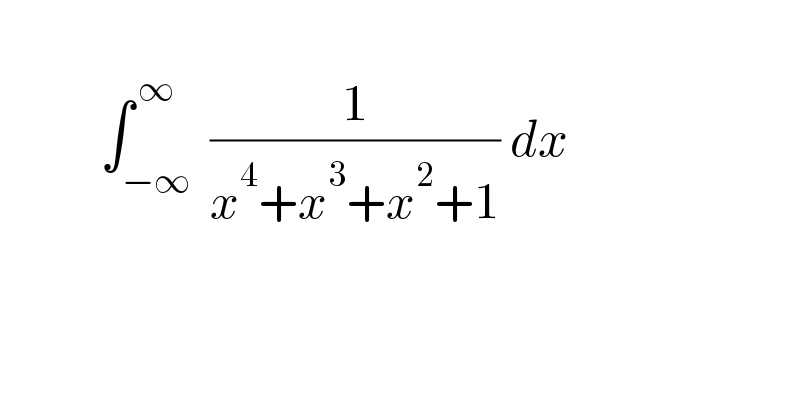
$$\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\int_{−\infty} ^{\:\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\:{dx} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$
Answered by phanphuoc last updated on 21/Sep/21
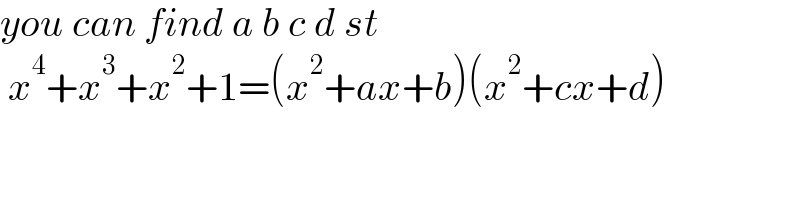
$${you}\:{can}\:{find}\:{a}\:{b}\:{c}\:{d}\:{st} \\ $$$$\:{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}=\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{ax}+{b}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{cx}+{d}\right) \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 21/Sep/21
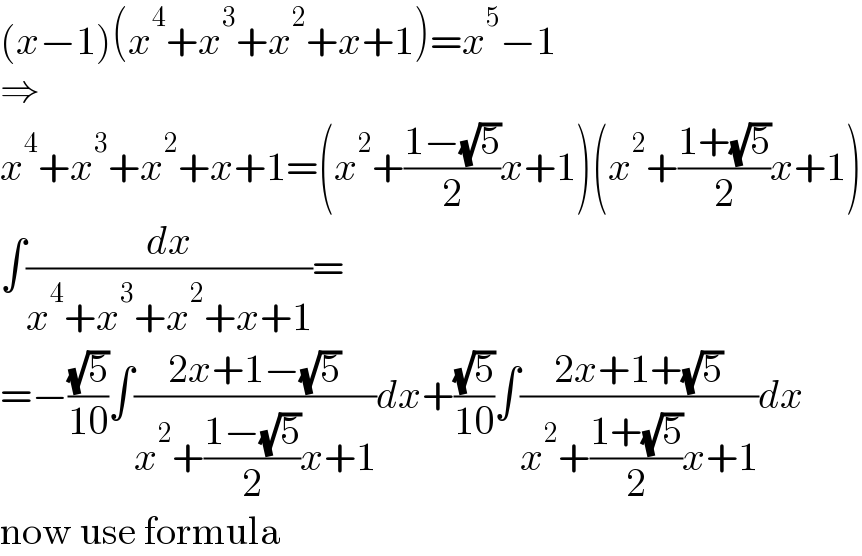
$$\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{5}} −\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}=\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\int\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}}= \\ $$$$=−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{10}}\int\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}+\mathrm{1}}{dx}+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{10}}\int\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}+\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{now}\:\mathrm{use}\:\mathrm{formula} \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 21/Sep/21
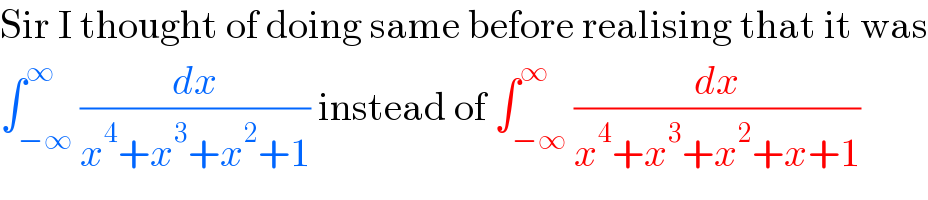
$$\mathrm{Sir}\:\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{thought}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{doing}\:\mathrm{same}\:\mathrm{before}\:\mathrm{realising}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{was} \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} \frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\:\mathrm{instead}\:\mathrm{of}\:\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} \frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 21/Sep/21
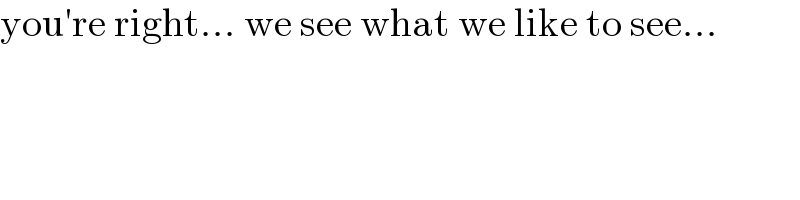
$$\mathrm{you}'\mathrm{re}\:\mathrm{right}…\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{see}\:\mathrm{what}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{like}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{see}… \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 21/Sep/21

$$\mathcal{G}{ood}\:\mathcal{S}{aying}:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{see}\:\mathrm{what}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{like}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{see}! \\ $$
Answered by mindispower last updated on 22/Sep/21
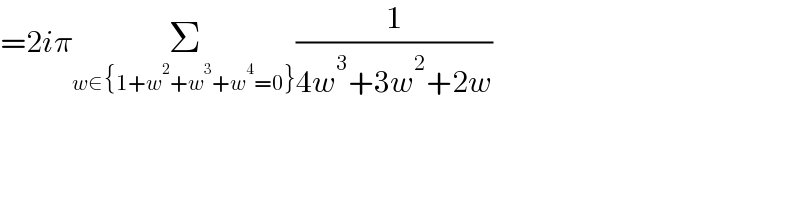
$$=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\underset{{w}\in\left\{\mathrm{1}+{w}^{\mathrm{2}} +{w}^{\mathrm{3}} +{w}^{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{0}\right\}} {\sum}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}{w}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{3}{w}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{w}} \\ $$
