Question Number 63433 by minh2001 last updated on 04/Jul/19
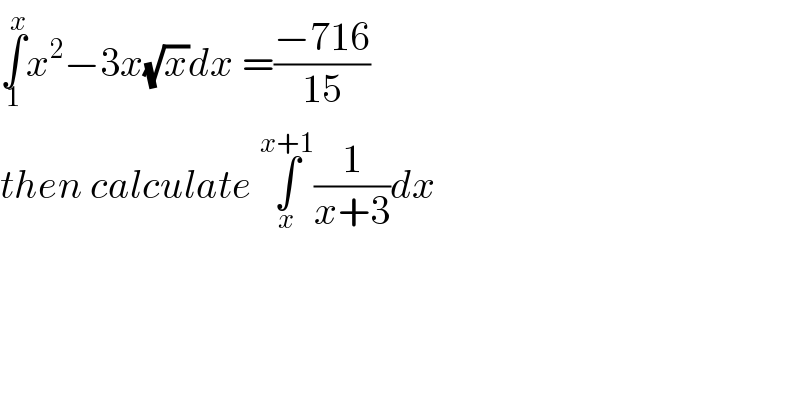
$$\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{x}} {\int}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}\sqrt{{x}}{dx}\:=\frac{−\mathrm{716}}{\mathrm{15}} \\ $$$${then}\:{calculate}\:\underset{{x}} {\overset{{x}+\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\mathrm{3}}{dx} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 04/Jul/19

$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{borders}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{independent}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{integral}\:\mathrm{variable} \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 04/Jul/19
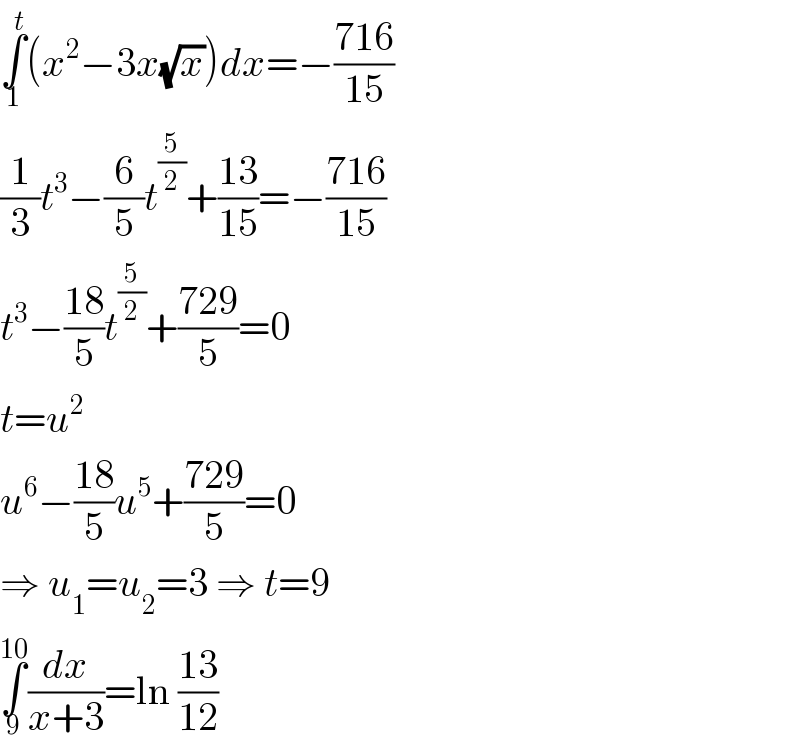
$$\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{t}} {\int}}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}\sqrt{{x}}\right){dx}=−\frac{\mathrm{716}}{\mathrm{15}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}{t}^{\mathrm{3}} −\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{5}}{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}} +\frac{\mathrm{13}}{\mathrm{15}}=−\frac{\mathrm{716}}{\mathrm{15}} \\ $$$${t}^{\mathrm{3}} −\frac{\mathrm{18}}{\mathrm{5}}{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}} +\frac{\mathrm{729}}{\mathrm{5}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${t}={u}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${u}^{\mathrm{6}} −\frac{\mathrm{18}}{\mathrm{5}}{u}^{\mathrm{5}} +\frac{\mathrm{729}}{\mathrm{5}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{u}_{\mathrm{1}} ={u}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{3}\:\Rightarrow\:{t}=\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{9}} {\overset{\mathrm{10}} {\int}}\frac{{dx}}{{x}+\mathrm{3}}=\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{\mathrm{13}}{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$
