Question Number 105112 by bemath last updated on 26/Jul/20
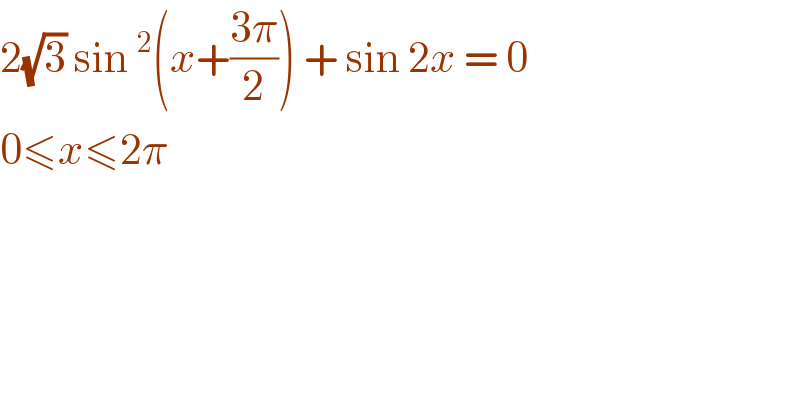
$$\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:+\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{0}\leqslant{x}\leqslant\mathrm{2}\pi\: \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 28/Jul/20
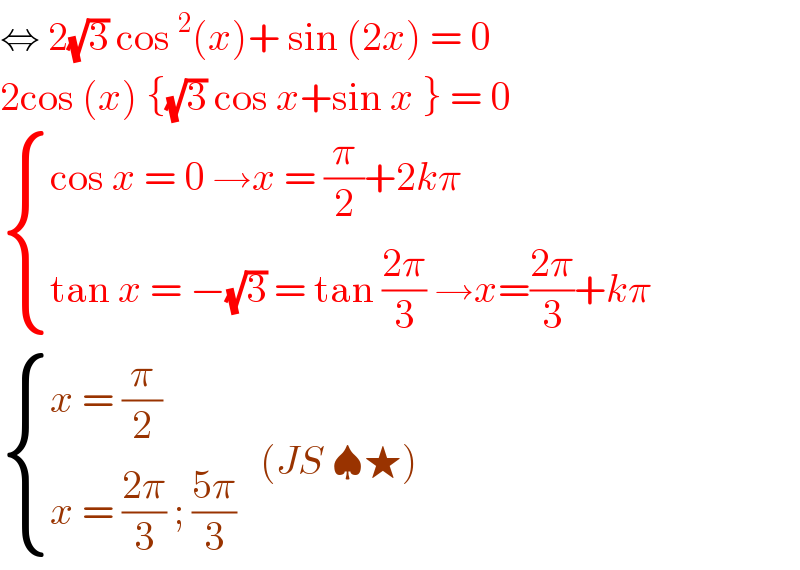
$$\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right)+\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2cos}\:\left({x}\right)\:\left\{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\right\}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\rightarrow{x}\:=\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2}{k}\pi}\\{\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\:=\:−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:=\:\mathrm{tan}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}\:\rightarrow{x}=\frac{\mathrm{2}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}+{k}\pi}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{{x}\:=\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}}\\{{x}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}\:;\:\frac{\mathrm{5}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}}\end{cases}\:\:\:\left({JS}\:\spadesuit\bigstar\right) \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 26/Jul/20
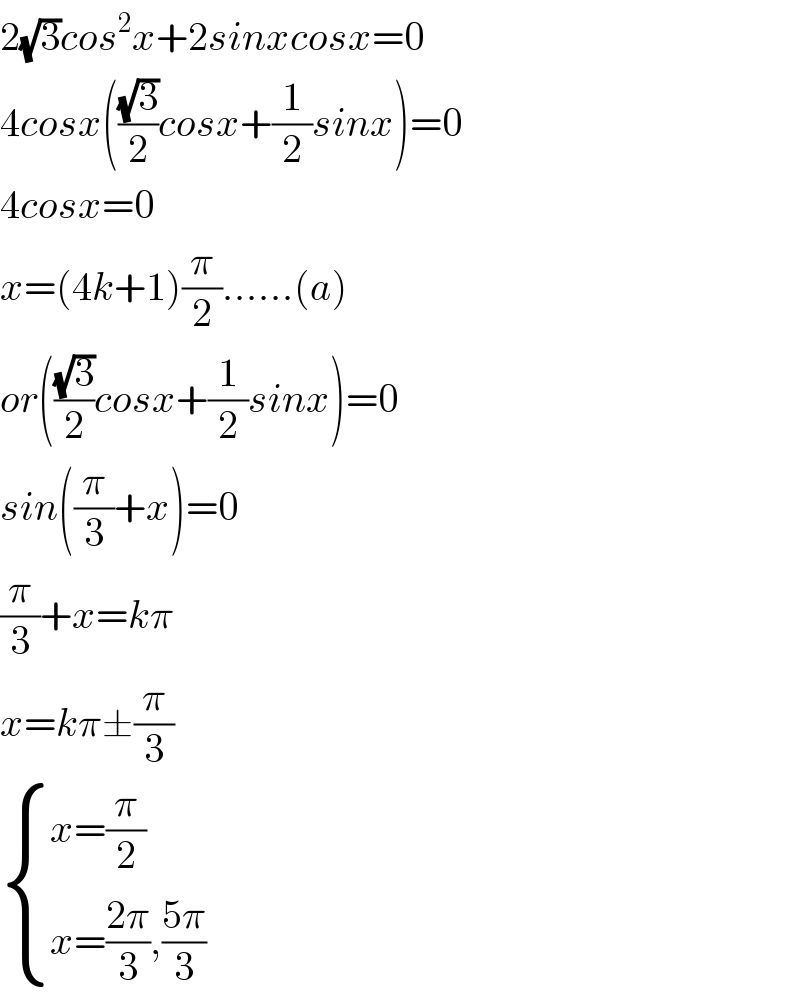
$$\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}+\mathrm{2}{sinxcosx}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}{cosx}\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}{cosx}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{sinx}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}{cosx}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\left(\mathrm{4}{k}+\mathrm{1}\right)\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}……\left({a}\right) \\ $$$${or}\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}{cosx}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{sinx}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${sin}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}+{x}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}+{x}={k}\pi \\ $$$${x}={k}\pi\pm\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{{x}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}}\\{{x}=\frac{\mathrm{2}\pi}{\mathrm{3}},\frac{\mathrm{5}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}}\end{cases} \\ $$
