Question Number 97218 by bobhans last updated on 07/Jun/20
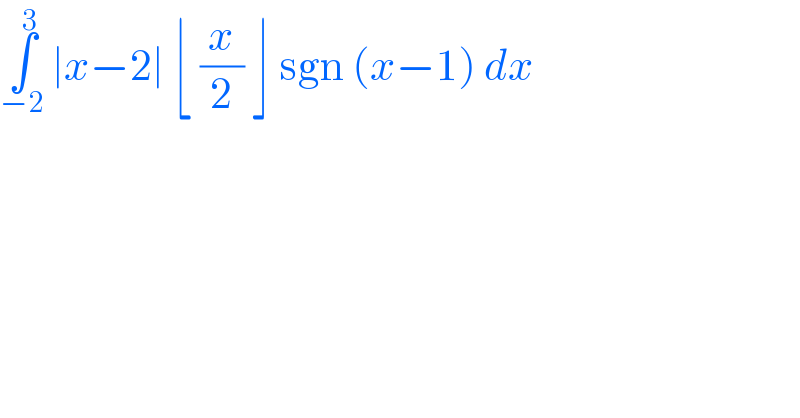
$$\underset{−\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\mathrm{3}} {\int}}\:\mid{x}−\mathrm{2}\mid\:\lfloor\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\rfloor\:\mathrm{sgn}\:\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:{dx}\: \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 07/Jun/20
![sgn(x−1)=1 , when x>1 sgn(x−1)=−1, when x<1 J= −∫_(−2) ^1 ∣x−2∣ ⌊ (x/2) ⌋ dx + ∫_1 ^3 ∣x−2∣ ⌊ (x/2) ⌋ dx J = ∫_(−2) ^1 (x−2) ⌊(x/2)⌋ dx− ∫_1 ^2 (x−2) ⌊(x/2)⌋ dx + ∫_2 ^3 (x−2) ⌊(x/2)⌋ dx J= ∫_(−2) ^3 (x−2)⌊(x/2)⌋dx−2∫_1 ^2 (x−2) ⌊(x/2)⌋ dx let x=2z J=∫_(−1) ^(3/2) (2z−2)⌊z⌋.2 dz−2∫_(1/2) ^1 (2z−2)⌊z⌋.2dz J=∫_(−1) ^(3/2) (4z−4)⌊z⌋ dz−∫_(1/2) ^1 (8z−8)⌊z⌋ dz J=∫_(−1) ^0 (4−4z)dz + ∫_1 ^(3/2) (4z−4)dz J=[(4z−2z^2 )]_(−1) ^( 0) + [(2z^2 −4z)]_( 1) ^(3/2) J= 0−(−4−2)+2((9/4)−1)−4((3/2)−1) J = 6 + 2((5/4))−4((1/2)) J = 6 +(5/2)−2 = 4+(5/2) = ((13)/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q97222.png)
$$\mathrm{sgn}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{1}\:,\:\mathrm{when}\:{x}>\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{sgn}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)=−\mathrm{1},\:\mathrm{when}\:{x}<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{J}=\:−\underset{−\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\mid{x}−\mathrm{2}\mid\:\lfloor\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\rfloor\:{dx}\:+\: \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{3}} {\int}}\:\mid{x}−\mathrm{2}\mid\:\lfloor\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\rfloor\:{dx}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{J}\:=\:\underset{−\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\:\lfloor\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor\:{dx}− \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}} {\int}}\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\:\lfloor\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor\:{dx}\:+\:\underset{\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\mathrm{3}} {\int}}\:\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\:\lfloor\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor\:{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{J}=\:\underset{−\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\mathrm{3}} {\int}}\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\lfloor\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor{dx}−\mathrm{2}\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}} {\int}}\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\:\lfloor\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor\:{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{let}\:{x}=\mathrm{2}{z}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{J}=\underset{−\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} {\int}}\left(\mathrm{2z}−\mathrm{2}\right)\lfloor\mathrm{z}\rfloor.\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{dz}−\mathrm{2}\underset{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\left(\mathrm{2z}−\mathrm{2}\right)\lfloor\mathrm{z}\rfloor.\mathrm{2dz} \\ $$$$\mathrm{J}=\underset{−\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} {\int}}\left(\mathrm{4z}−\mathrm{4}\right)\lfloor\mathrm{z}\rfloor\:\mathrm{dz}−\underset{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\left(\mathrm{8z}−\mathrm{8}\right)\lfloor\mathrm{z}\rfloor\:\mathrm{dz} \\ $$$$\mathrm{J}=\underset{−\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{0}} {\int}}\:\left(\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{4z}\right)\mathrm{dz}\:+\:\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} {\int}}\:\left(\mathrm{4z}−\mathrm{4}\right)\mathrm{dz} \\ $$$$\mathrm{J}=\left[\left(\mathrm{4z}−\mathrm{2z}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right]_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\:\mathrm{0}} \:+\:\left[\left(\mathrm{2z}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4z}\right)\right]_{\:\mathrm{1}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{J}=\:\mathrm{0}−\left(−\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{2}\right)+\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}}−\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{4}\left(\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{J}\:=\:\mathrm{6}\:+\:\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)−\mathrm{4}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{J}\:=\:\mathrm{6}\:+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{2}\:=\:\mathrm{4}+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{13}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 07/Jun/20
![A =∫_(−2) ^3 ∣x−2∣[(x/2)]δ(x−1) dx with δ(x−1) =1 if x>1 and δ(x−1)=−1if x<1 changement (x/2) =t give A =∫_(−1) ^(3/2) ∣2t−2∣[t]δ(2t−1)2dt =4 ∫_(−1) ^(3/2) ∣t−1∣ [t]δ(2t−1)dt =4 ( ∫_(−1) ^0 (1−t)(−1)(−1)dt +∫_0 ^(1/2) (1−t)0 (−1)dt +∫_(1/2) ^1 (1−t)0(1)dt +∫_1 ^(3/2) (t−1)1dt) =4( ∫_(−1) ^0 (1−t)dt +∫_1 ^(3/2) (t−1)dt) =4{ [t−(t^2 /2)]_(−1) ^0 +[ (t^2 /2)−t]_1 ^(3/2) } =4{ −(−1−(1/2))+(9/8)−(3/2)−(−(1/2))} =4{(9/8) +(1/2)} =(9/2) +2 =((13)/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q97228.png)
$$\mathrm{A}\:=\int_{−\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{3}} \:\mid\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\mid\left[\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]\delta\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:\mathrm{dx}\:\:\mathrm{with}\:\delta\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:=\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{x}>\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{and}\:\delta\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)=−\mathrm{1if}\:\mathrm{x}<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{changement}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{give} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}\:=\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} \mid\mathrm{2t}−\mathrm{2}\mid\left[\mathrm{t}\right]\delta\left(\mathrm{2t}−\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{2dt}\:=\mathrm{4}\:\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\mid\mathrm{t}−\mathrm{1}\mid\:\left[\mathrm{t}\right]\delta\left(\mathrm{2t}−\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{dt} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}\:\left(\:\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{0}} \:\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{t}\right)\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{dt}\:+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{t}\right)\mathrm{0}\:\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{dt}\:+\int_{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{t}\right)\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{dt}\right. \\ $$$$\left.+\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} \left(\mathrm{t}−\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{1dt}\right)\:=\mathrm{4}\left(\:\:\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{0}} \left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{t}\right)\mathrm{dt}\:\:+\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\left(\mathrm{t}−\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{dt}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}\left\{\:\:\left[\mathrm{t}−\frac{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right]_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{0}} \:+\left[\:\frac{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{t}\right]_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} \right\}\:=\mathrm{4}\left\{\:−\left(−\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{8}}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}−\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right\} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}\left\{\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{8}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right\}\:=\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\mathrm{2}\:=\frac{\mathrm{13}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
