Question Number 94079 by Rio Michael last updated on 16/May/20
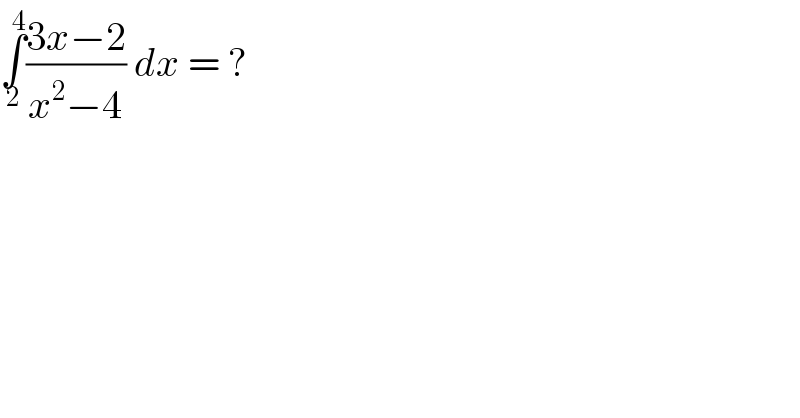
$$\underset{\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\mathrm{4}} {\int}}\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{2}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}\:{dx}\:=\:? \\ $$
Answered by Kunal12588 last updated on 16/May/20
![(3/2)[∫_2 ^4 ((2x)/(x^2 −4))dx−(4/3)∫_2 ^4 (dx/(x^2 −4))dx] =(3/2)[ln∣x^2 −4∣−(1/3)ln∣((x−2)/(x+2))∣]_2 ^4 =(3/2)[ln∣(((x^2 −4)(x+2)^(1/3) )/((x−2)^(1/3) ))∣]_2 ^4 =(3/2)[ln∣(x−2)^(2/3) (x+2)^(4/3) ∣]_2 ^4 =[ln∣(x−2)(x+2)^2 ∣]_2 ^4 ohh no! it′s divergent](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q94083.png)
$$\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}{dx}−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}}\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}{dx}\right] \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[{ln}\mid{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\mid−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}{ln}\mid\frac{{x}−\mathrm{2}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\mid\right]_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[{ln}\mid\frac{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{3}} }{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{3}} }\mid\right]_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[{ln}\mid\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}/\mathrm{3}} \left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{4}/\mathrm{3}} \mid\right]_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$=\left[{ln}\mid\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \mid\right]_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${ohh}\:{no}!\:{it}'{s}\:{divergent} \\ $$
Answered by niroj last updated on 16/May/20
![∫_2 ^( 4) (( 3x−2)/(x^2 −4))dx = [ 2∫ (1/(x+2))dx +∫(1/(x−2))dx]_2 ^4 = [2∫ (1/(x+2))dx +∫(1/(x−2))dx]_2 ^4 = [2log (x+2)+log(x−2)]_2 ^4 = [log(x+2)^2 +log(x−2)]_2 ^4 = [log {(x+2)^2 (x−2}]_2 ^4 = {log (4+2)^2 (4−2)−log (2+2)^2 (2−2)] = log 36.2−log16×0 = log 72 //. = 1.857](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q94086.png)
$$\:\:\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\:\mathrm{4}} \:\frac{\:\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\:=\:\left[\:\mathrm{2}\int\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{dx}\:\:\:\:+\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{dx}\right]_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\:=\:\:\left[\mathrm{2}\int\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{dx}\:\:\:\:+\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{dx}\right]_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$=\:\left[\mathrm{2log}\:\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)+\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\:=\:\left[\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\:=\:\left[\mathrm{log}\:\left\{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\right\}\right]_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \right. \\ $$$$=\:\left\{\mathrm{log}\:\left(\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{log}\:\left(\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{2}\right)\right] \\ $$$$\:=\:\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{36}.\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{log16}×\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:=\:\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{72}\://. \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\:\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{857} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by i jagooll last updated on 17/May/20
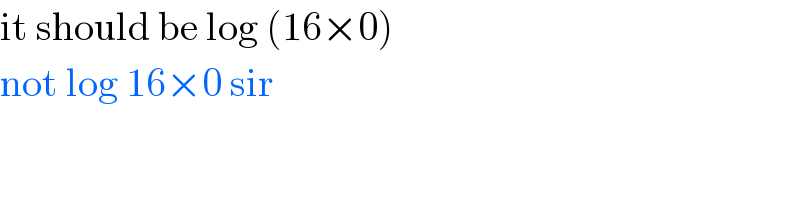
$$\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{should}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{log}\:\left(\mathrm{16}×\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{16}×\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{sir}\: \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 17/May/20
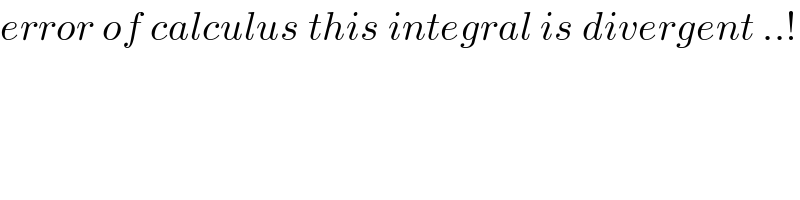
$${error}\:{of}\:{calculus}\:{this}\:{integral}\:{is}\:{divergent}\:..! \\ $$
Commented by Kunal12588 last updated on 16/May/20
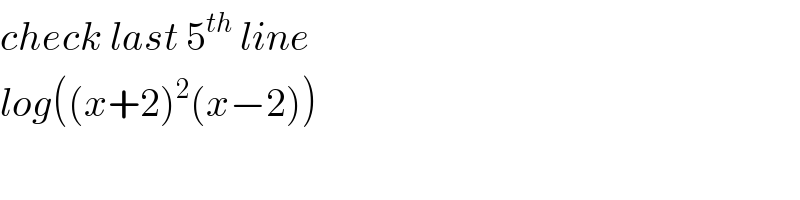
$${check}\:{last}\:\mathrm{5}^{{th}} \:{line} \\ $$$${log}\left(\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\right) \\ $$
Answered by Rio Michael last updated on 16/May/20
![what i got is, ((3x−2)/((x−2)(x+2))) = (1/(x−2)) −(2/(x−2)) ⇒ ∫_2 ^4 ((3x−2)/(x^2 +2))dx = lim_(t→2) [∫_t ^4 ((1/(x−2))−(2/(x+2)))dx] = lim_(t→2) [ ln(x−2)−2ln(x+2)]_t ^4 = lim_(t→2) [ln 2 −2ln 6 −(ln( t−2)−2 ln(t +2)] = +∞ diverges.](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q94094.png)
$$\:\mathrm{what}\:\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{got}\:\mathrm{is},\: \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{2}}{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\mathrm{4}} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{2}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}}{dx}\:=\:\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\underset{{t}} {\overset{\mathrm{4}} {\int}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right){dx}\right]\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\:\mathrm{lim}}\:\left[\:\mathrm{ln}\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{2ln}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\right]_{{t}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}\:−\mathrm{2ln}\:\mathrm{6}\:−\left(\mathrm{ln}\left(\:{t}−\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{ln}\left({t}\:+\mathrm{2}\right)\right]\:=\:+\infty\right. \\ $$$$\mathrm{diverges}. \\ $$
Commented by i jagooll last updated on 17/May/20
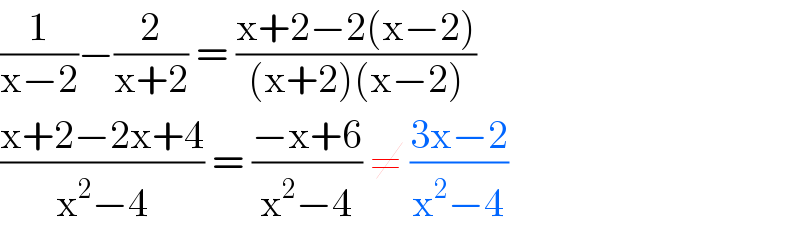
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)}{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}\:=\:\frac{−\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}\:\neq\:\frac{\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
