Question Number 25787 by ibraheem160 last updated on 14/Dec/17
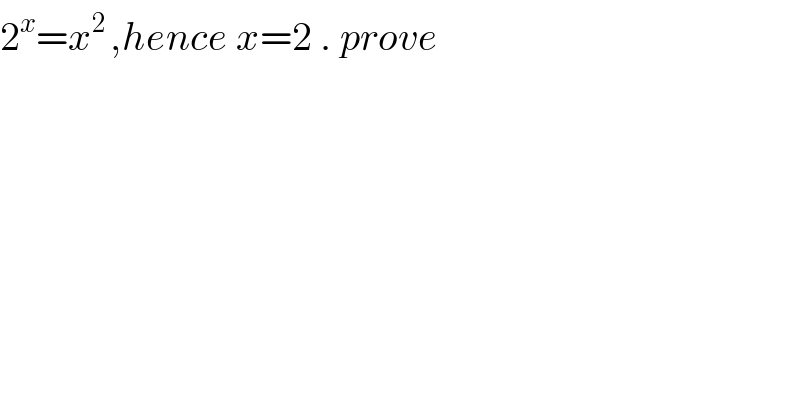
$$\mathrm{2}^{{x}} ={x}^{\mathrm{2}\:} ,{hence}\:{x}=\mathrm{2}\:.\:{prove} \\ $$
Commented by mrW1 last updated on 14/Dec/17
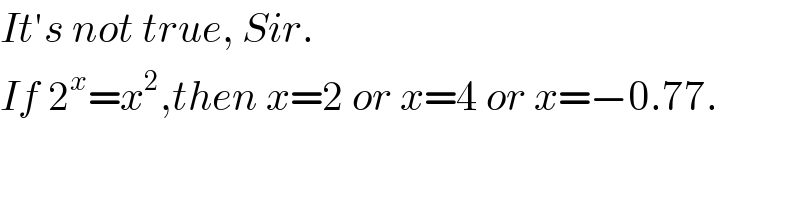
$${It}'{s}\:{not}\:{true},\:{Sir}. \\ $$$${If}\:\mathrm{2}^{{x}} ={x}^{\mathrm{2}} ,{then}\:{x}=\mathrm{2}\:{or}\:{x}=\mathrm{4}\:{or}\:{x}=−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{77}. \\ $$
Commented by mrW1 last updated on 15/Dec/17
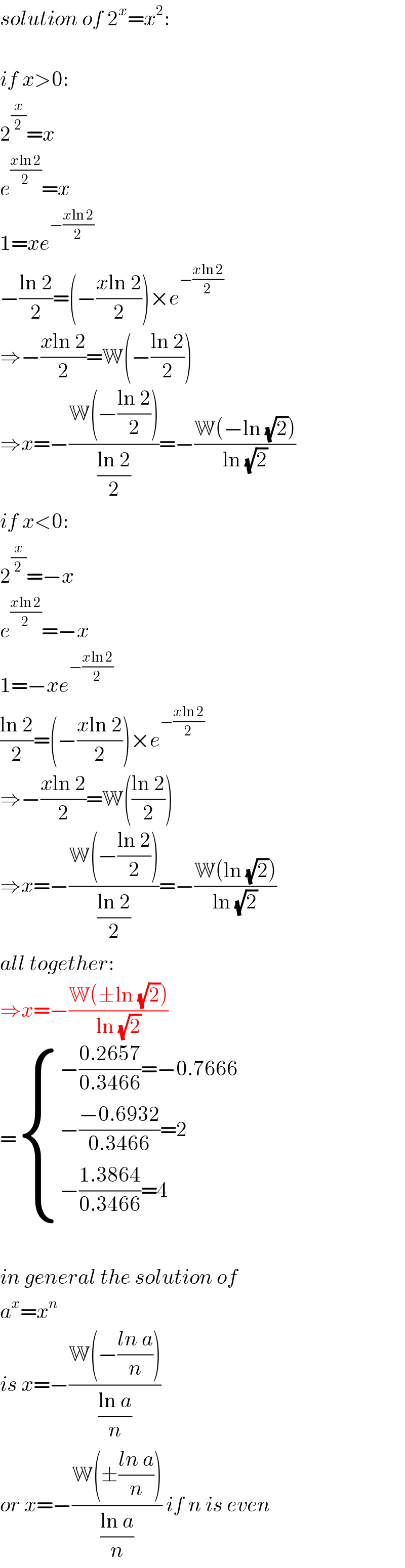
$${solution}\:{of}\:\mathrm{2}^{{x}} ={x}^{\mathrm{2}} : \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${if}\:{x}>\mathrm{0}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}^{\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} ={x} \\ $$$${e}^{\frac{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}} ={x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}={xe}^{−\frac{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$−\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}=\left(−\frac{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)×{e}^{−\frac{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow−\frac{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathbb{W}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=−\frac{\mathbb{W}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}}=−\frac{\mathbb{W}\left(−\mathrm{ln}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{ln}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$${if}\:{x}<\mathrm{0}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}^{\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} =−{x} \\ $$$${e}^{\frac{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}} =−{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}=−{xe}^{−\frac{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}=\left(−\frac{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)×{e}^{−\frac{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow−\frac{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathbb{W}\left(\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=−\frac{\mathbb{W}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}}=−\frac{\mathbb{W}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{ln}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$${all}\:{together}: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=−\frac{\mathbb{W}\left(\pm\mathrm{ln}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{ln}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$=\begin{cases}{−\frac{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{2657}}{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{3466}}=−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{7666}}\\{−\frac{−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{6932}}{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{3466}}=\mathrm{2}}\\{−\frac{\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{3864}}{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{3466}}=\mathrm{4}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${in}\:{general}\:{the}\:{solution}\:{of} \\ $$$${a}^{{x}} ={x}^{{n}} \\ $$$${is}\:{x}=−\frac{\mathbb{W}\left(−\frac{{ln}\:{a}}{{n}}\right)}{\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{a}}{{n}}} \\ $$$${or}\:{x}=−\frac{\mathbb{W}\left(\pm\frac{{ln}\:{a}}{{n}}\right)}{\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{a}}{{n}}}\:{if}\:{n}\:{is}\:{even} \\ $$
