Question Number 90200 by Ar Brandon last updated on 21/Apr/20
![26≡R_1 [37] 1 ≡R_2 [3] 2≡R_3 [5] Find R_1 , R_2 and R_3](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q90200.png)
$$\mathrm{26}\equiv\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{1}} \left[\mathrm{37}\right] \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}\:\:\equiv\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{2}} \left[\mathrm{3}\right] \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}\equiv\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{3}} \left[\mathrm{5}\right] \\ $$$$\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{1}} ,\:\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 22/Apr/20
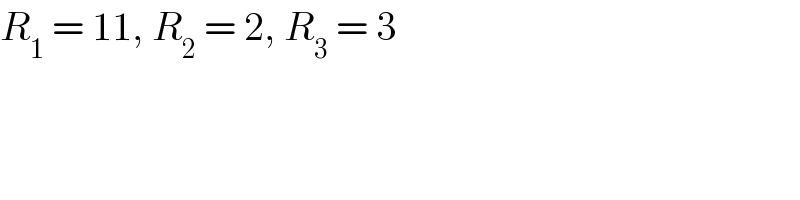
$${R}_{\mathrm{1}} \:=\:\mathrm{11},\:{R}_{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:\mathrm{2},\:{R}_{\mathrm{3}} \:=\:\mathrm{3} \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 22/Apr/20

$$\mathrm{Thanks},\:\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{how}? \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 22/Apr/20

$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{question}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{actually} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{26}\:\equiv\:{R}_{\mathrm{1}} \:\left(\mathrm{mod}\:\mathrm{37}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{1}} \:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{reminder}\:\mathrm{when}\:\mathrm{26}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{divided}\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{37} \\ $$$$\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{rightly}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{11}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{say} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{definition}\:{a}\:\equiv\:{b}\:\left(\mathrm{mod}\:{n}\right)\:\Leftrightarrow\:{n}\:\mid\left({a}−{b}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:{a}−{b}\:=\:{nk}\:,\:{k}\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{26}\:\equiv\:{R}_{\mathrm{1}} \:\left(\mathrm{mod}\:\mathrm{37}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:\:\mathrm{26}\:=\:\mathrm{37}\:{k}\:+\:{R} \\ $$$${k}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\:\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{1}} \:=\:\mathrm{26} \\ $$$${k}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\:{R}_{\mathrm{1}} \:=\:−\mathrm{11} \\ $$$${k}\:=\:−\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\:{R}_{\mathrm{1}} \:=\:\mathrm{63} \\ $$$$\mathrm{these}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{just}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{elements}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{set}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{least}\:\mathrm{residue}\:\mathrm{mod}\:\mathrm{37}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 22/Apr/20
$$\mathrm{Thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:−\:\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 22/Apr/20

$${how}\:{can}\:{you}\:{say} \\ $$$$\mathrm{26}\equiv{R}_{\mathrm{1}} \:{mod}\:\mathrm{37}\:\Rightarrow{R}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{11}? \\ $$$${that}\:{means}\:{then}\:\mathrm{26}=\mathrm{37}{k}+\mathrm{11}. \\ $$$${this}\:{is}\:{wrong}! \\ $$$${clearly}: \\ $$$${R}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{26}\:{since}\:\mathrm{26}\equiv\mathrm{26}\:{mod}\:\mathrm{37} \\ $$$${R}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${R}_{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 22/Apr/20
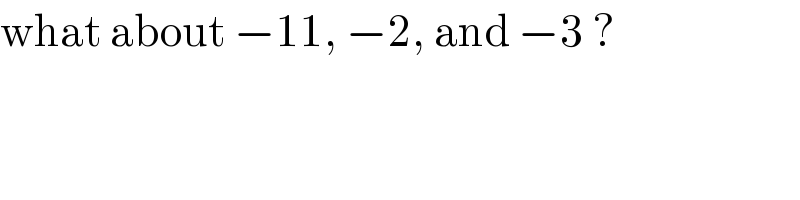
$$\mathrm{what}\:\mathrm{about}\:−\mathrm{11},\:−\mathrm{2},\:\mathrm{and}\:−\mathrm{3}\:? \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 22/Apr/20
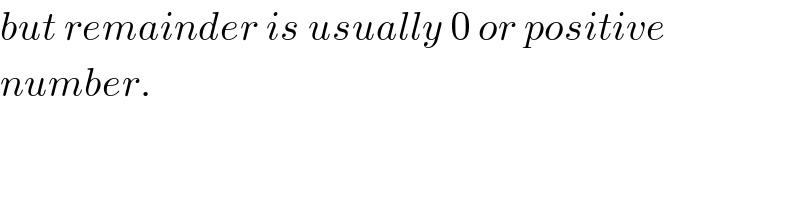
$${but}\:{remainder}\:{is}\:{usually}\:\mathrm{0}\:{or}\:{positive} \\ $$$${number}. \\ $$
