Question Number 24839 by kosarrr last updated on 27/Nov/17

$$\frac{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} +\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}} }=\left(\mathrm{0}/\mathrm{04}\right)^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Commented by behi.8.3.4.17@gmail.com last updated on 27/Nov/17

$$\boldsymbol{{LHS}}=\frac{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2x}} \left(\mathrm{5}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2x}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{5}}}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{1}} =\left(\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{100}}\right)^{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}} =\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{25}}\right)^{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}} =\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)^{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{5}^{−\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{1}=−\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\Rightarrow−\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow−\mathrm{2x}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{−\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:\:\blacksquare \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 27/Nov/17
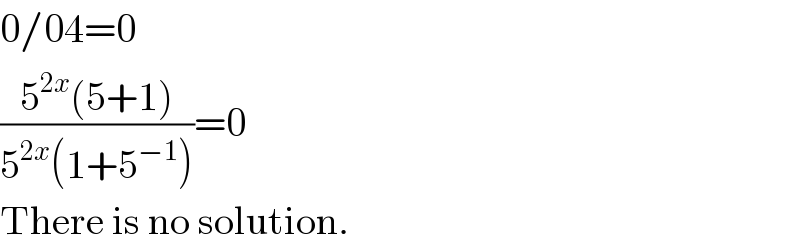
$$\mathrm{0}/\mathrm{04}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \left(\mathrm{5}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{5}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{There}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{solution}. \\ $$
Answered by nnnavendu last updated on 27/Nov/17

$$\mathrm{ans}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2x}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}} =−\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{squring}\:\mathrm{both}\:\mathrm{side} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(−\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2x}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{4x}+\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{4x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4x}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{4x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4x}−\mathrm{4x}=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{0x}=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}=−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{0}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}=\alpha\left(\mathrm{infinite}\right) \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 27/Nov/17

$${x}=\infty\:\mathrm{will}\:\mathrm{bring}\:\mathrm{LHS}\:\mathrm{to} \\ $$$$\frac{\infty}{\infty}\:\mathrm{form}.\:\mathrm{So}\:\mathrm{infinity}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{valid} \\ $$$$\mathrm{answer}. \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} +\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}} } \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \left(\mathrm{5}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{5}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{6}/\mathrm{5}}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$
