Question Number 122999 by ZiYangLee last updated on 21/Nov/20
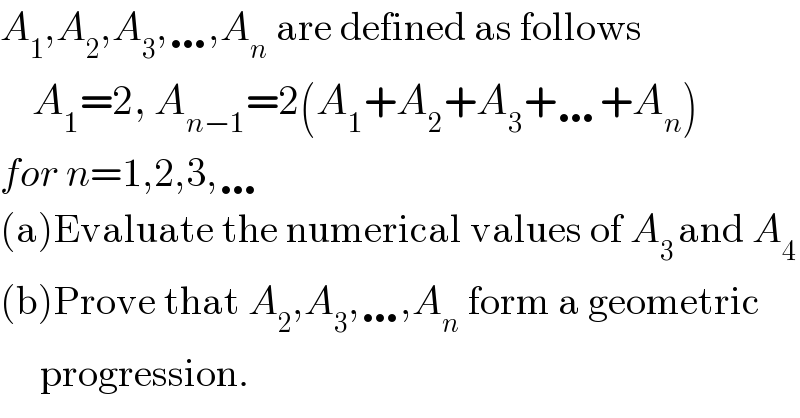
$${A}_{\mathrm{1}} ,{A}_{\mathrm{2}} ,{A}_{\mathrm{3}} ,\ldots,{A}_{{n}} \:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{defined}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{follows} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{A}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{2},\:{A}_{{n}−\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{2}\left({A}_{\mathrm{1}} +{A}_{\mathrm{2}} +{A}_{\mathrm{3}} +\ldots+{A}_{{n}} \right) \\ $$$${for}\:{n}=\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{3},\ldots \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{a}\right)\mathrm{Evaluate}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{numerical}\:\mathrm{values}\:\mathrm{of}\:{A}_{\mathrm{3}\:} \mathrm{and}\:{A}_{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{b}\right)\mathrm{Prove}\:\mathrm{that}\:{A}_{\mathrm{2}} ,{A}_{\mathrm{3}} ,\ldots,{A}_{{n}} \:\mathrm{form}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{geometric} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{progression}. \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 21/Nov/20
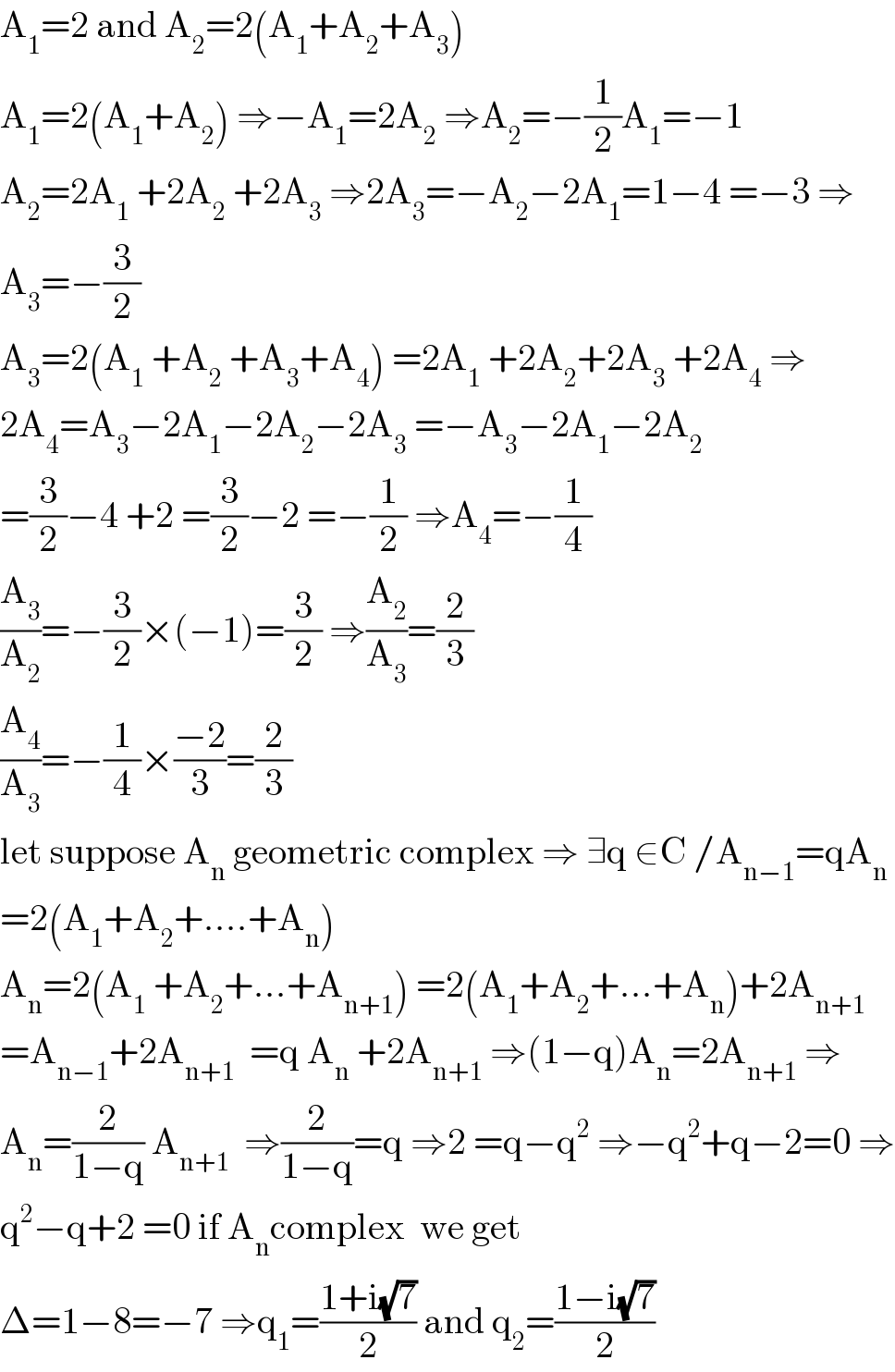
$$\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{3}} \right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:\Rightarrow−\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{2}} \:\Rightarrow\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{1}} =−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{3}} \:\Rightarrow\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{3}} =−\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{4}\:=−\mathrm{3}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{3}} =−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{4}} \right)\:=\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{3}} \:+\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{4}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{3}} \:=−\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{4}\:+\mathrm{2}\:=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{2}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{4}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} }=−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}×\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{3}} }=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{3}} }=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}×\frac{−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{suppose}\:\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}} \:\mathrm{geometric}\:\mathrm{complex}\:\Rightarrow\:\exists\mathrm{q}\:\in\mathrm{C}\:/\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{qA}_{\mathrm{n}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} +….+\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}} \right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} +…+\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \right)\:=\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{2}} +…+\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}} \right)+\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \:\:=\mathrm{q}\:\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}} \:+\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \:\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{q}\right)\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{2A}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{q}}\:\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \:\:\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{q}}=\mathrm{q}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}\:=\mathrm{q}−\mathrm{q}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\Rightarrow−\mathrm{q}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{q}−\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{q}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{q}+\mathrm{2}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{complex}\:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get}\: \\ $$$$\Delta=\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{8}=−\mathrm{7}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{i}\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{i}\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by ZiYangLee last updated on 21/Nov/20

$$\mathrm{wow}… \\ $$
