Question Number 40396 by LXZ last updated on 21/Jul/18

$${A}\:{block}\:{lying}\:{on}\:{a}\:{horizontal}\:{conv}− \\ $$$${eyor}\:{belt}\:{moving}\:{at}\:\:{a}\:{constant}\: \\ $$$${velocity}\:{receives}\:{a}\:{velocity}\:\mathrm{5}{m}/{s} \\ $$$${at}\:{t}=\mathrm{0}\:{sec}.\:{relative}\:{to}\:{the}\:{ground}\: \\ $$$${in}\:{the}\:{direction}\:{opposite}\:{to}\:{the}\:{dir}− \\ $$$${ction}\:{of}\:{motion}\:{of}\:{the}\:{conveyor}. \\ $$$${Aftert}=\mathrm{4}{sec},{the}\:{velocity}\:{of}\:{the}\: \\ $$$${block}\:{becomes}\:{equal}\:{to}\:{the}\:{velocity} \\ $$$${of}\:{the}\:{belt}\:.\:{the}\:{coefficient}\:{of}\: \\ $$$${friction}\:{between}\:{the}\:{block}\:{and}\:{the} \\ $$$${belt}\:{is}\:\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{2}\:.\:{then}\:{the}\:{velocity}\:{of}\:{the} \\ $$$${conveyor}\:{belt}\:{is}:\:\:\left({g}=\mathrm{10}{m}/{s}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\left({A}\right)\:\mathrm{13}\:{m}/{s}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left({B}\right)\:\:−\mathrm{13}{m}/{s} \\ $$$$\left({C}\right)\mathrm{3}{m}/{s}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left({D}\right)\:\:\:\mathrm{6}{m}/{s} \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 22/Jul/18
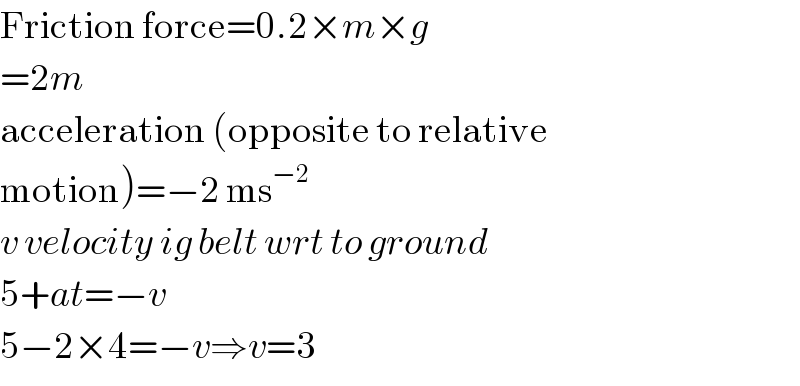
$$\mathrm{Friction}\:\mathrm{force}=\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{2}×{m}×{g}\: \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}{m} \\ $$$$\mathrm{acceleration}\:\left(\mathrm{opposite}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{relative}\right. \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{motion}\right)=−\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{ms}^{−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${v}\:{velocity}\:{ig}\:{belt}\:{wrt}\:{to}\:{ground} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}+{at}=−{v} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{4}=−{v}\Rightarrow{v}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$
