Question Number 32316 by NECx last updated on 23/Mar/18

$${A}\:{gas}\:{expands}\:{according}\:{to}\:{the} \\ $$$${law}\:{pv}={constant},{where}\:{p}\:{is}\:{the} \\ $$$${pressure}\:{and}\:{v}\:{is}\:{the}\:{volume}\:{of} \\ $$$${the}\:{gas}.{Initially},{v}=\mathrm{1000}{m}^{\mathrm{3}} \:{and} \\ $$$${p}=\mathrm{40}{N}/{m}^{\mathrm{2}} .{If}\:{the}\:{pressure}\:{is} \\ $$$${decreased}\:{at}\:{the}\:{rate}\:{of}\:\mathrm{5}{Nm}^{−\mathrm{2}} {min}^{−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${find}\:{the}\:{rate}\:{at}\:{which}\:{the}\:{gas}\:{is} \\ $$$${expanding}\:{when}\:{its}\:{volume}\:{is} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2000}{m}^{\mathrm{3}.} \\ $$
Commented by NECx last updated on 23/Mar/18
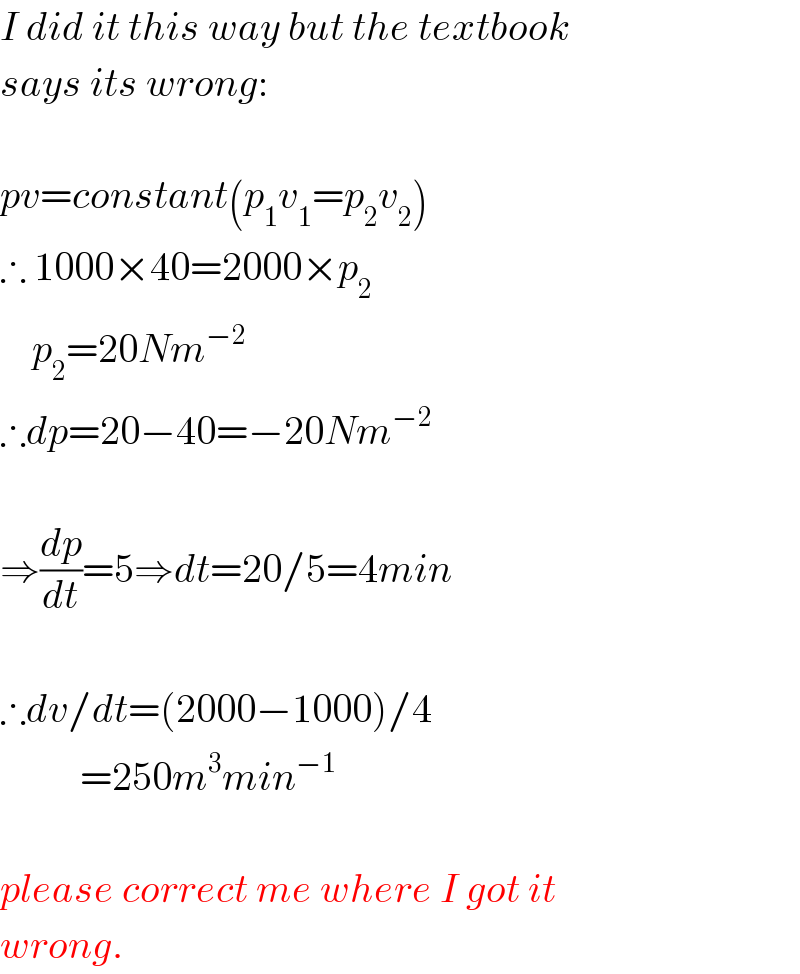
$${I}\:{did}\:{it}\:{this}\:{way}\:{but}\:{the}\:{textbook} \\ $$$${says}\:{its}\:{wrong}: \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${pv}={constant}\left({p}_{\mathrm{1}} {v}_{\mathrm{1}} ={p}_{\mathrm{2}} {v}_{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\mathrm{1000}×\mathrm{40}=\mathrm{2000}×{p}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{p}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{20}{Nm}^{−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\therefore{dp}=\mathrm{20}−\mathrm{40}=−\mathrm{20}{Nm}^{−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{dp}}{{dt}}=\mathrm{5}\Rightarrow{dt}=\mathrm{20}/\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{4}{min} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\therefore{dv}/{dt}=\left(\mathrm{2000}−\mathrm{1000}\right)/\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{250}{m}^{\mathrm{3}} {min}^{−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${please}\:{correct}\:{me}\:{where}\:{I}\:{got}\:{it} \\ $$$${wrong}. \\ $$
Commented by NECx last updated on 23/Mar/18
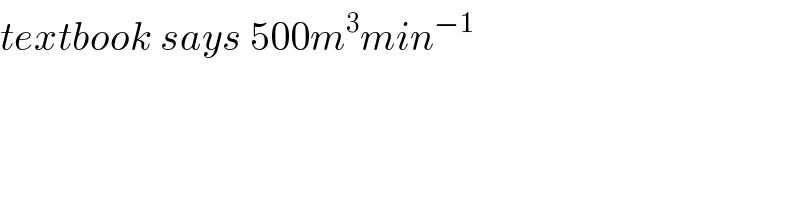
$${textbook}\:{says}\:\mathrm{500}{m}^{\mathrm{3}} {min}^{−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Commented by mrW2 last updated on 23/Mar/18
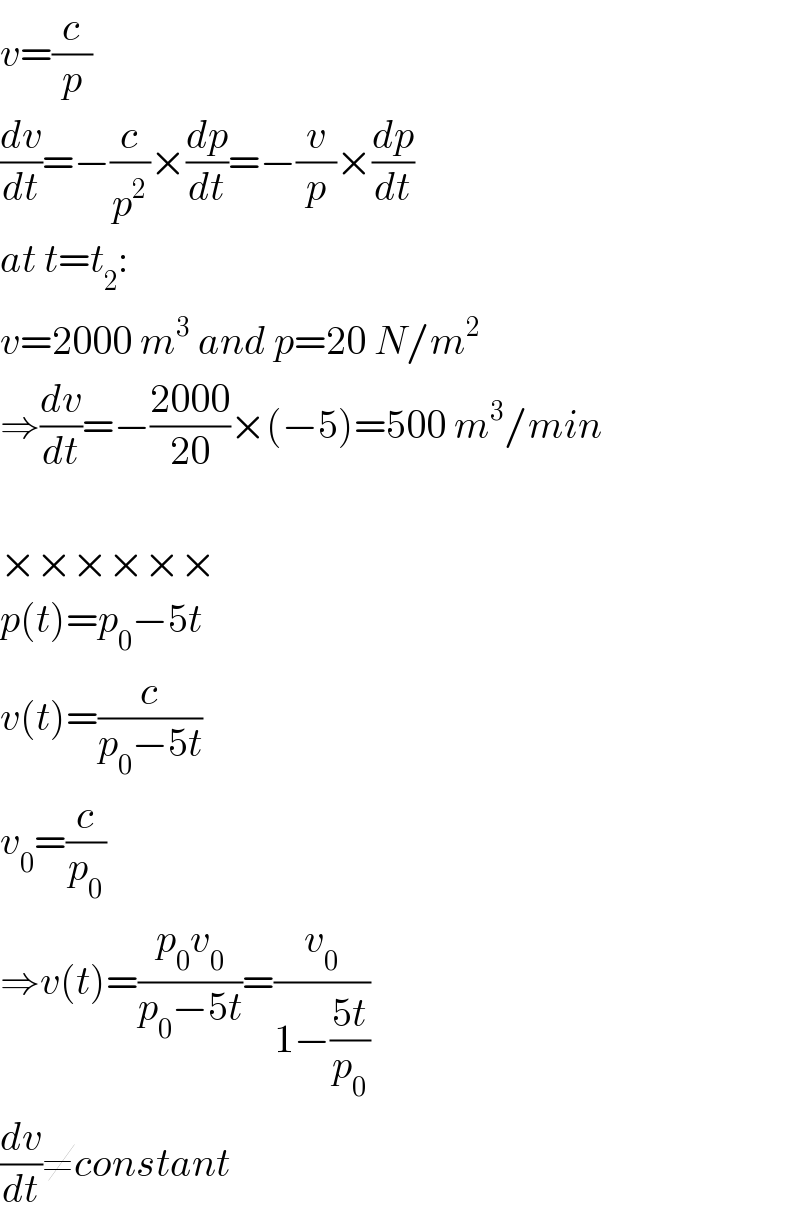
$${v}=\frac{{c}}{{p}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dv}}{{dt}}=−\frac{{c}}{{p}^{\mathrm{2}} }×\frac{{dp}}{{dt}}=−\frac{{v}}{{p}}×\frac{{dp}}{{dt}} \\ $$$${at}\:{t}={t}_{\mathrm{2}} : \\ $$$${v}=\mathrm{2000}\:{m}^{\mathrm{3}} \:{and}\:{p}=\mathrm{20}\:{N}/{m}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{dv}}{{dt}}=−\frac{\mathrm{2000}}{\mathrm{20}}×\left(−\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{500}\:{m}^{\mathrm{3}} /{min} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$×××××× \\ $$$${p}\left({t}\right)={p}_{\mathrm{0}} −\mathrm{5}{t} \\ $$$${v}\left({t}\right)=\frac{{c}}{{p}_{\mathrm{0}} −\mathrm{5}{t}} \\ $$$${v}_{\mathrm{0}} =\frac{{c}}{{p}_{\mathrm{0}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{v}\left({t}\right)=\frac{{p}_{\mathrm{0}} {v}_{\mathrm{0}} }{{p}_{\mathrm{0}} −\mathrm{5}{t}}=\frac{{v}_{\mathrm{0}} }{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{5}{t}}{{p}_{\mathrm{0}} }} \\ $$$$\frac{{dv}}{{dt}}\neq{constant} \\ $$
Commented by NECx last updated on 23/Mar/18
$${thank}\:{you}\:{so}\:{much} \\ $$
