Question Number 144246 by SOMEDAVONG last updated on 23/Jun/21
![A=lim_(n→+∝) [(1/(1^2 +3(1)+2)) + (1/(2^2 +3(2)+2)) +..+ (1/(n^2 +3n+2))]](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q144246.png)
$$\mathrm{A}=\underset{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow+\propto} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{2}}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\mathrm{2}}\:+..+\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3n}+\mathrm{2}}\right] \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 23/Jun/21
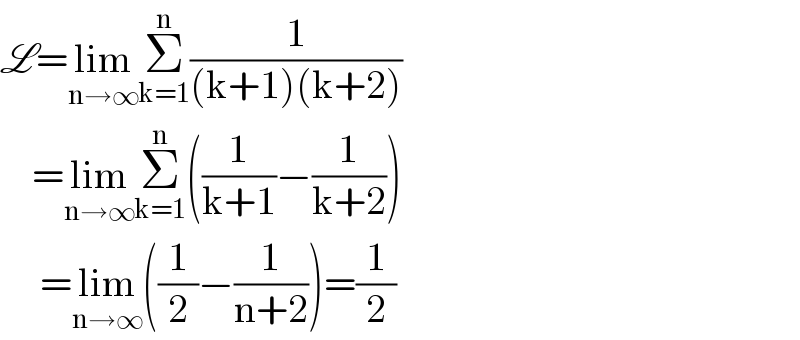
$$\mathscr{L}=\underset{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:=\underset{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\underset{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{2}}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by SOMEDAVONG last updated on 24/Jun/21

$$\mathrm{Thanks}\:\mathrm{sir}! \\ $$
