Question Number 110594 by Aina Samuel Temidayo last updated on 29/Aug/20
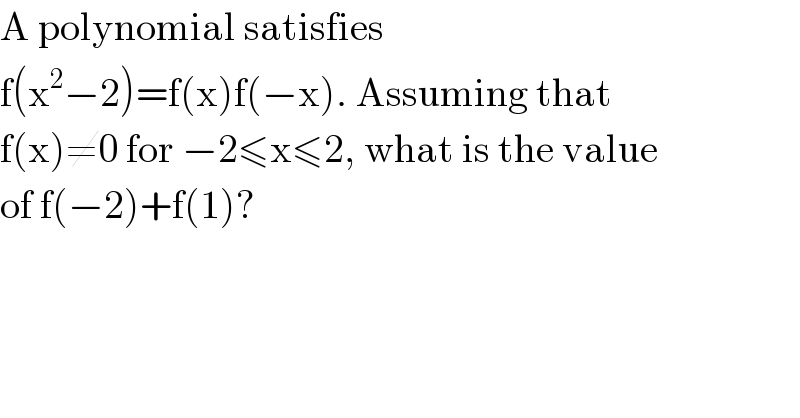
Answered by Aziztisffola last updated on 29/Aug/20
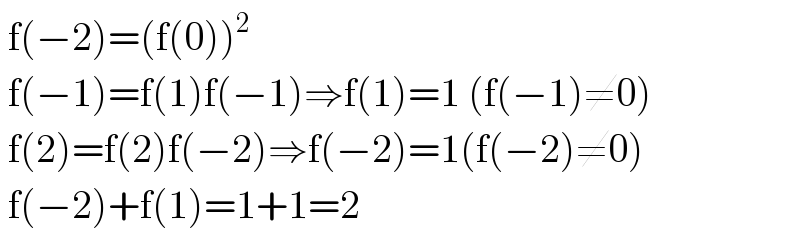
Commented by Aina Samuel Temidayo last updated on 29/Aug/20

Commented by Aziztisffola last updated on 29/Aug/20
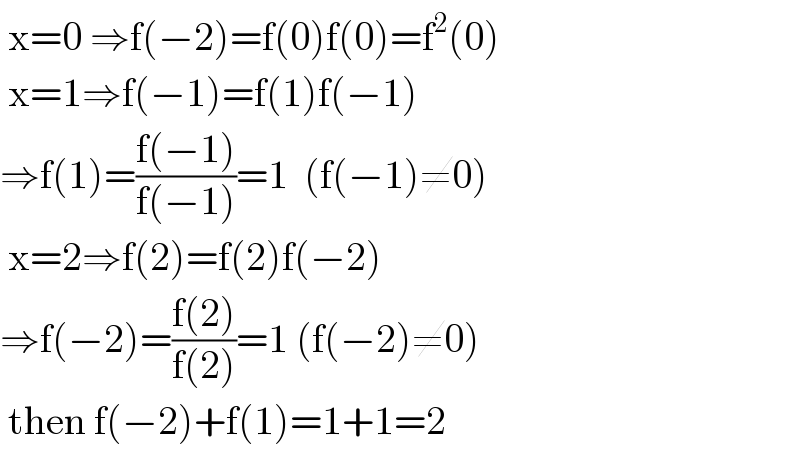
Commented by Aina Samuel Temidayo last updated on 03/Sep/20

