Question Number 108921 by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Aug/20
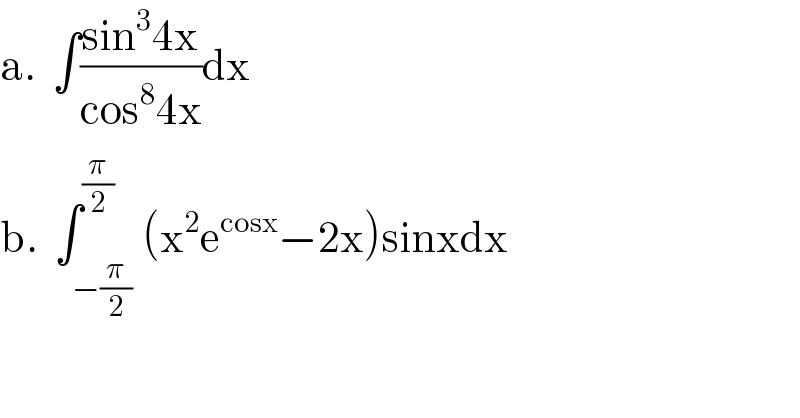
$$\mathrm{a}.\:\:\int\frac{\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{4x}}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{8}} \mathrm{4x}}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{b}.\:\:\int_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{cosx}} −\mathrm{2x}\right)\mathrm{sinxdx} \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 20/Aug/20
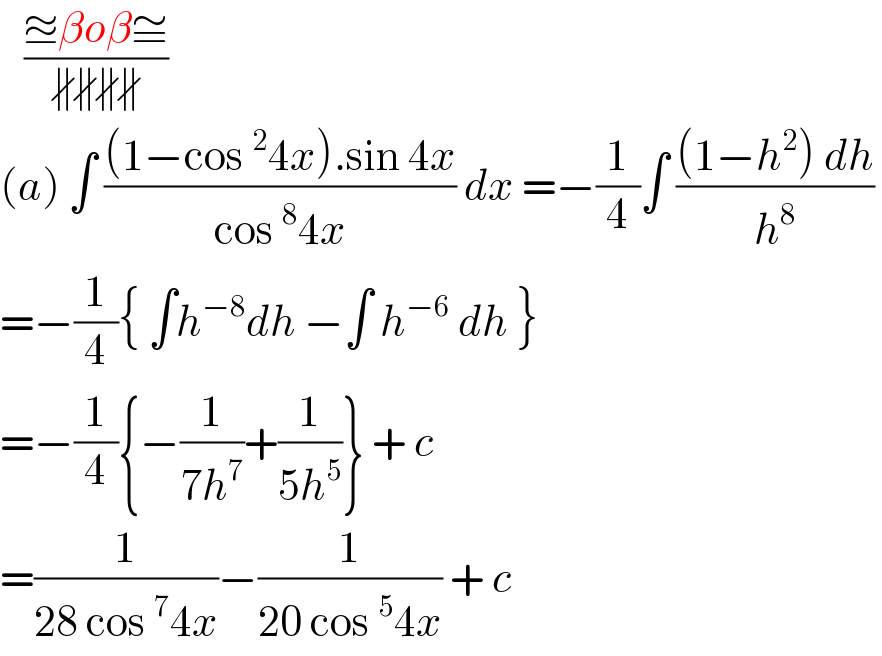
$$\:\:\:\frac{\approxeq\beta{o}\beta\cong}{\nparallel\nparallel\nparallel\nparallel} \\ $$$$\left({a}\right)\:\int\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{4}{x}\right).\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{4}{x}}{\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{8}} \mathrm{4}{x}}\:{dx}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\int\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}−{h}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:{dh}}{{h}^{\mathrm{8}} }\: \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left\{\:\int{h}^{−\mathrm{8}} {dh}\:−\int\:{h}^{−\mathrm{6}} \:{dh}\:\right\} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left\{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{7}{h}^{\mathrm{7}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}{h}^{\mathrm{5}} }\right\}\:+\:{c} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{28}\:\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{7}} \mathrm{4}{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{20}\:\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{5}} \mathrm{4}{x}}\:+\:{c} \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Aug/20
thanks
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Aug/20
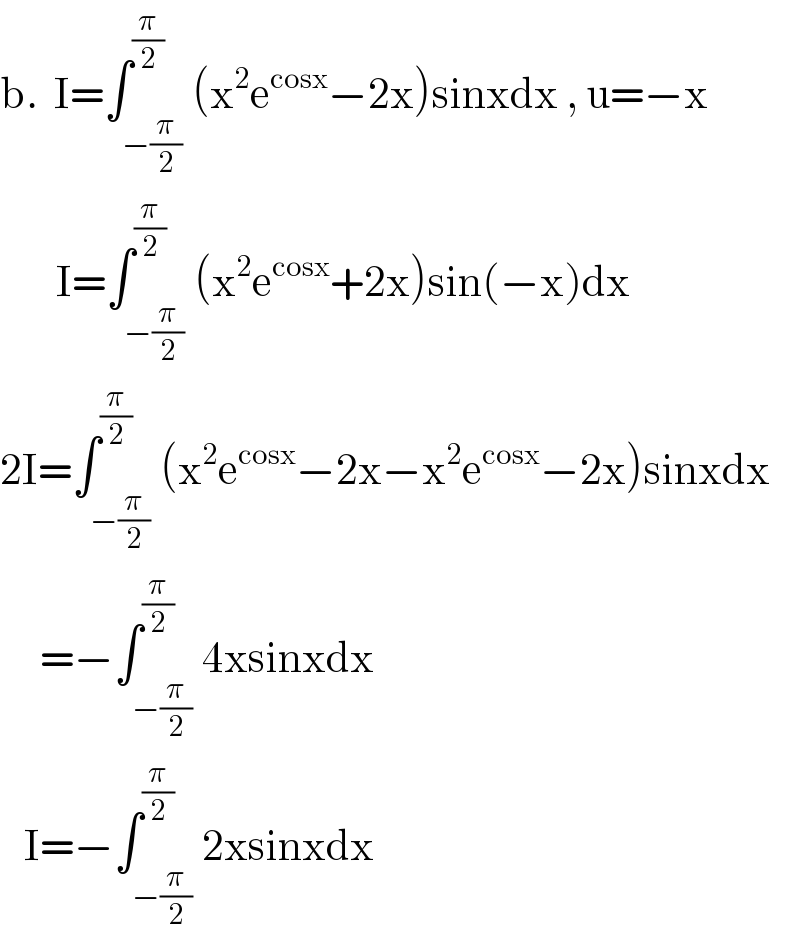
$$\mathrm{b}.\:\:\mathrm{I}=\int_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{cosx}} −\mathrm{2x}\right)\mathrm{sinxdx}\:,\:\mathrm{u}=−\mathrm{x} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{I}=\int_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{cosx}} +\mathrm{2x}\right)\mathrm{sin}\left(−\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2I}=\int_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{cosx}} −\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{cosx}} −\mathrm{2x}\right)\mathrm{sinxdx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=−\int_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{4xsinxdx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\mathrm{I}=−\int_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{2xsinxdx} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 20/Aug/20
![∫_(−(π/2)) ^(π/2) (x^2 e^(cosx) −2x)sinxdx=∫_(−(π/2)) ^(π/2) −(x^2 e^(cosx) −2x)sinxdx=I 2I=∫_(−(π/2)) ^(π/2) −4xsinxdx −(I/4)=∫_0 ^(π/2) xsinxdx −(I/4)=−[xcosx]_0 ^(π/2) +[sinx]_0 ^(π/2) I=−4](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q108944.png)
$$\int_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{{cosx}} −\mathrm{2}{x}\right){sinxdx}=\int_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} −\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{{cosx}} −\mathrm{2}{x}\right){sinxdx}={I} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{I}=\int_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} −\mathrm{4}{xsinxdx} \\ $$$$−\frac{{I}}{\mathrm{4}}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {xsinxdx} \\ $$$$−\frac{{I}}{\mathrm{4}}=−\left[{xcosx}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} +\left[{sinx}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$${I}=−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Aug/20
Cool !
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Aug/20
Hey bro, what do you think of Q108491 ? ��
