Question Number 175353 by Eulerian last updated on 28/Aug/22

$$\:\mathrm{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{bx}+\mathrm{c}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{x}\:=\:\frac{−\mathrm{b}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4ac}}}{\mathrm{2a}} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{Example}: \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{values}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{equation} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5x}+\mathrm{4}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{In}\:\mathrm{order}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{solve}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{that},\:\mathrm{let}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{first}\:\mathrm{take} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{look}\:\mathrm{on}\:\mathrm{what}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{values}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{a},\:\mathrm{b}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{c}\: \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{1x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\:\mathrm{5x}\:+\:\mathrm{4}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{a}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\:;\:\mathrm{b}\:=\:\mathrm{5}\:;\:\mathrm{c}\:=\:\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{Now},\:\mathrm{using}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{quadratic}\:\mathrm{formula} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{x}\:=\:\frac{−\mathrm{5}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{4}\right)}}{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)}\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:=\:\frac{−\mathrm{5}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{25}−\mathrm{16}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:=\:\frac{−\mathrm{5}\pm\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by Mr.D.N. last updated on 28/Aug/22
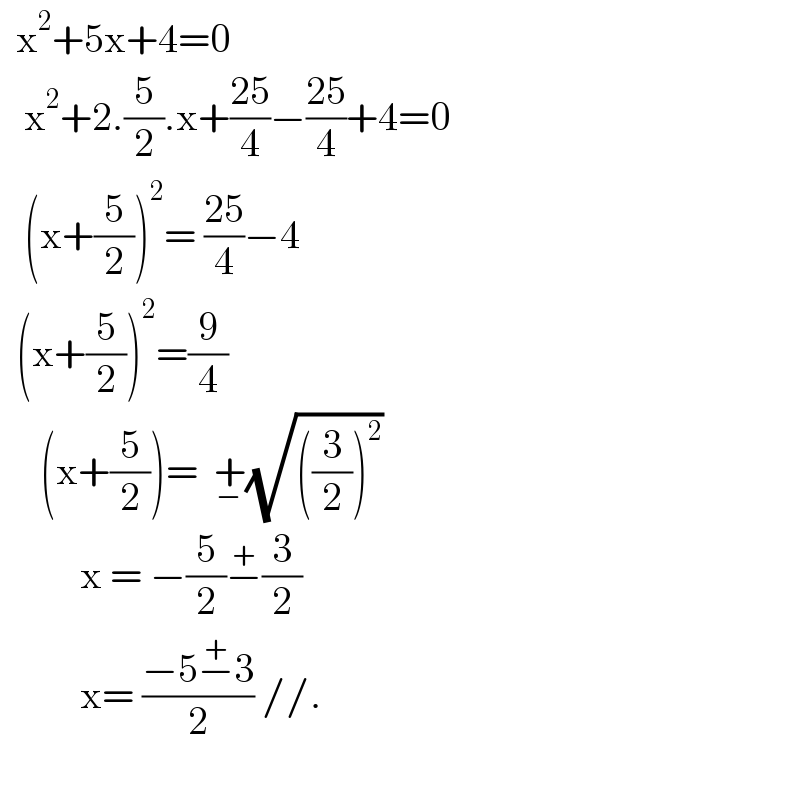
$$\:\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5x}+\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}.\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}.\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{4}}−\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{4}}+\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\:\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{4}}−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\:\:\left(\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\:\:\underset{−} {+}\sqrt{\left(\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{x}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\overset{+} {−}\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{x}=\:\frac{−\mathrm{5}\overset{+} {−}\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\://. \\ $$$$\:\:\:\: \\ $$
