Question Number 108984 by bemath last updated on 20/Aug/20
![B_≈ eM_≈ ath_≈ (1)Σ_(n = 1) ^(100) [ (2/(4n^2 −1)) ] ? (2) (2/(4.9)) + (2/(9.14)) + (2/(14.19)) + ... + (2/(49.54)) ? (3) Given a quadratic equation x^2 (Σ_(i = 1) ^2 2)+ x(Σ_(i = 1) ^5 i)−(2/3)(Σ_(i = 1) ^3 i) = 0 has the roots are x_1 and x_2 with x_1 < x_2 . Find the value of x_1 +8x_2 .](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q108984.png)
$$\:\:\:\underset{\approx} {\mathcal{B}}{e}\underset{\approx} {\mathcal{M}}{at}\underset{\approx} {{h}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\underset{{n}\:=\:\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{100}} {\sum}}\left[\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{4}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\:\right]\:? \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{9}}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{9}.\mathrm{14}}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{14}.\mathrm{19}}\:+\:…\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{49}.\mathrm{54}}\:? \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{3}\right)\:{Given}\:{a}\:{quadratic}\:{equation} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\underset{{i}\:=\:\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}} {\sum}}\mathrm{2}\right)+\:{x}\left(\underset{{i}\:=\:\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{5}} {\sum}}{i}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\underset{{i}\:=\:\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{3}} {\sum}}{i}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${has}\:{the}\:{roots}\:{are}\:{x}_{\mathrm{1}} \:{and}\:{x}_{\mathrm{2}} \:{with}\: \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{1}} \:<\:{x}_{\mathrm{2}} .\:{Find}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:{x}_{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{8}{x}_{\mathrm{2}} . \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 20/Aug/20

$${thank}\:{you}\:{both} \\ $$
Answered by nimnim last updated on 20/Aug/20
![(1) S=Σ_(n=1) ^(100) [(1/(2n−1))−(1/(2n+1))] S=[(1/1)−(1/3)]+[(1/3)−(1/5)]+....+[(1/(197))−(1/(199))]+[(1/(199))−(1/(201))] S=(1/1)−(1/(201))=((200)/(201))](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q108988.png)
$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{S}=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{100}} {\sum}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\right] \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{S}=\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right]+\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\right]+….+\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{197}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{199}}\right]+\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{199}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{201}}\right] \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{S}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{201}}=\frac{\mathrm{200}}{\mathrm{201}} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 20/Aug/20
![you answer is not correct if [...] mean floor because [x+y]≠[x]+[y]](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q109050.png)
$$\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{correct}\:\mathrm{if}\:\left[…\right]\:\mathrm{mean}\:\mathrm{floor}\:\mathrm{because} \\ $$$$\left[\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}\right]\neq\left[\mathrm{x}\right]+\left[\mathrm{y}\right] \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 20/Aug/20
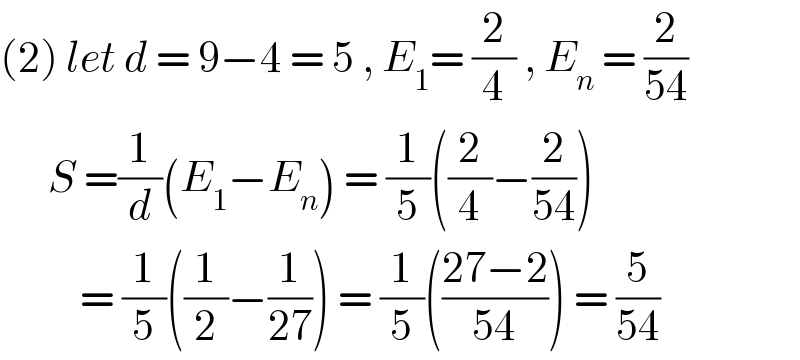
$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:{let}\:{d}\:=\:\mathrm{9}−\mathrm{4}\:=\:\mathrm{5}\:,\:{E}_{\mathrm{1}} =\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{4}}\:,\:{E}_{{n}} \:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{54}}\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:{S}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{d}}\left({E}_{\mathrm{1}} −{E}_{{n}} \right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{4}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{54}}\right)\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{27}}\right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{27}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{54}}\right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{54}} \\ $$
Answered by nimnim last updated on 20/Aug/20
![(2) Let S=(2/(4.9))+(2/(9.14))+(2/(14.19))+....+(2/(49.54)) ⇒ S=(2/5)[(5/(4.9))+(5/(9.14))+(5/(14.19))+....+(5/(49.54))] ⇒S=(2/5)[(1/4)−(1/9)+(1/9)−(1/(14))+(1/(14))−(1/(19))+....+(1/(49))−(1/(54))] ⇒S=(2/5)[(1/4)−(1/(54))]=(2/5)×((25)/(108)) ⇒S=(5/(54))★](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q108995.png)
$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:{Let}\:{S}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{9}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{9}.\mathrm{14}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{14}.\mathrm{19}}+….+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{49}.\mathrm{54}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{S}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{9}}+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{9}.\mathrm{14}}+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{14}.\mathrm{19}}+….+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{49}.\mathrm{54}}\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{S}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{14}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{14}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{19}}+….+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{49}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{54}}\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{S}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{54}}\right]=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}×\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{108}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{S}=\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{54}}\bigstar \\ $$$$\:\:\:\: \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 20/Aug/20
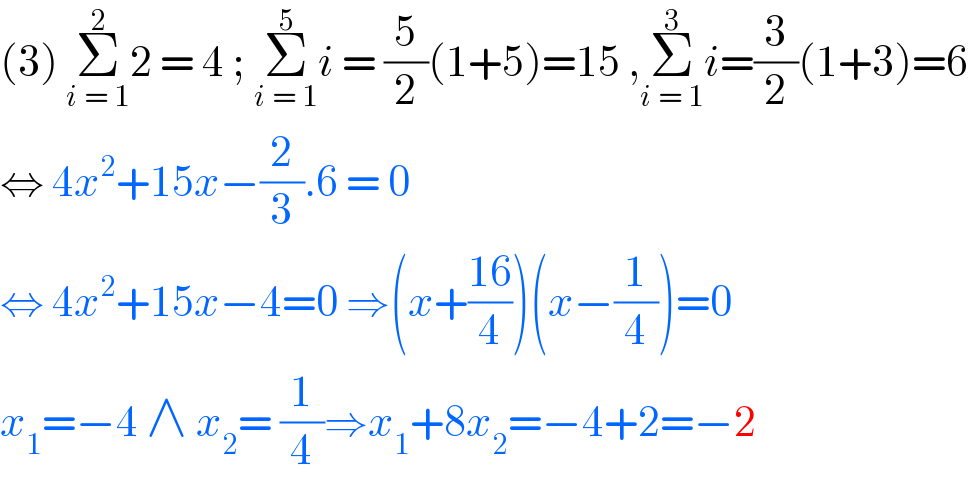
$$\left(\mathrm{3}\right)\:\underset{{i}\:=\:\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}} {\sum}}\mathrm{2}\:=\:\mathrm{4}\:;\:\underset{{i}\:=\:\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{5}} {\sum}}{i}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{15}\:,\underset{{i}\:=\:\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{3}} {\sum}}{i}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{15}{x}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}.\mathrm{6}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{15}{x}−\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{16}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\left({x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{1}} =−\mathrm{4}\:\wedge\:{x}_{\mathrm{2}} =\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\Rightarrow{x}_{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{8}{x}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{2}=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 20/Aug/20
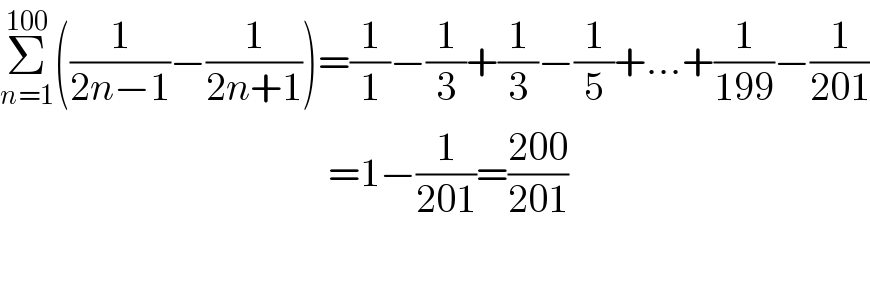
$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{100}} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}+…+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{199}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{201}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{201}}=\frac{\mathrm{200}}{\mathrm{201}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 20/Aug/20
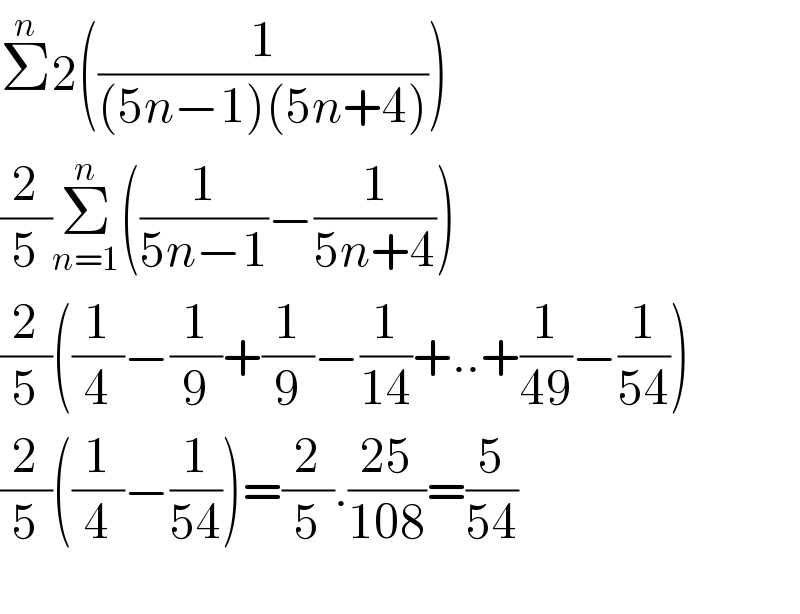
$$\overset{{n}} {\sum}\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{5}{n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{5}{n}+\mathrm{4}\right)}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}{n}−\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}{n}+\mathrm{4}}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{14}}+..+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{49}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{54}}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{54}}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}.\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{108}}=\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{54}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 20/Aug/20
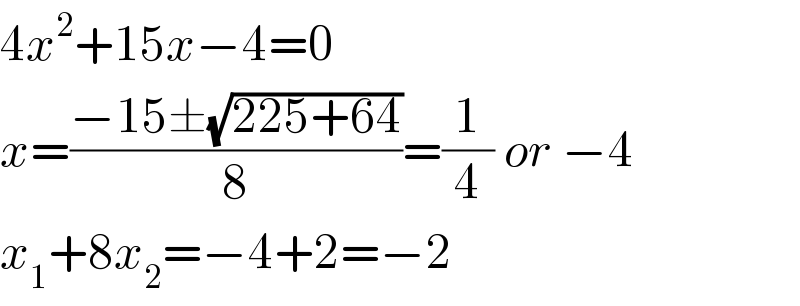
$$\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{15}{x}−\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\frac{−\mathrm{15}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{225}+\mathrm{64}}}{\mathrm{8}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\:{or}\:−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{8}{x}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{2}=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
