Question Number 108047 by bemath last updated on 14/Aug/20
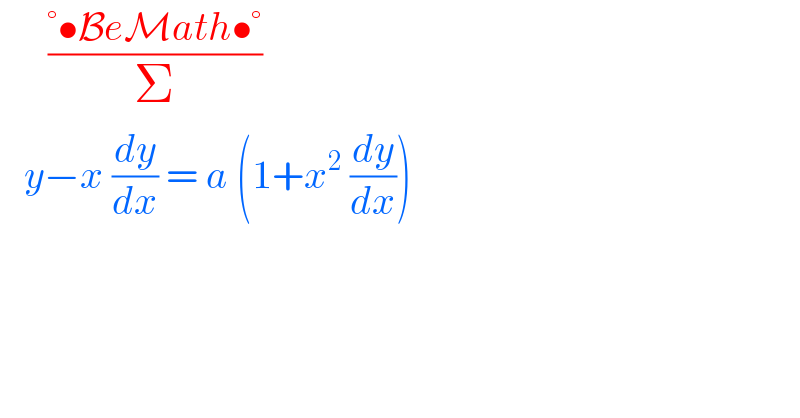
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{°\bullet\mathcal{B}{e}\mathcal{M}{ath}\bullet°}{\Sigma} \\ $$$$\:\:\:{y}−{x}\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:=\:{a}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\right)\: \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 14/Aug/20
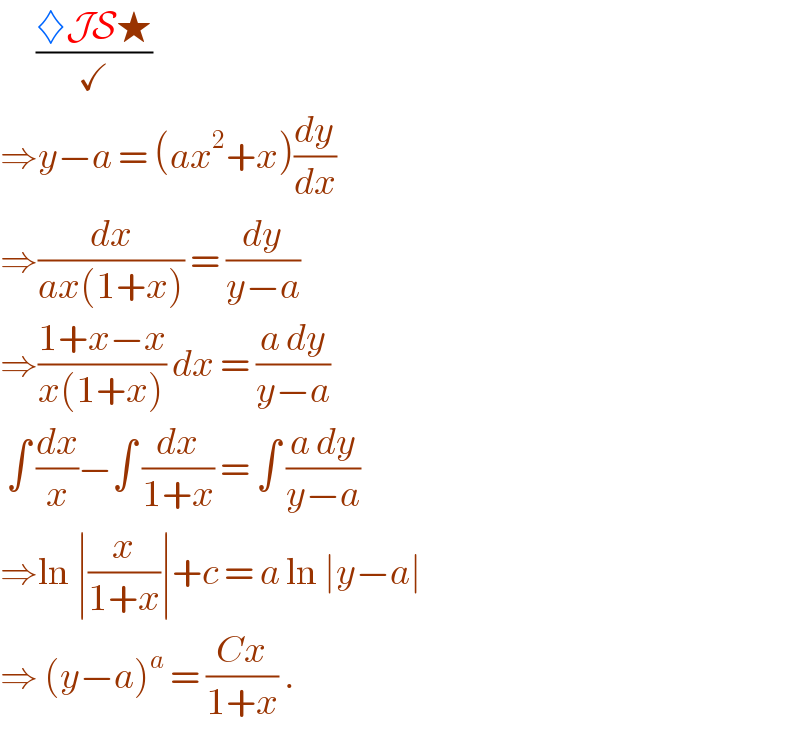
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\diamondsuit\mathcal{JS}\bigstar}{\checkmark} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}−{a}\:=\:\left({ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}\right)\frac{{dy}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{dx}}{{ax}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}\:=\:\frac{{dy}}{{y}−{a}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}+{x}−{x}}{{x}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}\:{dx}\:=\:\frac{{a}\:{dy}}{{y}−{a}} \\ $$$$\:\int\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}}−\int\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\:=\:\int\:\frac{{a}\:{dy}}{{y}−{a}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{ln}\:\mid\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\mid+{c}\:=\:{a}\:\mathrm{ln}\:\mid{y}−{a}\mid\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\left({y}−{a}\right)^{{a}} \:=\:\frac{{Cx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\:.\: \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 14/Aug/20

$${cooll}\:{nice} \\ $$
