Question Number 178988 by cortano1 last updated on 23/Oct/22
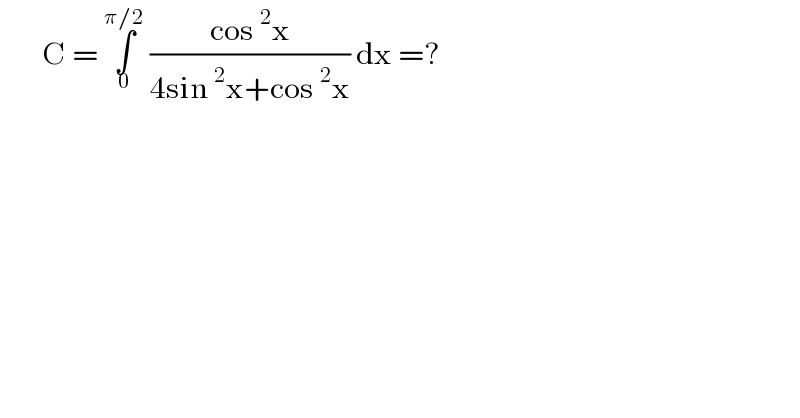
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{C}\:=\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{4sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}\:\mathrm{dx}\:=? \\ $$
Answered by qaz last updated on 23/Oct/22
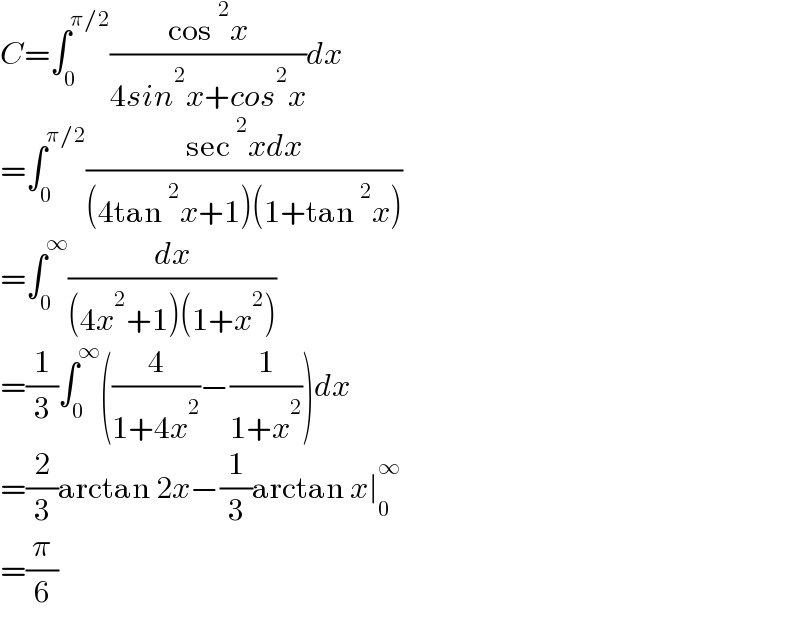
$${C}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{\mathrm{4}{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}+{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{sec}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {xdx}}{\left(\mathrm{4tan}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{tan}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right)} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{arctan}\:\mathrm{2}{x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{arctan}\:{x}\mid_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \\ $$$$=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$
