Question Number 178254 by lapache last updated on 14/Oct/22

$${Calcul} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}−\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\propto} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{4}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}−\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\propto} {\sum}}\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}!} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}−\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\propto} {\sum}}\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} }{{n}!} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}−\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\propto} {\sum}}{ln}\left(\frac{{n}}{{n}−\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 14/Oct/22

$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${e}^{{x}} =\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{{n}!} \\ $$$$\left({e}^{{x}} \right)'=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{{n}!}\right)' \\ $$$${e}^{{x}} =\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{nx}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} }{{n}!} \\ $$$${xe}^{{x}} =\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{nx}^{{n}} }{{n}!} \\ $$$$\left({xe}^{{x}} \right)'=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(\frac{{nx}^{{n}} }{{n}!}\right)' \\ $$$$\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right){e}^{{x}} =\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} }{{n}!} \\ $$$${with}\:{x}=\mathrm{1}: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{e}=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}!} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{3}\right)\:{similarly} \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 14/Oct/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 14/Oct/22

$$\left(\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\underset{{k}=\mathrm{2}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{{k}}{{k}−\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}}×\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}×…×\frac{{n}}{{n}−\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:{n}\right) \\ $$$$=\infty \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 14/Oct/22
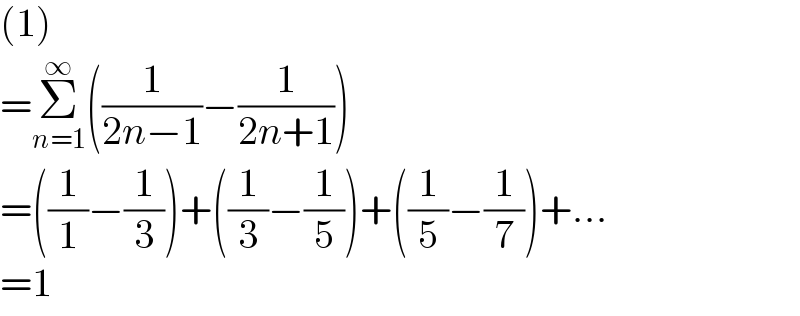
$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$$=\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)+\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)+\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{7}}\right)+… \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by lapache last updated on 14/Oct/22

$${Thank} \\ $$
