Question Number 163111 by SANOGO last updated on 03/Jan/22
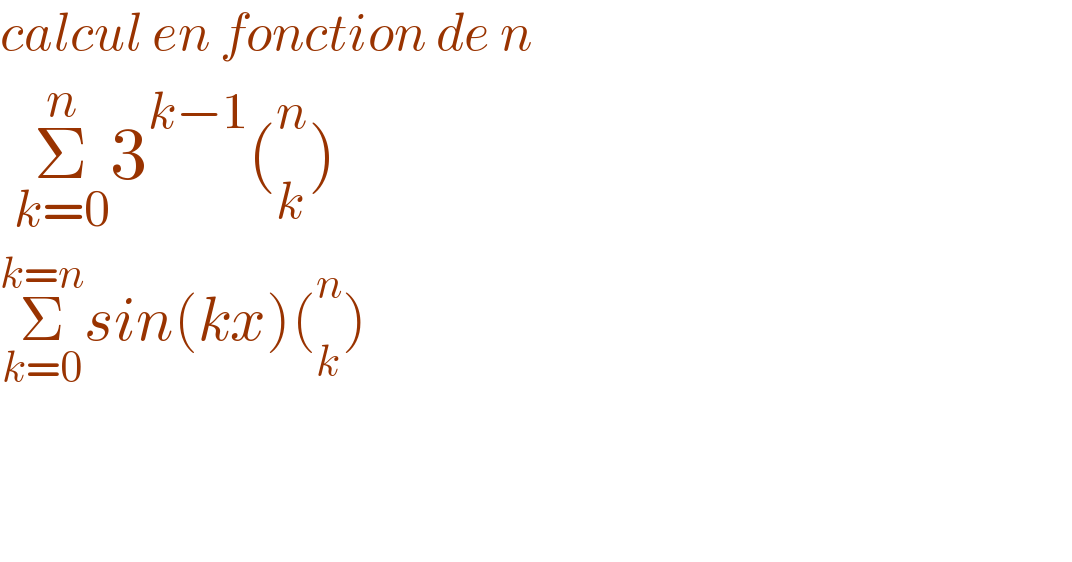
$${calcul}\:{en}\:{fonction}\:{de}\:{n} \\ $$$$\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\mathrm{3}^{{k}−\mathrm{1}} \left(_{{k}} ^{{n}} \right) \\ $$$$\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{k}={n}} {\sum}}{sin}\left({kx}\right)\left(_{{k}} ^{{n}} \right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 04/Jan/22
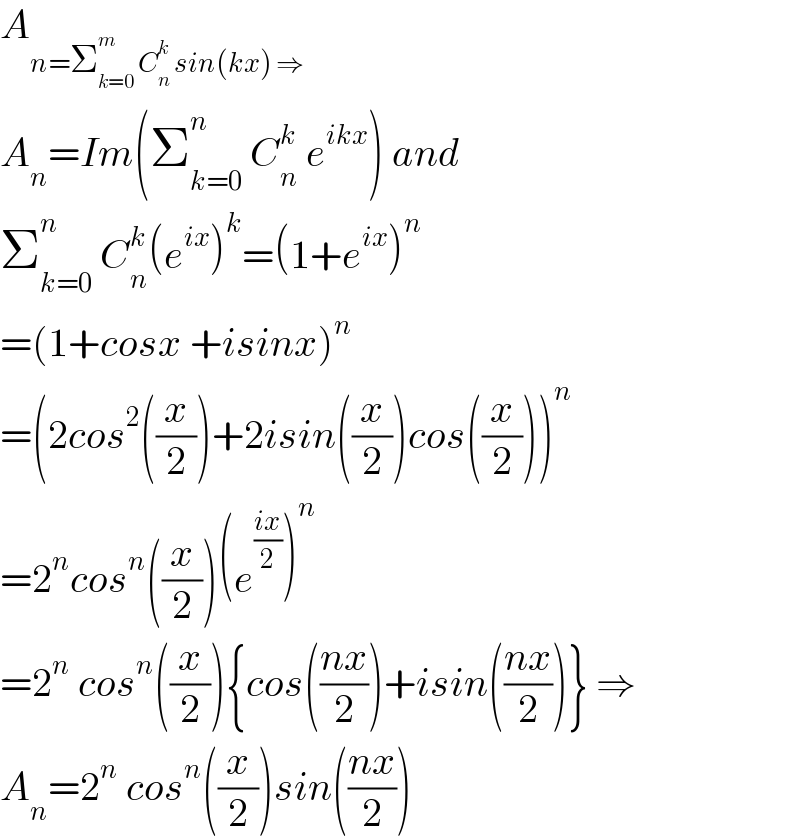
$${A}_{{n}=\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{m}} \:{C}_{{n}} ^{{k}} \:{sin}\left({kx}\right)\:\Rightarrow} \\ $$$${A}_{{n}} ={Im}\left(\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:{C}_{{n}} ^{{k}} \:{e}^{{ikx}} \right)\:{and} \\ $$$$\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:{C}_{{n}} ^{{k}} \left({e}^{{ix}} \right)^{{k}} =\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{ix}} \right)^{{n}} \\ $$$$=\left(\mathrm{1}+{cosx}\:+{isinx}\right)^{{n}} \\ $$$$=\left(\mathrm{2}{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\mathrm{2}{isin}\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){cos}\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right)^{{n}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}^{{n}} {cos}^{{n}} \left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\left({e}^{\frac{{ix}}{\mathrm{2}}} \right)^{{n}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}^{{n}} \:{cos}^{{n}} \left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\left\{{cos}\left(\frac{{nx}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)+{isin}\left(\frac{{nx}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right\}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${A}_{{n}} =\mathrm{2}^{{n}} \:{cos}^{{n}} \left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){sin}\left(\frac{{nx}}{\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$
Commented by SANOGO last updated on 04/Jan/22
$${merci}\:{bien} \\ $$
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 04/Jan/22
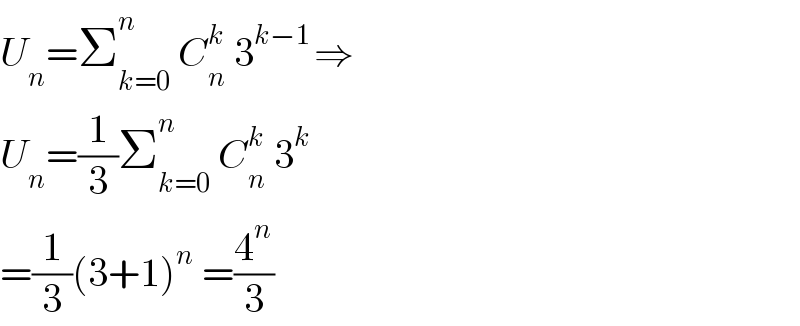
$${U}_{{n}} =\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}\:} \:{C}_{{n}} ^{{k}} \:\mathrm{3}^{{k}−\mathrm{1}\:} \Rightarrow \\ $$$${U}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:{C}_{{n}} ^{{k}} \:\mathrm{3}^{{k}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \:=\frac{\mathrm{4}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
