Question Number 98423 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 13/Jun/20
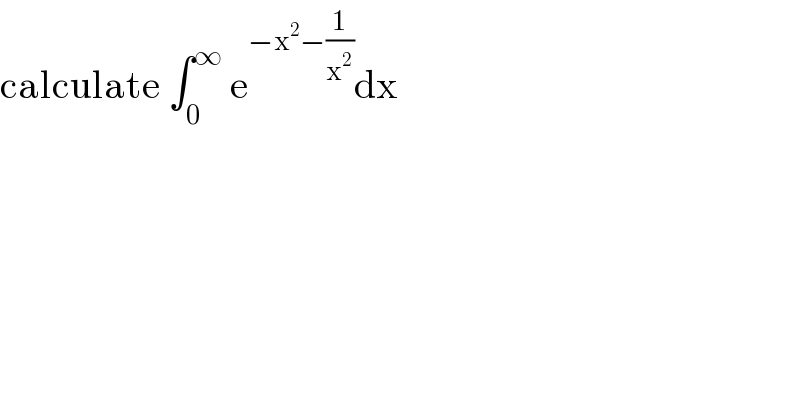
$$\mathrm{calculate}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Answered by maths mind last updated on 14/Jun/20
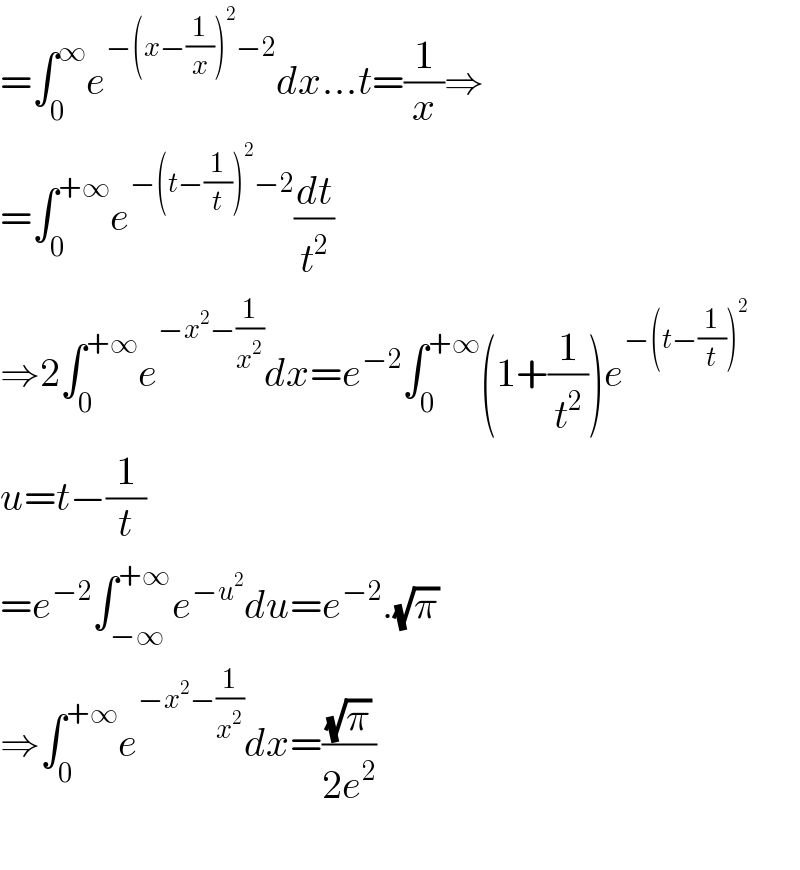
$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−\left({x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}} {dx}…{t}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\Rightarrow \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} {e}^{−\left({t}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}} \frac{{dt}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} {e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} {dx}={e}^{−\mathrm{2}} \int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right){e}^{−\left({t}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${u}={t}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}} \\ $$$$={e}^{−\mathrm{2}} \int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} {e}^{−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} } {du}={e}^{−\mathrm{2}} .\sqrt{\pi} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} {e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} {dx}=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}{e}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 14/Jun/20

$$\mathrm{thanks}\:\mathrm{sir}. \\ $$
Commented by maths mind last updated on 14/Jun/20

$${withe}\:{pleasur} \\ $$
