Question Number 102417 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 09/Jul/20
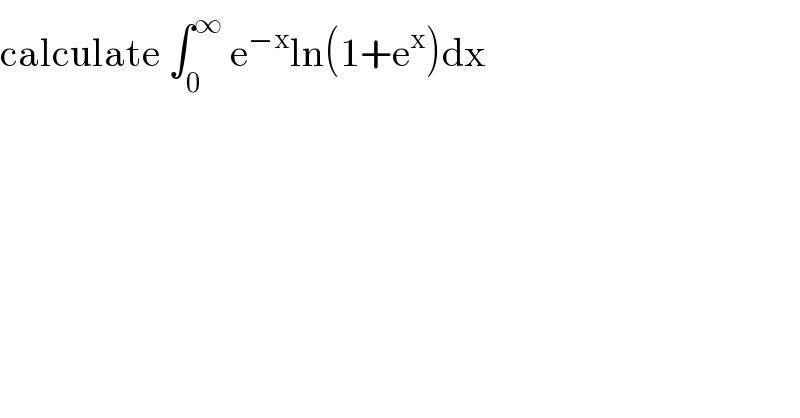
$$\mathrm{calculate}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Answered by floor(10²Eta[1]) last updated on 09/Jul/20
![u=ln(e^x +1)⇒du=(e^x /(e^x +1))dx dv=e^(−x) dx⇒v=−e^(−x) [−e^(−x) ln(e^x +1)]_0 ^∞ +∫_0 ^∞ (1/(e^x +1))dx ln(2)+∫_0 ^∞ (1/(e^x +1))dx=I u=e^x ⇒(du/u)=dx ∫_1 ^∞ (1/(u(u+1)))du=∫_1 ^∞ ((1/u)−(1/(u+1)))du lim_(a→∞) [ln(u)−ln(u+1)]_1 ^a =ln(2)) ⇒I=ln(2)+ln(2)=ln(4).](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q102426.png)
$$\mathrm{u}=\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{du}=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} +\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{dv}=\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{dx}\Rightarrow\mathrm{v}=−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\left[−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} +\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} +\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} +\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx}=\mathrm{I} \\ $$$$\mathrm{u}=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{u}}=\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{u}\left(\mathrm{u}+\mathrm{1}\right)}\mathrm{du}=\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{u}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{u}+\mathrm{1}}\right)\mathrm{du} \\ $$$$\left.\underset{\mathrm{a}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{u}\right)−\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{u}+\mathrm{1}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{a}} =\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{I}=\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{4}\right). \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 10/Jul/20

$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Answered by OlafThorendsen last updated on 09/Jul/20
![I = ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x) ln(1+e^x )dx I = ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x) ln[e^x (1+e^(−x) )]dx I = ∫_0 ^∞ [xe^(−x) +e^(−x) ln(1+e^(−x) )]dx I = [−(x+1)e^(−x) +(1+e^(−x) )(1−ln(1+e^(−x) ))]_0 ^(+∞) I = (0+1)−(−1+2(1−ln2)) I = 2ln2](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q102428.png)
$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{e}^{−{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{x}} \right){dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{e}^{−{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left[{e}^{{x}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−{x}} \right)\right]{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\left[{xe}^{−{x}} +{e}^{−{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−{x}} \right)\right]{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\:\left[−\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right){e}^{−{x}} +\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−{x}} \right)\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−{x}} \right)\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\left(\mathrm{0}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\left(−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{ln2}\right)\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\mathrm{2ln2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 10/Jul/20
![I =∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x) ln(1+e^x )dx by parts u^′ =e^(−x) and v =ln(1+e^x ) I =[−e^(−x) ln(1+e^x )]_0 ^∞ +∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x) ×(e^x /(1+e^x ))dx =ln(2)+∫_0 ^∞ (dx/(1+e^x )) 4hangement e^x =t give ∫_0 ^∞ (dx/(1+e^x )) = ∫_1 ^(+∞ ) (dt/(t(1+t))) =∫_1 ^(+∞) ((1/t)−(1/(t+1)))dt =[ln∣(t/(t+1))∣]_1 ^(+∞) =−ln((1/2)) =ln(2) ⇒ I =2ln(2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q102695.png)
$$\mathrm{I}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right)\mathrm{dx}\:\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{parts}\:\mathrm{u}^{'} \:=\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{v}\:=\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\left[−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} ×\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }\mathrm{dx}\:=\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{4hangement}\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:=\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{give}\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty\:} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{dt}}{\mathrm{t}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}\right)} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{t}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{1}}\right)\mathrm{dt}\:=\left[\mathrm{ln}\mid\frac{\mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{1}}\mid\right]_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \:=−\mathrm{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:=\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\mathrm{2ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$
