Question Number 60893 by mathsolverby Abdo last updated on 26/May/19
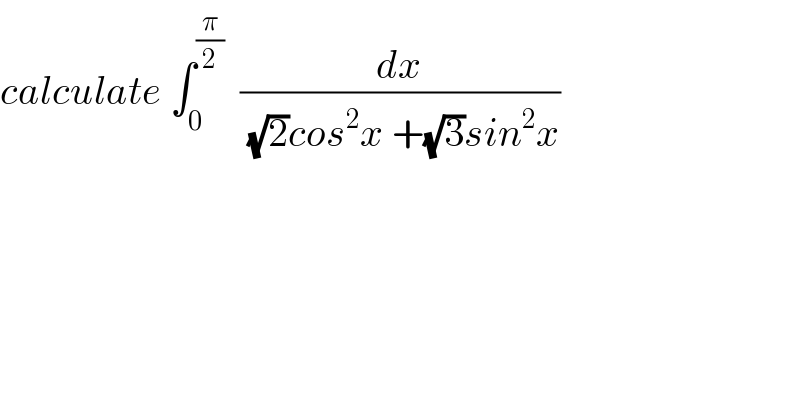
$${calculate}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\frac{{dx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}} \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 27/May/19
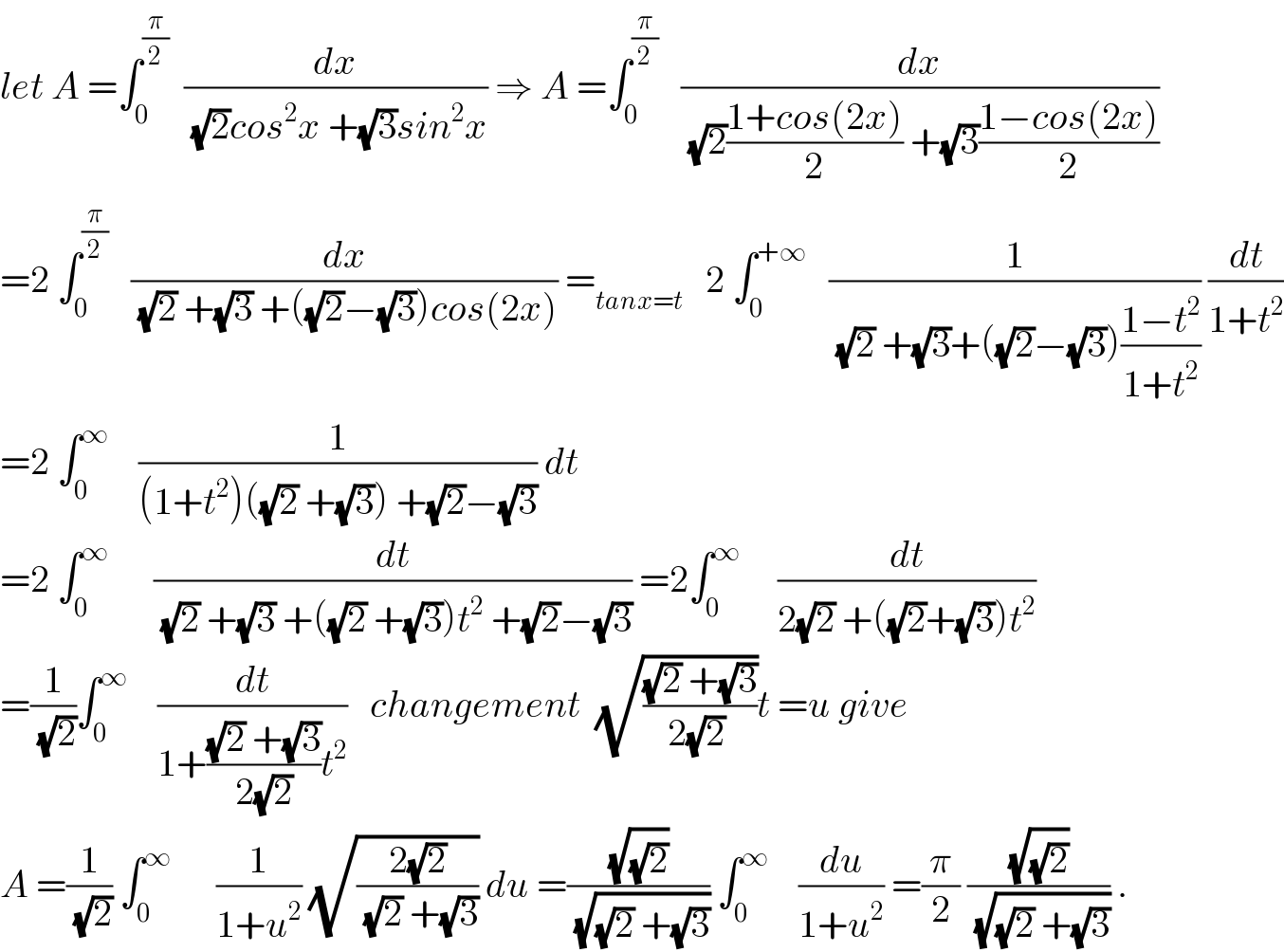
$${let}\:{A}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\frac{{dx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}\:\Rightarrow\:{A}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\frac{\mathrm{1}+{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\frac{\mathrm{1}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:+\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\right){cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}\:=_{{tanx}={t}} \:\:\:\mathrm{2}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\right)\frac{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\right)\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\:{dt} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dt}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:+\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\right){t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\:=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\right){t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\:\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:{changement}\:\:\sqrt{\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:}}{t}\:={u}\:{give} \\ $$$${A}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}}\:{du}\:=\frac{\sqrt{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}}{\:\sqrt{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\:\frac{{du}}{\mathrm{1}+{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:\frac{\sqrt{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}}{\:\sqrt{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}}\:. \\ $$
Answered by Prithwish sen last updated on 27/May/19
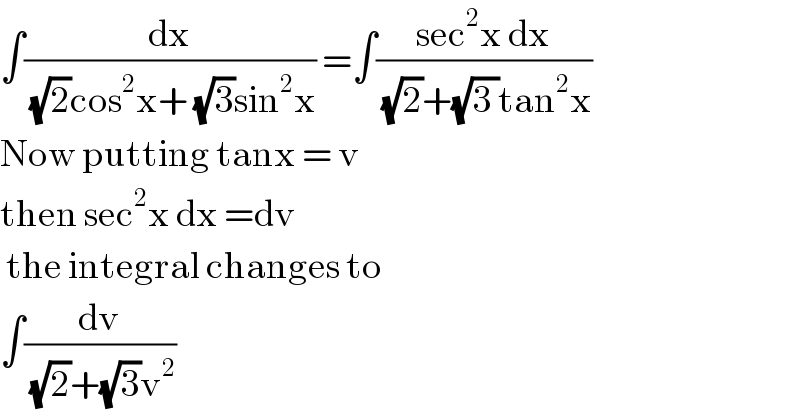
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}+\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}\:=\int\frac{\mathrm{sec}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{dx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}\:}\mathrm{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Now}\:\mathrm{putting}\:\mathrm{tanx}\:=\:\mathrm{v} \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{sec}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{dx}\:=\mathrm{dv} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{integral}\:\mathrm{changes}\:\mathrm{to} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} }\: \\ $$
