Question Number 130136 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 22/Jan/21
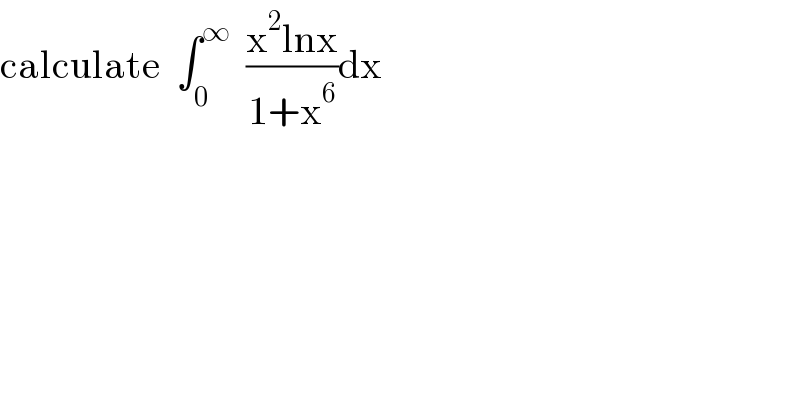
$$\mathrm{calculate}\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{lnx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{6}} }\mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 22/Jan/21
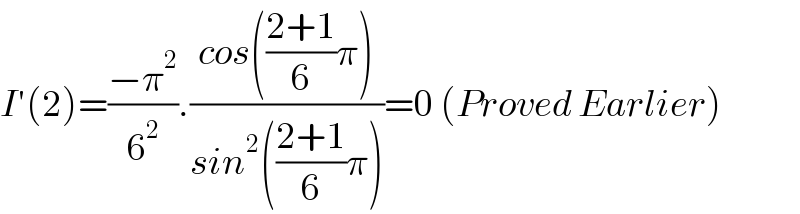
$${I}'\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\frac{−\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{2}} }.\frac{{cos}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\pi\right)}{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\pi\right)}=\mathrm{0}\:\left({Proved}\:{Earlier}\right) \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 22/Jan/21
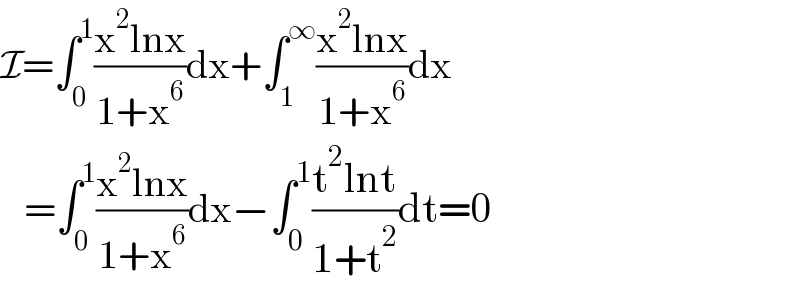
$$\mathcal{I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{lnx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{6}} }\mathrm{dx}+\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{lnx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{6}} }\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{lnx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{6}} }\mathrm{dx}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{lnt}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{dt}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 23/Jan/21
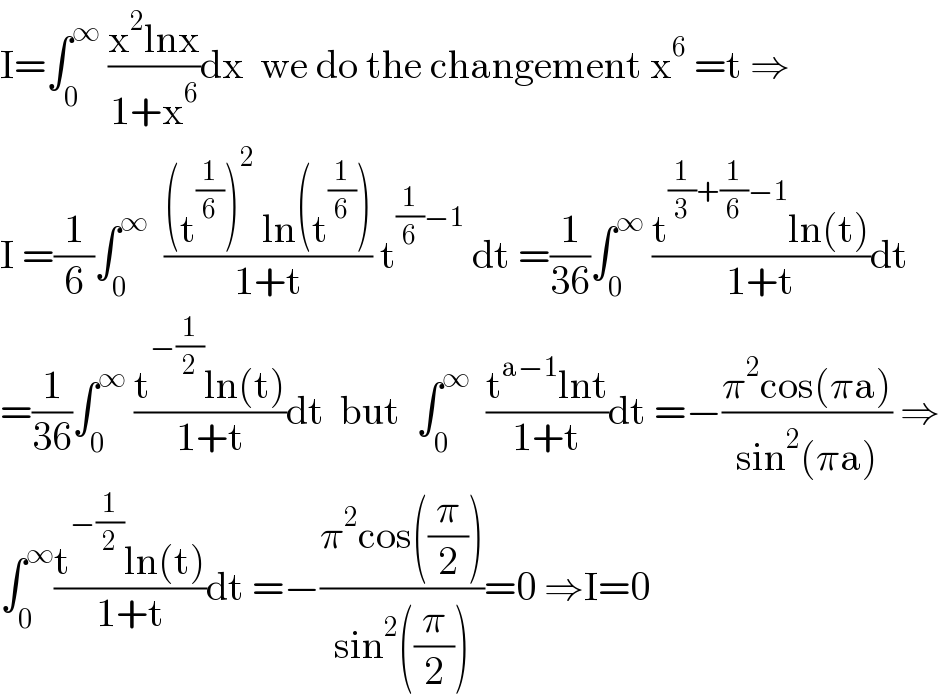
$$\mathrm{I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{lnx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{6}} }\mathrm{dx}\:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{do}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{changement}\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{6}} \:=\mathrm{t}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}} \right)}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}}\:\mathrm{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}−\mathrm{1}} \:\mathrm{dt}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{36}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}−\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}}\mathrm{dt} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{36}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{t}^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}}\mathrm{dt}\:\:\mathrm{but}\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{a}−\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{lnt}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}}\mathrm{dt}\:=−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\left(\pi\mathrm{a}\right)}{\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\pi\mathrm{a}\right)}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{t}^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}}\mathrm{dt}\:=−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{I}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
