Question Number 39135 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 02/Jul/18
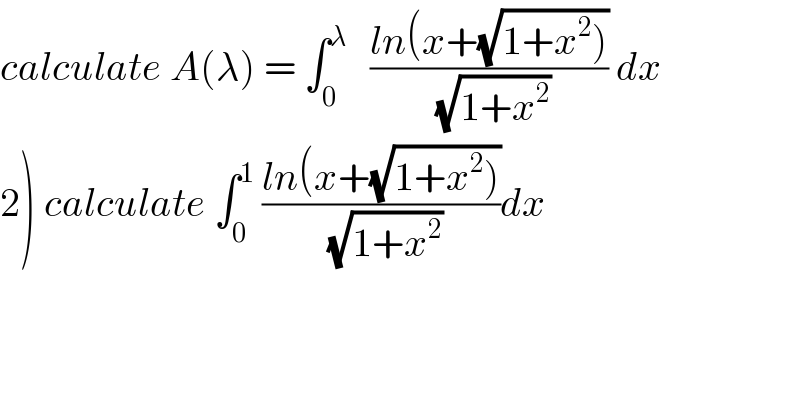
$${calculate}\:{A}\left(\lambda\right)\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\lambda} \:\:\:\frac{{ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{\left.\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\right.}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:{dx} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:{calculate}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{\left.\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\right.}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dx} \\ $$
Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 03/Jul/18
![let integrate by parts u^′ =(1/( (√(1+x^2 )))) and v=ln(x+(√(1+x^2 ))) A(λ) =[ln^2 (x+(√(1+x^2 )))]_0 ^λ −∫_0 ^λ ((ln(x+(√(1+x^2 ))))/( (√(1+x^2 ))))dx ⇒2A(λ)=ln^2 (λ+(√(1+λ^2 ))) ⇒ A(λ)=(1/2)ln^2 (λ +(√(1+λ^2 ))) 2) ∫_0 ^1 ((ln(1+(√(1+x^2 )))/( (√(1+x^2 )))))dx=A(1)=(1/2)ln^2 (2+(√2)).](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q39159.png)
$${let}\:{integrate}\:{by}\:{parts}\:{u}^{'} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:{and}\:{v}={ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{\left.\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\right. \\ $$$${A}\left(\lambda\right)\:=\left[{ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\lambda} \:−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\lambda} \:\:\:\:\frac{{ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{A}\left(\lambda\right)={ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\lambda+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\lambda^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${A}\left(\lambda\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\lambda\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\lambda^{\mathrm{2}} }\right) \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\left.\right)\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right.}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\right){dx}={A}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{2}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right). \\ $$
Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 03/Jul/18

$${A}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 03/Jul/18
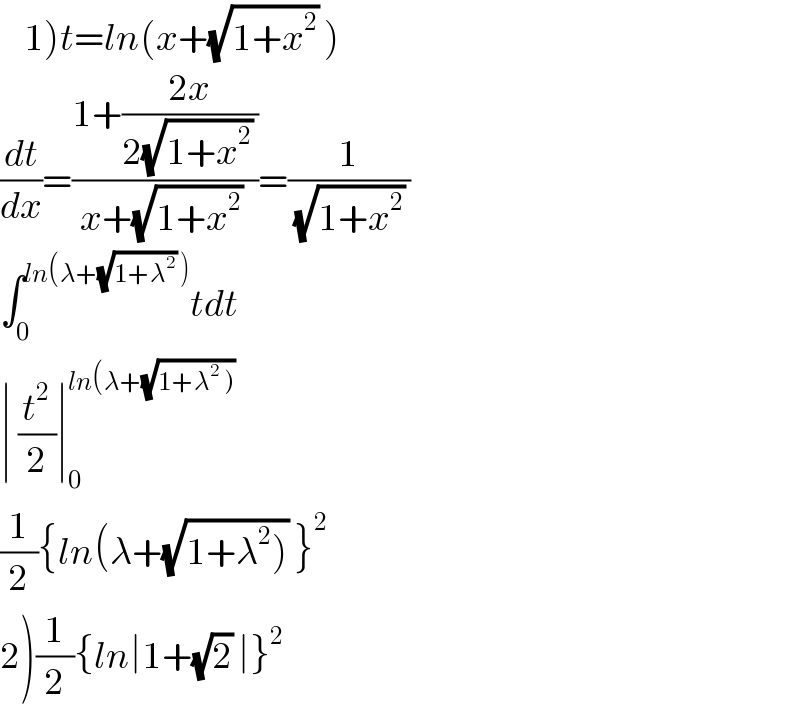
$$\left.\:\:\:\:\mathrm{1}\right){t}={ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\right)\:\: \\ $$$$\frac{{dt}}{{dx}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:}}{{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{ln}\left(\lambda+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\lambda^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\right)} {tdt} \\ $$$$\mid\:\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\mid_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{ln}\left(\lambda+\sqrt{\left.\mathrm{1}+\lambda^{\mathrm{2}} \:\right)}\right.} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left\{{ln}\left(\lambda+\sqrt{\left.\mathrm{1}+\lambda^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\:\right\}^{\mathrm{2}} \right. \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left\{{ln}\mid\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\mid\right\}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
