Question Number 53600 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 23/Jan/19
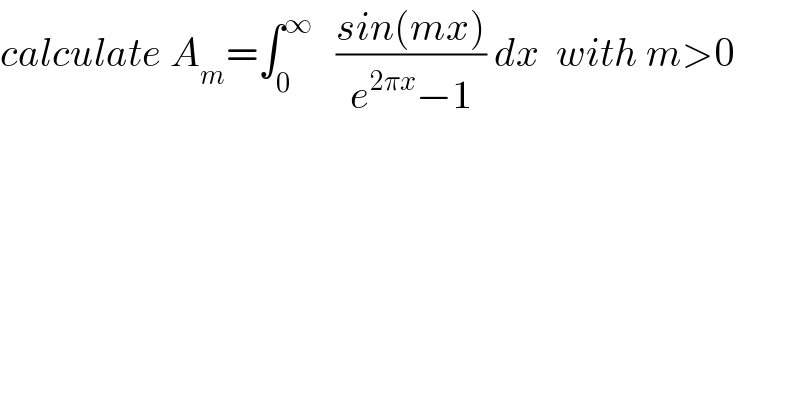
$${calculate}\:{A}_{{m}} =\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{sin}\left({mx}\right)}{{e}^{\mathrm{2}\pi{x}} −\mathrm{1}}\:{dx}\:\:{with}\:{m}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 24/Jan/19
![we have A_m =∫_0 ^∞ ((e^(−2πx) sin(mx))/(1−e^(−2πx) )) dx =Im(∫_0 ^∞ ((e^(−2πx) e^(imx) )/(1−e^(−2πx) ))dx) but ∫_0 ^∞ (e^(−(2π−im)x) /(1−e^(−2πx) ))dx =∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(2π−im)x) (Σ_(p=0) ^∞ e^(−2πp x) ) =Σ_(p=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(2π−im+2pπ)x) dx =Σ_(p=0) ^∞ [−(1/(2π−im+2pπ)) e^(−(2π−im+2pπ)x) ]^(+∞) _0 =Σ_(p=0) ^∞ (1/((2+2p)π −im)) =Σ_(p=0) ^∞ (((2+2p)π+im)/((2+2p)^2 π^2 +m^2 )) ⇒ A_m =Σ_(p=0) ^∞ (m/(4(p+1)^2 π^2 +m^2 )) and A_m can be calculated by fourier series ....be continued...](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q53669.png)
$${we}\:{have}\:{A}_{{m}} =\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{e}^{−\mathrm{2}\pi{x}} \:{sin}\left({mx}\right)}{\mathrm{1}−{e}^{−\mathrm{2}\pi{x}} }\:{dx}\:={Im}\left(\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{e}^{−\mathrm{2}\pi{x}} {e}^{{imx}} }{\mathrm{1}−{e}^{−\mathrm{2}\pi{x}} }{dx}\right)\:{but} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{e}^{−\left(\mathrm{2}\pi−{im}\right){x}} }{\mathrm{1}−{e}^{−\mathrm{2}\pi{x}} }{dx}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{e}^{−\left(\mathrm{2}\pi−{im}\right){x}} \left(\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{e}^{−\mathrm{2}\pi{p}\:{x}} \right) \\ $$$$=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−\left(\mathrm{2}\pi−{im}+\mathrm{2}{p}\pi\right){x}} {dx}\:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\left[−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\pi−{im}+\mathrm{2}{p}\pi}\:{e}^{−\left(\mathrm{2}\pi−{im}+\mathrm{2}{p}\pi\right){x}} \underset{\mathrm{0}} {\right]}^{+\infty} \\ $$$$=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{2}{p}\right)\pi\:−{im}}\:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{2}{p}\right)\pi+{im}}{\left(\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{2}{p}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \pi^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{m}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${A}_{{m}} =\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\:\frac{{m}}{\mathrm{4}\left({p}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \pi^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{m}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:{and}\:{A}_{{m}} \:{can}\:{be}\:{calculated}\:{by}\:{fourier}\:{series} \\ $$$$….{be}\:{continued}… \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
