Question Number 63215 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 30/Jun/19
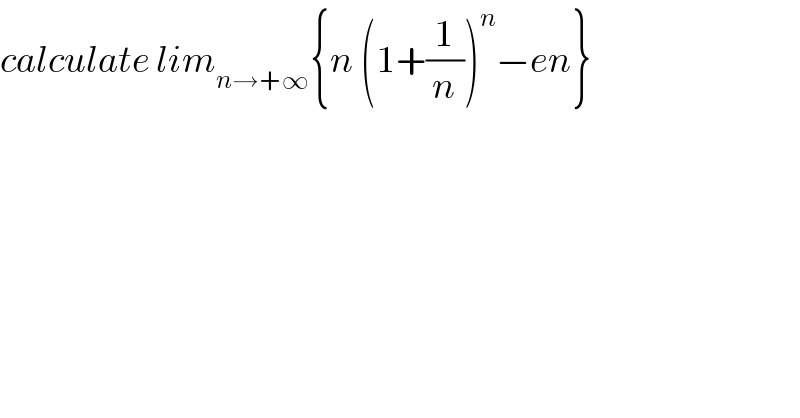
$${calculate}\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \left\{{n}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} −{en}\right\} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 01/Jul/19
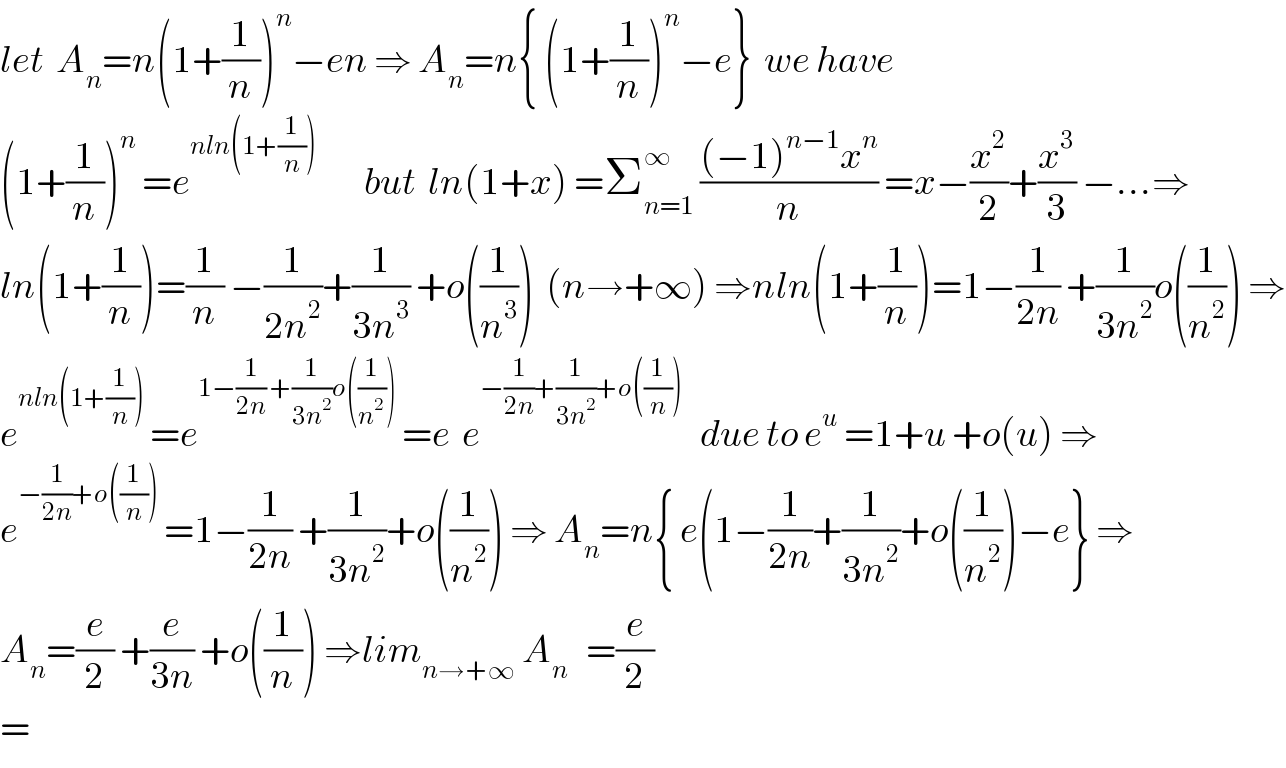
$${let}\:\:{A}_{{n}} ={n}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} −{en}\:\Rightarrow\:{A}_{{n}} ={n}\left\{\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} −{e}\right\}\:\:{we}\:{have} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} \:={e}^{{nln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{but}\:\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} {x}^{{n}} }{{n}}\:={x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}\:−…\Rightarrow \\ $$$${ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{n}^{\mathrm{3}} }\:+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} }\right)\:\:\left({n}\rightarrow+\infty\right)\:\Rightarrow{nln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)=\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${e}^{{nln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)} \:={e}^{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)} \:={e}\:\:{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)} \:\:\:{due}\:{to}\:{e}^{{u}} \:=\mathrm{1}+{u}\:+{o}\left({u}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)} \:=\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\:\Rightarrow\:{A}_{{n}} ={n}\left\{\:{e}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)−{e}\right\}\:\Rightarrow\right. \\ $$$${A}_{{n}} =\frac{{e}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{{e}}{\mathrm{3}{n}}\:+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)\:\Rightarrow{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:{A}_{{n}} \:\:\:=\frac{{e}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$= \\ $$
