Question Number 87168 by mathocean1 last updated on 03/Apr/20

$${Calculate}\:{these}\:{limits}: \\ $$$${Please}\:{sirs}\:{detail}\: \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 03/Apr/20
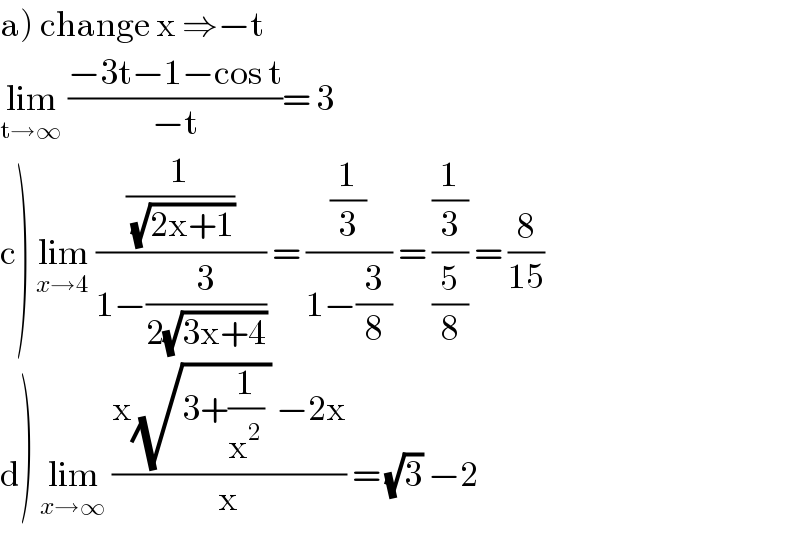
$$\left.\mathrm{a}\right)\:\mathrm{change}\:\mathrm{x}\:\Rightarrow−\mathrm{t}\: \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{t}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{−\mathrm{3t}−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{t}}{−\mathrm{t}}=\:\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{c}\right)\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{4}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}}}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3x}+\mathrm{4}}}}\:=\:\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{8}}}\:=\:\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}}{\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{8}}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{15}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{d}\right)\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:}\:−\mathrm{2x}}{\mathrm{x}}\:=\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by mathocean1 last updated on 03/Apr/20

Commented by john santu last updated on 03/Apr/20

$$\underset{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\mathrm{or}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}} \\ $$
Commented by mathocean1 last updated on 03/Apr/20

$${li}\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {{m}} \\ $$
Commented by TANMAY PANACEA. last updated on 03/Apr/20
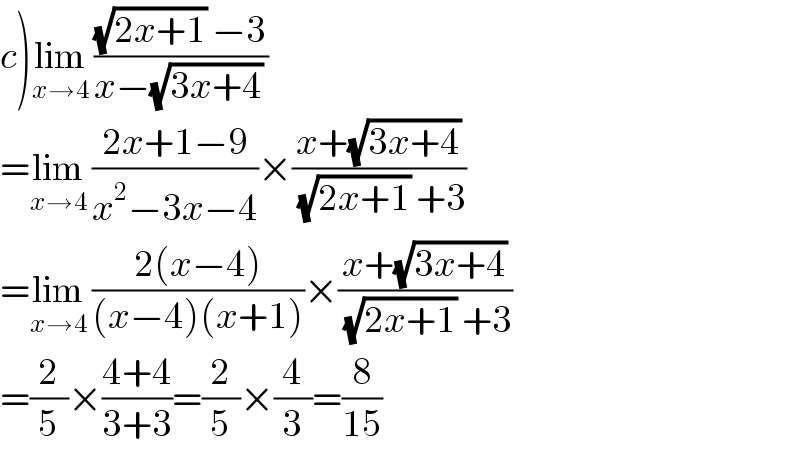
$$\left.{c}\right)\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{4}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:−\mathrm{3}}{{x}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{4}}\:} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{4}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{9}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{4}}×\frac{{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{4}}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:+\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{4}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}\left({x}−\mathrm{4}\right)}{\left({x}−\mathrm{4}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}×\frac{{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{4}}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:+\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}×\frac{\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}×\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{15}} \\ $$
Commented by TANMAY PANACEA. last updated on 03/Apr/20
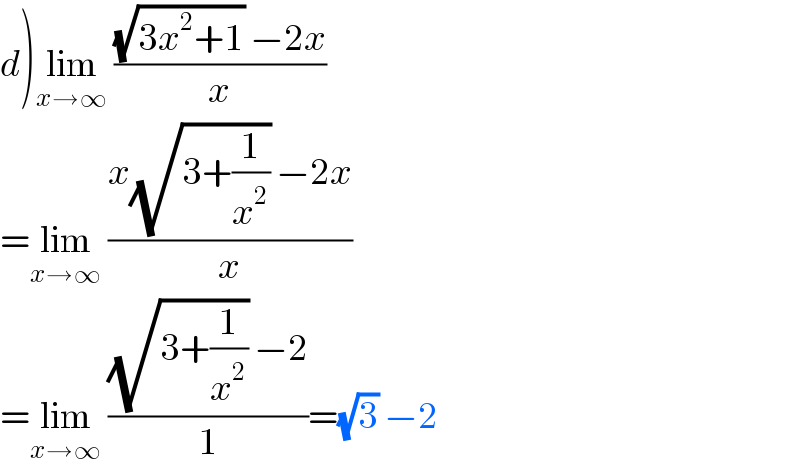
$$\left.{d}\right)\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\:−\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:−\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}}=\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 03/Apr/20
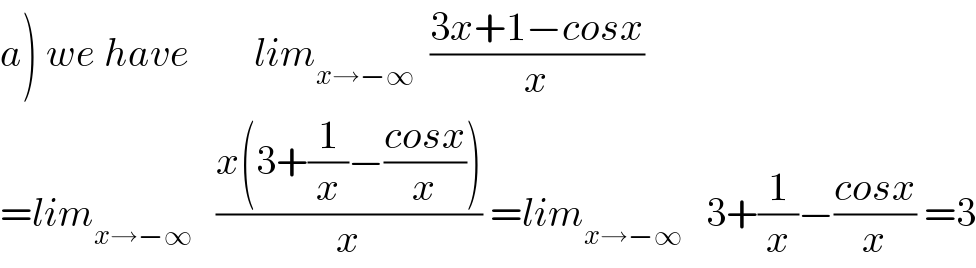
$$\left.{a}\right)\:{we}\:{have}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}−{cosx}}{{x}} \\ $$$$={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{x}\left(\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}−\frac{{cosx}}{{x}}\right)}{{x}}\:={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} \:\:\:\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}−\frac{{cosx}}{{x}}\:=\mathrm{3} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 03/Apr/20
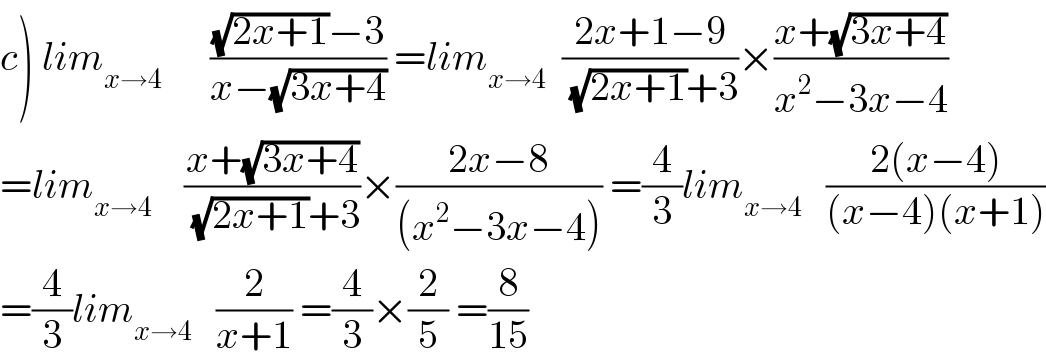
$$\left.{c}\right)\:{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{4}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}−\mathrm{3}}{{x}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{4}}}\:={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{4}} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{9}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}+\mathrm{3}}×\frac{{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{4}}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{4}} \:\:\:\:\frac{{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{4}}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}+\mathrm{3}}×\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{8}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{4}\right)}\:=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}}{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{4}} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{2}\left({x}−\mathrm{4}\right)}{\left({x}−\mathrm{4}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}}{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{4}} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}}×\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{15}} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 03/Apr/20
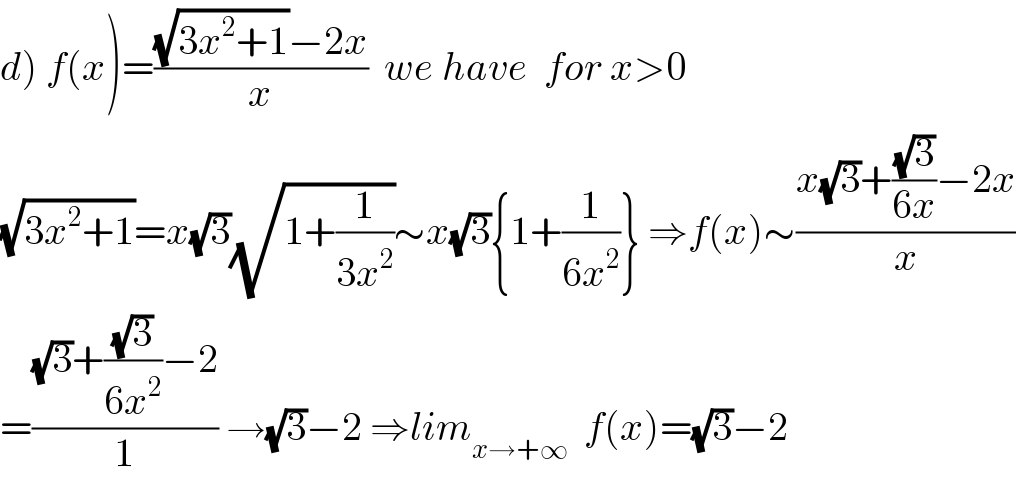
$$\left.{d}\right)\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}−\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}}\:\:{we}\:{have}\:\:{for}\:{x}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}={x}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\sim{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\left\{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right\}\:\Rightarrow{f}\left({x}\right)\sim\frac{{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{6}{x}}−\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}}\:\rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}−\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 03/Apr/20
![b) let f(x)=((x^2 +1)/(x[x])) changement x=−t give f(x)=((t^2 +1)/(−t[−t])) (x→−∞ ⇒t→ +∞) and we have [−t] =α−[t] with α =0 or −1 ⇒[−t]∼−[t]∼−t ⇒ lim_(x→−∞) f(x) =lim_(t→+∞) −((t^2 +1)/(t(−t))) =lim_(t→+∞) ((t^2 +1)/t^2 ) =1](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q87228.png)
$$\left.{b}\right)\:{let}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{{x}\left[{x}\right]}\:\:{changement}\:{x}=−{t}\:{give} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}{−{t}\left[−{t}\right]}\:\:\:\:\left({x}\rightarrow−\infty\:\Rightarrow{t}\rightarrow\:+\infty\right)\:\:{and}\:{we}\:{have} \\ $$$$\left[−{t}\right]\:=\alpha−\left[{t}\right]\:\:{with}\:\alpha\:=\mathrm{0}\:{or}\:−\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\left[−{t}\right]\sim−\left[{t}\right]\sim−{t}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} \:\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:={lim}_{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:\:−\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{{t}\left(−{t}\right)}\:={lim}_{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 03/Apr/20
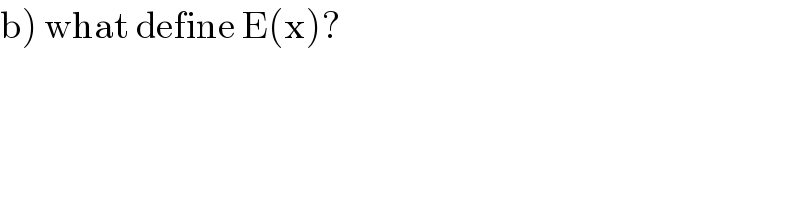
$$\left.\mathrm{b}\right)\:\mathrm{what}\:\mathrm{define}\:\mathrm{E}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)? \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 03/Apr/20
![why E(x)= [ x ] ? E(x) = μ ?](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q87231.png)
$$\mathrm{why}\:\mathrm{E}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\:\left[\:\mathrm{x}\:\right]\:?\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{E}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\:\mu\:?\: \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 03/Apr/20

$${E}\left({x}\right)={x}\:\:{at}\:\infty \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 03/Apr/20
![x =[x] +r with 0≤r<1 ⇒(x/([x])) =1+(r/([x])) ⇒(x/([x])) ∼ 1 (x→+∞)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q87240.png)
$${x}\:=\left[{x}\right]\:+{r}\:\:{with}\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant{r}<\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\frac{{x}}{\left[{x}\right]}\:=\mathrm{1}+\frac{{r}}{\left[{x}\right]}\:\Rightarrow\frac{{x}}{\left[{x}\right]}\:\sim\:\mathrm{1}\:\:\left({x}\rightarrow+\infty\right) \\ $$
Commented by mathocean1 last updated on 03/Apr/20

$$\mathrm{E}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{x}\leqslant\mathrm{E}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)+\mathrm{1} \\ $$
