Question Number 163709 by amin96 last updated on 09/Jan/22
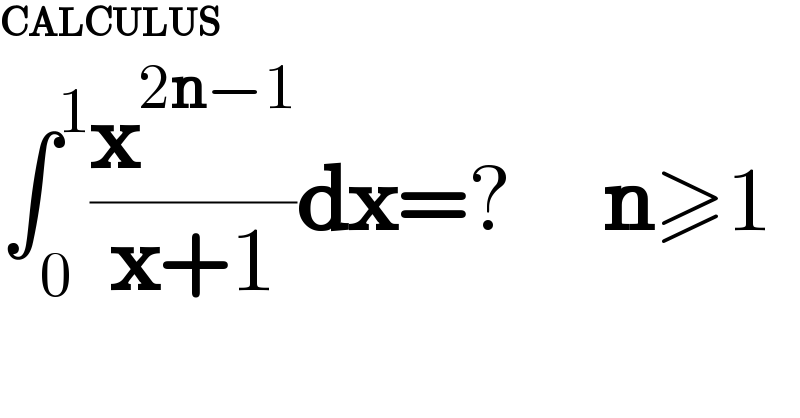
$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{CALCULUS}} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{n}}−\mathrm{1}} }{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}+\mathrm{1}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{dx}}=?\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{n}}\geqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 09/Jan/22
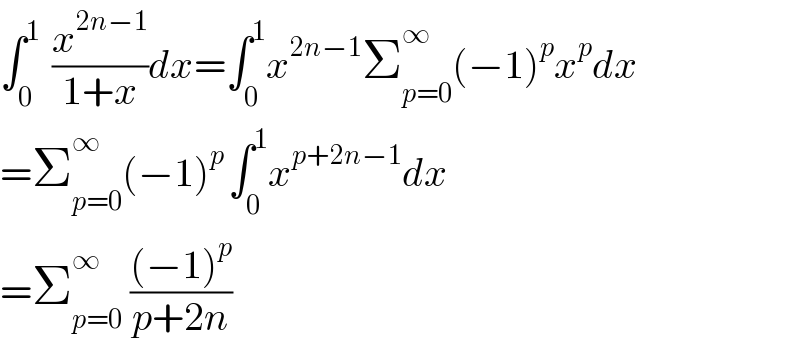
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}\:} \:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}}{dx}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}} \sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty\:} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}} {x}^{{p}} {dx} \\ $$$$=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}\:} \int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {x}^{{p}+\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}} {dx} \\ $$$$=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty\:} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}} }{{p}+\mathrm{2}{n}} \\ $$
