Question Number 126845 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 24/Dec/20
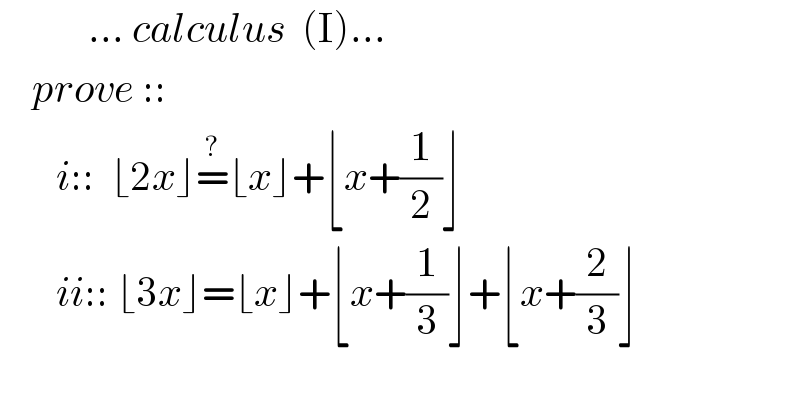
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:…\:{calculus}\:\:\left(\mathrm{I}\right)… \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{prove}\:::\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{i}::\:\:\lfloor\mathrm{2}{x}\rfloor\overset{?} {=}\lfloor{x}\rfloor+\lfloor{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{ii}::\:\lfloor\mathrm{3}{x}\rfloor=\lfloor{x}\rfloor+\lfloor{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\rfloor+\lfloor{x}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\rfloor \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by floor(10²Eta[1]) last updated on 24/Dec/20
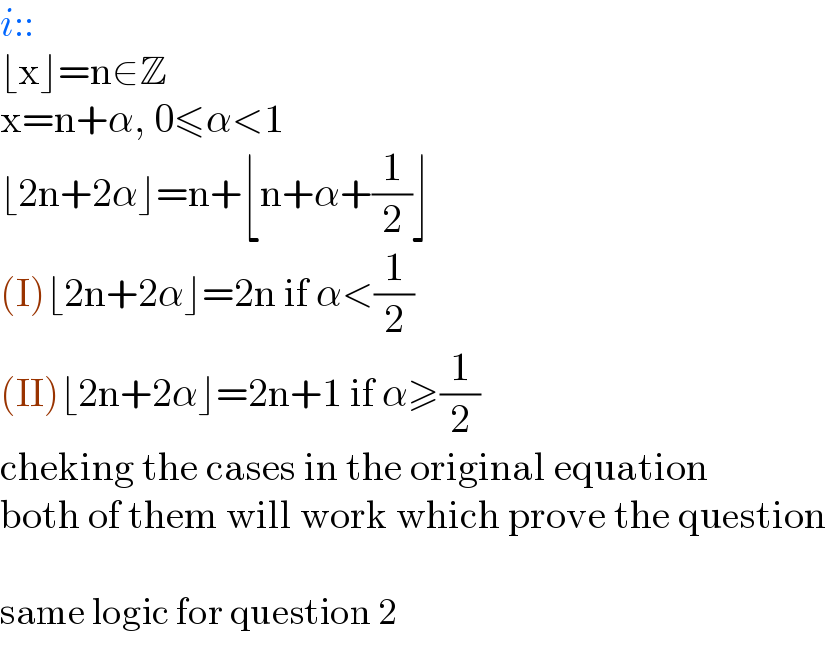
$${i}:: \\ $$$$\lfloor\mathrm{x}\rfloor=\mathrm{n}\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{n}+\alpha,\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant\alpha<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\lfloor\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{2}\alpha\rfloor=\mathrm{n}+\lfloor\mathrm{n}+\alpha+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{I}\right)\lfloor\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{2}\alpha\rfloor=\mathrm{2n}\:\mathrm{if}\:\alpha<\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{II}\right)\lfloor\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{2}\alpha\rfloor=\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{if}\:\alpha\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{cheking}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{cases}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{original}\:\mathrm{equation} \\ $$$$\mathrm{both}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{them}\:\mathrm{will}\:\mathrm{work}\:\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{prove}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{question} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{same}\:\mathrm{logic}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{question}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 24/Dec/20
![[x]=n ⇒n≤x <n+1 ⇒2n≤2x<2n+2 we have [2n,2n+2[ =[2n,2n+1[∪[2n+1,2n+2[ if 2x∈[2n,2n+1[ ⇒[2x]=2n and x∈[n,n+(1/2)[ ⇒[x]=n x+(1/2)∈[n+(1/2),n+1[ ⇒[x+(1/2)]=n ⇒[x]+[x+(1/2)]=n+n =2n=[2x] if 2x∈[2n+1,2n+2[ ⇒[2x]=2n+1 and x∈[n+(1/2),n+1[ ⇒[x]=n x+(1/2)∈[n+1,n+(3/2)[ ⇒[x+(1/2)]=n+1 ⇒[x]+[x+(1/2)]=n+n+1=2n+1 =[2x] in all cases the dquality is proved..](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q126858.png)
$$\left[\mathrm{x}\right]=\mathrm{n}\:\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}\leqslant\mathrm{x}\:<\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{2n}\leqslant\mathrm{2x}<\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{2}\:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have} \\ $$$$\left[\mathrm{2n},\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{2}\left[\:=\left[\mathrm{2n},\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1}\left[\cup\left[\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{2}\left[\right.\right.\right.\right.\right.\right. \\ $$$$\mathrm{if}\:\:\mathrm{2x}\in\left[\mathrm{2n},\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1}\left[\:\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{2x}\right]=\mathrm{2n}\:\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{x}\in\left[\mathrm{n},\mathrm{n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\:\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{x}\right]=\mathrm{n}\right.\right.\right.\right. \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\in\left[\mathrm{n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}},\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}\left[\:\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]=\mathrm{n}\:\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{x}\right]+\left[\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]=\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{n}\:=\mathrm{2n}=\left[\mathrm{2x}\right]\right.\right. \\ $$$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{2x}\in\left[\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{2}\left[\:\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{2x}\right]=\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{x}\in\left[\mathrm{n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}},\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}\left[\:\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{x}\right]=\mathrm{n}\right.\right.\right.\right. \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\in\left[\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1},\mathrm{n}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\:\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]=\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{x}\right]+\left[\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]=\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1}\right.\right. \\ $$$$=\left[\mathrm{2x}\right]\:\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{all}\:\mathrm{cases}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{dquality}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{proved}.. \\ $$
Answered by mindispower last updated on 24/Dec/20
![[x]=n ⇒n≤x<n+1 x∈[n,n+(1/3)[⇒ [x]=[x+(1/3)]=[x+(2/3)]=n 3x∈[3n,3n+1[⇒[3x]=3n=[x]+[x+(1/3)]+[x+(2/3)] x∈[n+(1/3);n+(2/3)[ ⇒[x]=[x+(1/3)]=n [x+(2/3)]=n+1 3x∈[3n+1,3n+2[⇒[3x]=[x[+[x+(1/3)]+[x+(2/3)]=3n+1 and sam for x∈[n+(2/3),n+1[](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q126863.png)
$$\left[{x}\right]={n} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{n}\leqslant{x}<{n}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${x}\in\left[{n},{n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left[\Rightarrow\right.\right. \\ $$$$\left[{x}\right]=\left[{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right]=\left[{x}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right]={n} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{x}\in\left[\mathrm{3}{n},\mathrm{3}{n}+\mathrm{1}\left[\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{3}{x}\right]=\mathrm{3}{n}=\left[{x}\right]+\left[{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right]+\left[{x}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right]\right.\right. \\ $$$${x}\in\left[{n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}};{n}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\left[\right.\right. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left[{x}\right]=\left[{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right]={n} \\ $$$$\left[{x}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right]={n}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{x}\in\left[\mathrm{3}{n}+\mathrm{1},\mathrm{3}{n}+\mathrm{2}\left[\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{3}{x}\right]=\left[{x}\left[+\left[{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right]+\left[{x}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right]=\mathrm{3}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right.\right.\right.\right. \\ $$$${and}\:{sam}\:{for}\:{x}\in\left[{n}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}},{n}+\mathrm{1}\left[\right.\right. \\ $$
