Question Number 176276 by cortano1 last updated on 15/Sep/22
![coeff of x^2 from [6+8x−(3/2)x^2 ]^5](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q176276.png)
$$\mathrm{coeff}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{from}\: \\ $$$$\:\:\left[\mathrm{6}+\mathrm{8x}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\right]^{\mathrm{5}} \: \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 15/Sep/22
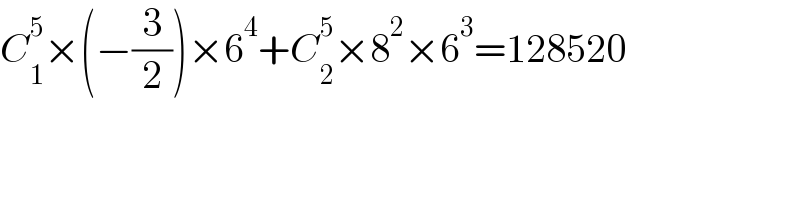
$${C}_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{5}} ×\left(−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)×\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{4}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{5}} ×\mathrm{8}^{\mathrm{2}} ×\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{128520} \\ $$
Commented by cortano1 last updated on 16/Sep/22

$$\mathrm{nice}\:.\: \\ $$
Commented by cortano1 last updated on 16/Sep/22
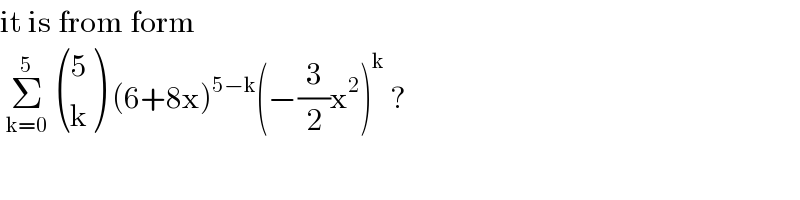
$$\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{form}\: \\ $$$$\:\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{5}} {\sum}}\:\begin{pmatrix}{\mathrm{5}}\\{\mathrm{k}}\end{pmatrix}\:\left(\mathrm{6}+\mathrm{8x}\right)^{\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{k}} \left(−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{k}} \:? \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 16/Sep/22

$${no},\:{i}\:{applied}\:{no}\:{formula}. \\ $$$${to}\:{get}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{we}\:{need} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}.\:{one}\:{term}\:−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{and}\:\mathrm{4}\:{terms}\:\mathrm{6}, \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{to}\:{select}\:{the}\:{term}\:−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} ,\:{there}\:{are} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{C}_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{5}} \:{ways},\:{therefore}\:{we}\:{get} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{C}_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{5}} ×\left(−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)×\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{4}} . \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}.\:\:{two}\:{terms}\:\mathrm{8}{x}\:{and}\:\mathrm{3}\:{terms}\:\mathrm{6}, \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{to}\:{select}\:{two}\:{terms}\:\mathrm{8}{x}\:,\:{there}\:{are} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{C}_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{5}} \:{ways},\:{therefore}\:{we}\:{get} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{C}_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{5}} ×\mathrm{8}^{\mathrm{2}} ×\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{3}} . \\ $$$${totally}\:{we}\:{get} \\ $$$${C}_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{5}} ×\left(−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)×\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{4}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{5}} ×\mathrm{8}^{\mathrm{2}} ×\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 18/Sep/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 16/Sep/22
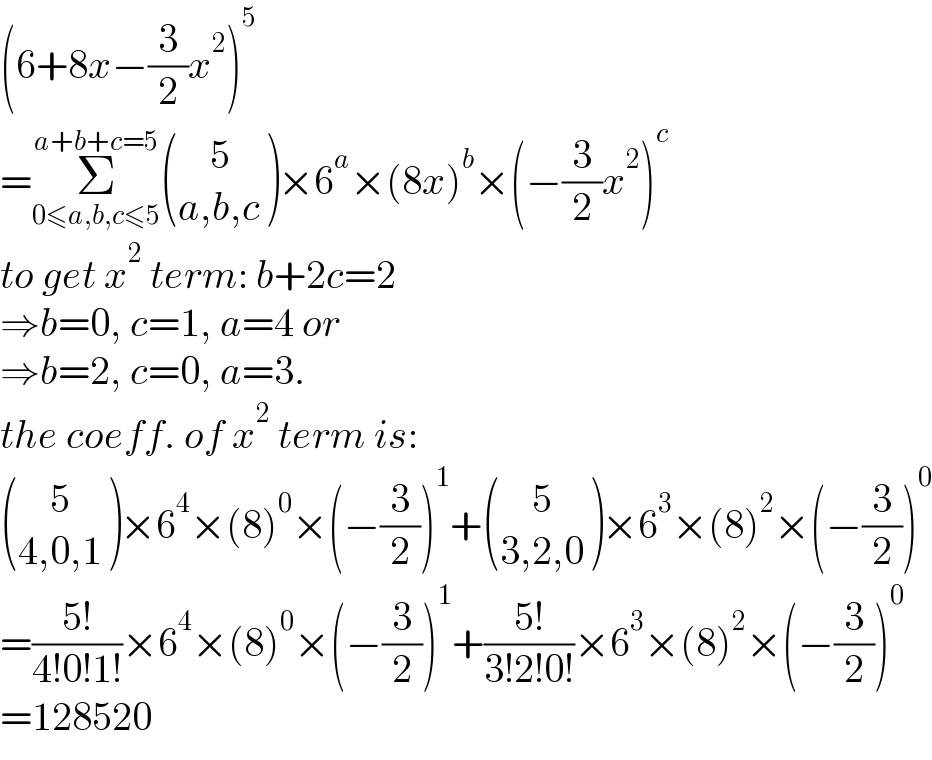
$$\left(\mathrm{6}+\mathrm{8}{x}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$=\underset{\mathrm{0}\leqslant{a},{b},{c}\leqslant\mathrm{5}} {\overset{{a}+{b}+{c}=\mathrm{5}} {\sum}}\begin{pmatrix}{\:\:\:\:\mathrm{5}}\\{{a},{b},{c}}\end{pmatrix}×\mathrm{6}^{{a}} ×\left(\mathrm{8}{x}\right)^{{b}} ×\left(−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{{c}} \\ $$$${to}\:{get}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{term}:\:{b}+\mathrm{2}{c}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{b}=\mathrm{0},\:{c}=\mathrm{1},\:{a}=\mathrm{4}\:{or} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{b}=\mathrm{2},\:{c}=\mathrm{0},\:{a}=\mathrm{3}. \\ $$$${the}\:{coeff}.\:{of}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{term}\:{is}: \\ $$$$\begin{pmatrix}{\:\:\:\:\mathrm{5}}\\{\mathrm{4},\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}}\end{pmatrix}×\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{4}} ×\left(\mathrm{8}\right)^{\mathrm{0}} ×\left(−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{1}} +\begin{pmatrix}{\:\:\:\:\mathrm{5}}\\{\mathrm{3},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{0}}\end{pmatrix}×\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{3}} ×\left(\mathrm{8}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ×\left(−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{0}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{5}!}{\mathrm{4}!\mathrm{0}!\mathrm{1}!}×\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{4}} ×\left(\mathrm{8}\right)^{\mathrm{0}} ×\left(−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{1}} +\frac{\mathrm{5}!}{\mathrm{3}!\mathrm{2}!\mathrm{0}!}×\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{3}} ×\left(\mathrm{8}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ×\left(−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{0}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{128520} \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 25/Sep/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir}. \\ $$
