Question Number 89193 by jagoll last updated on 16/Apr/20
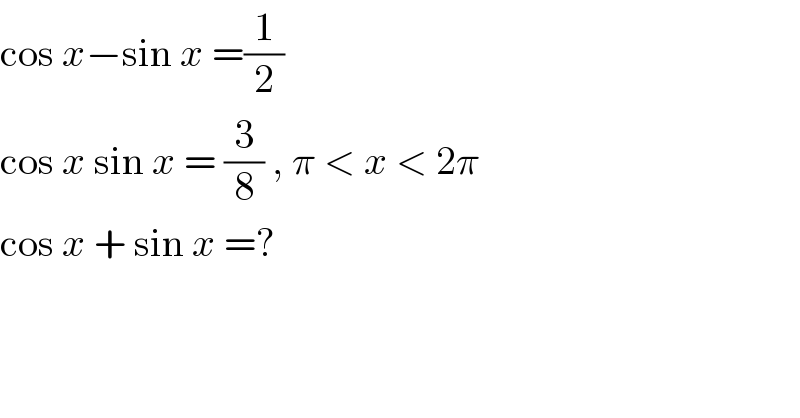
$$\mathrm{cos}\:{x}−\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{8}}\:,\:\pi\:<\:{x}\:<\:\mathrm{2}\pi \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:+\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:=? \\ $$
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 16/Apr/20
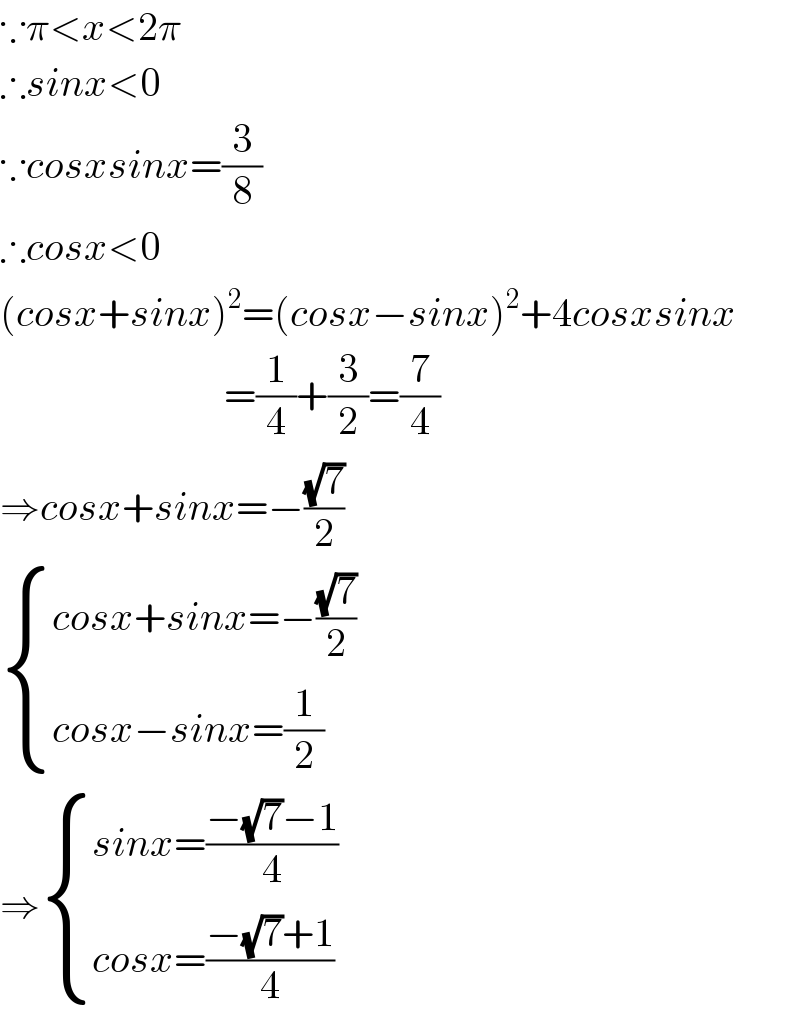
$$\because\pi<{x}<\mathrm{2}\pi \\ $$$$\therefore{sinx}<\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\because{cosxsinx}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$$\therefore{cosx}<\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({cosx}+{sinx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({cosx}−{sinx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{cosxsinx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{cosx}+{sinx}=−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{{cosx}+{sinx}=−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{2}}}\\{{cosx}−{sinx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{{sinx}=\frac{−\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}}\\{{cosx}=\frac{−\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}}\end{cases} \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 16/Apr/20
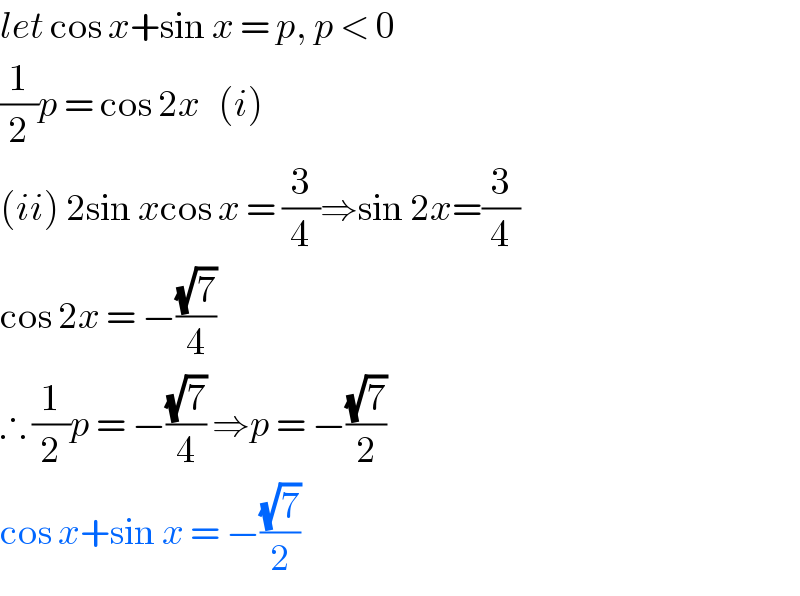
$${let}\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:=\:{p},\:{p}\:<\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{p}\:=\:\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:\:\:\left({i}\right) \\ $$$$\left({ii}\right)\:\mathrm{2sin}\:{x}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{4}}\Rightarrow\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:=\:−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{p}\:=\:−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{4}}\:\Rightarrow{p}\:=\:−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:=\:−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 16/Apr/20

$${thank}\:{you} \\ $$
