Question Number 114340 by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 18/Sep/20
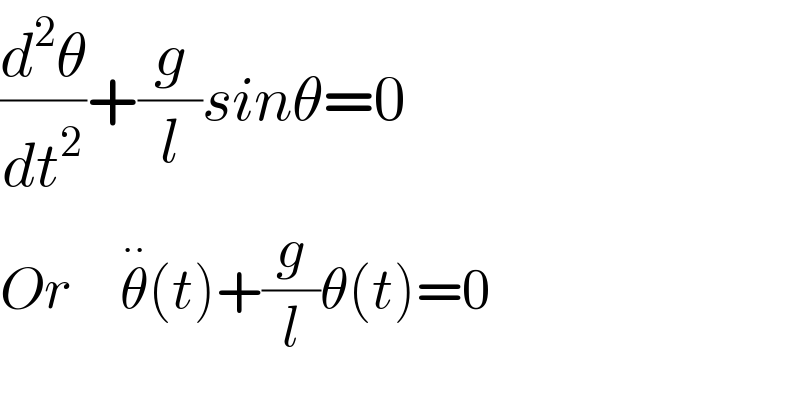
$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{g}}{{l}}{sin}\theta=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${Or}\:\:\:\:\:\overset{\centerdot\centerdot} {\theta}\left({t}\right)+\frac{{g}}{{l}}\theta\left({t}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 18/Sep/20

Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 18/Sep/20
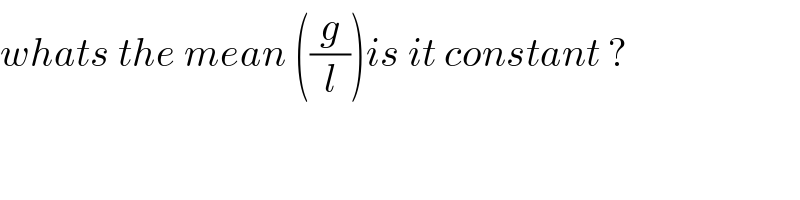
$${whats}\:{the}\:{mean}\:\left(\frac{{g}}{{l}}\right){is}\:{it}\:{constant}\:? \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 18/Sep/20

Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 18/Sep/20

$${Gravitational}\:{accelaration}\:{on}\:{simple}\:{pendulam}\:\:\left(−{g}\right) \\ $$$${On}\:{horizontal}\:{direction}\:\:−{gsin}\theta \\ $$$${S}={l}\theta \\ $$$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {s}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }={l}\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${l}\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }=−{gsin}\theta \\ $$$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{g}}{{l}}{sin}\theta=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Rio Michael last updated on 18/Sep/20
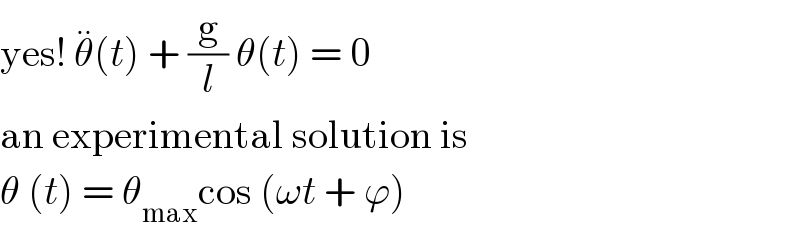
$$\mathrm{yes}!\:\overset{..} {\theta}\left({t}\right)\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{g}}{{l}}\:\theta\left({t}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{experimental}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{is} \\ $$$$\theta\:\left({t}\right)\:=\:\theta_{\mathrm{max}} \mathrm{cos}\:\left(\omega{t}\:+\:\varphi\right)\: \\ $$
