Question Number 97541 by mathocean1 last updated on 08/Jun/20
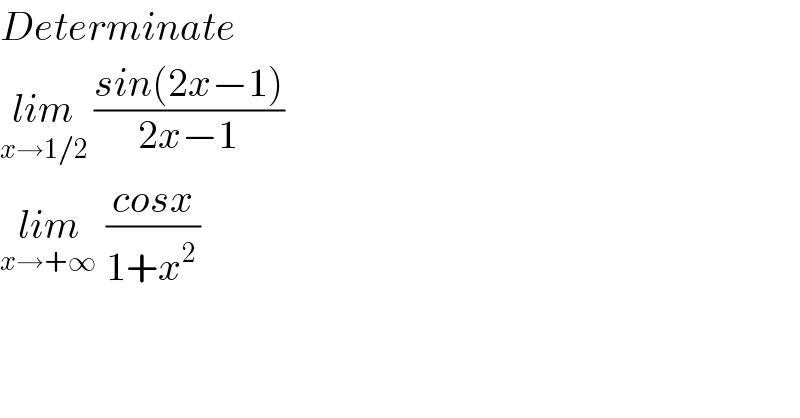
$${Determinate} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{2}} {{lim}}\:\frac{{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow+\infty\:} {{lim}}\:\frac{{cosx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}\:} } \\ $$
Commented by bobhans last updated on 08/Jun/20
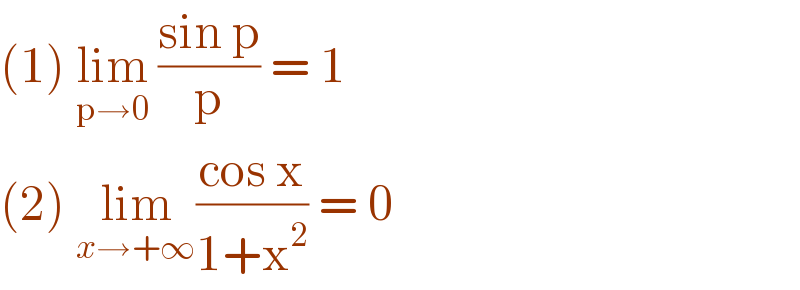
$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\underset{\mathrm{p}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{p}}{\mathrm{p}}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow+\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by mathocean1 last updated on 08/Jun/20
$${Please}\:{sir}\:{can}\:{you}\:{explain}… \\ $$
Answered by abdomathmax last updated on 08/Jun/20
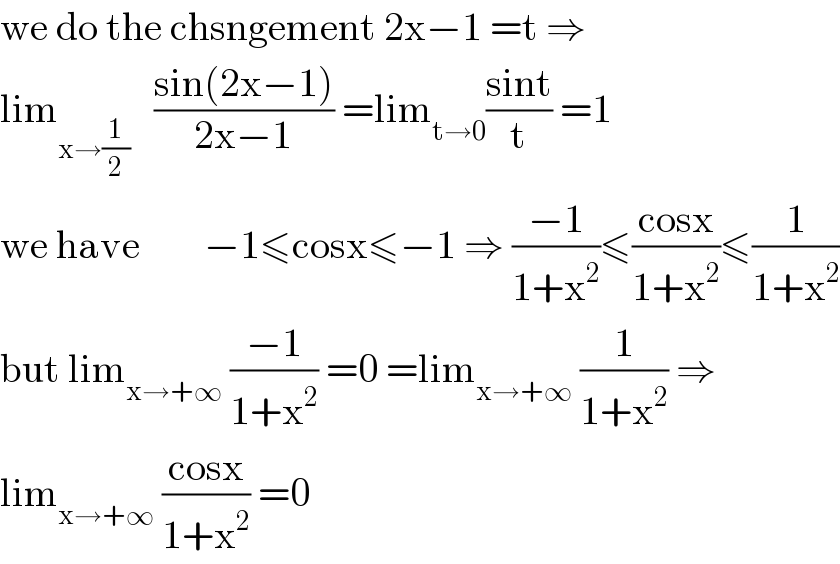
$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{do}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{chsngement}\:\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{1}\:=\mathrm{t}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{1}}\:=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \frac{\mathrm{sint}}{\mathrm{t}}\:=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{1}\leqslant\mathrm{cosx}\leqslant−\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\:\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{cosx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\mathrm{0}\:=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{cosx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
